Calculations from Balanced Equations
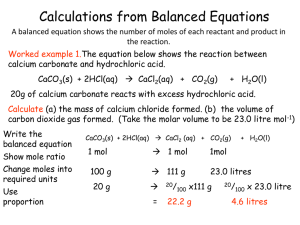
... Calculations from Balanced Equations A balanced equation shows the number of moles of each reactant and product in the reaction. Worked example 1.The equation below shows the reaction between calcium carbonate and hydrochloric acid. CaCO3(s) + 2HCl(aq) CaCl2(aq) + CO2(g) ...
... Calculations from Balanced Equations A balanced equation shows the number of moles of each reactant and product in the reaction. Worked example 1.The equation below shows the reaction between calcium carbonate and hydrochloric acid. CaCO3(s) + 2HCl(aq) CaCl2(aq) + CO2(g) ...
Comparison of homogeneous and heterogeneous catalysis
... of FFA to methyl esters increased with the increase in catalyst amount. With 0.5% H2SO4, the acid value reduced to 11.40 mg KOH/g which further reduced to 6.50 with 1.3% of H2SO4. The acid value of mahua oil was further reduced to 2.07 mg KOH/g with 1.5% (v/v) H2SO4. Further increase in the catalyst ...
... of FFA to methyl esters increased with the increase in catalyst amount. With 0.5% H2SO4, the acid value reduced to 11.40 mg KOH/g which further reduced to 6.50 with 1.3% of H2SO4. The acid value of mahua oil was further reduced to 2.07 mg KOH/g with 1.5% (v/v) H2SO4. Further increase in the catalyst ...
C2H5OH + 3 O2 → 2 CO2 + 3 H2O + HEAT Q = mc ∆T
... = ∆H / ∆S 329.2 K = 31.9 kJ / ∆S ∆S = 0.0969 kJ = 96.9 J *1:32. Microwaves are used to heat food. The microwave radiation is absorbed by moisture in the food. This heats the water and thus the food. How many photons having a wavelength of 3.0 mm would have to be absorbed by 1.0 g of water to raise i ...
... = ∆H / ∆S 329.2 K = 31.9 kJ / ∆S ∆S = 0.0969 kJ = 96.9 J *1:32. Microwaves are used to heat food. The microwave radiation is absorbed by moisture in the food. This heats the water and thus the food. How many photons having a wavelength of 3.0 mm would have to be absorbed by 1.0 g of water to raise i ...
הקימנידומרתב ןושארה קוחה
... 10. Two liters of N2 at 0 °C and 5 atm pressure are expanded isothermally against a constant pressure of 1 atm until the pressure of the gas is also 1 atm. Assuming the gas to be ideal, what are the values of w, ∆U, ∆H, and q for the process? Calculate the efficiency of this process. 11. Calculate t ...
... 10. Two liters of N2 at 0 °C and 5 atm pressure are expanded isothermally against a constant pressure of 1 atm until the pressure of the gas is also 1 atm. Assuming the gas to be ideal, what are the values of w, ∆U, ∆H, and q for the process? Calculate the efficiency of this process. 11. Calculate t ...
Combustion and Flue Gas Analysis
... between fuel and air in the combustion zone, excess air is required to achieve more complete combustion of the fuel. Without this extra air, the formation of partial products of combustion such as carbon monoxide and soot may occur. However, supplying too much excess air will decrease combustion eff ...
... between fuel and air in the combustion zone, excess air is required to achieve more complete combustion of the fuel. Without this extra air, the formation of partial products of combustion such as carbon monoxide and soot may occur. However, supplying too much excess air will decrease combustion eff ...
Combustion thermodynamics
... As it will be shown below, at least 9.5 m3 of air are required for the complete combustion of 1 m3 of methane at same p-T conditions (the molar stoichiometric air/fuel ratio is A0=9.5), with a maximum heat output of 55 MJ/kgCH4 (or 37 MJ/m3CH4, the higher heating value of methane) that would decreas ...
... As it will be shown below, at least 9.5 m3 of air are required for the complete combustion of 1 m3 of methane at same p-T conditions (the molar stoichiometric air/fuel ratio is A0=9.5), with a maximum heat output of 55 MJ/kgCH4 (or 37 MJ/m3CH4, the higher heating value of methane) that would decreas ...
No Slide Title
... A gas is confined inside of a cylinder at an initial pressure and volume pi = 1.00 atm and Vi = 2.000 L. 8000 J of heat is added to the gas under conditions of constant pressure. The final volume of the gas is Vf = 6.000 L. What are q, w, and E for the process? From the first law, E = q + w. Heat ...
... A gas is confined inside of a cylinder at an initial pressure and volume pi = 1.00 atm and Vi = 2.000 L. 8000 J of heat is added to the gas under conditions of constant pressure. The final volume of the gas is Vf = 6.000 L. What are q, w, and E for the process? From the first law, E = q + w. Heat ...
Homework Solutions Week 6
... When silver sulfate starts to precipitate, 97% of the calcium has precipitated. And when calcium from 97 to 99% precipitated, silver ion goes from 0 to 41% precipitated. 9-17 a) Why do many rivers in Box 9-1. lie on the line [HCO3-] = 2[Ca2+]? According to Box 9-1, the source of calcium in the river ...
... When silver sulfate starts to precipitate, 97% of the calcium has precipitated. And when calcium from 97 to 99% precipitated, silver ion goes from 0 to 41% precipitated. 9-17 a) Why do many rivers in Box 9-1. lie on the line [HCO3-] = 2[Ca2+]? According to Box 9-1, the source of calcium in the river ...
LoTOx™ System. Low temperature oxidation for NOx
... customer’s existing APC systems without significant changes or additional major process equipment. The small, modular system footprint allows flexibility of the equipment layout to meet unique spatial requirements for a variety of applications and industries. Custom-designed LoTOx™ systems are comme ...
... customer’s existing APC systems without significant changes or additional major process equipment. The small, modular system footprint allows flexibility of the equipment layout to meet unique spatial requirements for a variety of applications and industries. Custom-designed LoTOx™ systems are comme ...
Question 2 - The King`s School, Canterbury
... 1. (a) A student investigated the effect of light intensity on leaf size. The student collected 25 leaves from bramble plants at two different sites. One of the sites was a woodland with low light levels and the other, a woodland with high light levels. The student found the average surface area of ...
... 1. (a) A student investigated the effect of light intensity on leaf size. The student collected 25 leaves from bramble plants at two different sites. One of the sites was a woodland with low light levels and the other, a woodland with high light levels. The student found the average surface area of ...
Combustion
... oxygen than needed). The products of a complete combustion reaction are carbon dioxide gas, water vapour and energy. Using this information, write the balanced equation for the complete combustion of methane gas (CH4). Note: include energy as one of the products). Click for the Balanced ...
... oxygen than needed). The products of a complete combustion reaction are carbon dioxide gas, water vapour and energy. Using this information, write the balanced equation for the complete combustion of methane gas (CH4). Note: include energy as one of the products). Click for the Balanced ...
Heat
... 2) Note that the numerical value for C when expressed in J/K or J/C is identical. That is because we are using the change in temperature. Since the size of a degree Kelvin and a degree Celsius is the same, the numerical value for T is the same whether expressed in K or C. ...
... 2) Note that the numerical value for C when expressed in J/K or J/C is identical. That is because we are using the change in temperature. Since the size of a degree Kelvin and a degree Celsius is the same, the numerical value for T is the same whether expressed in K or C. ...
Energy
... The negative sign in the above equation occurs because we are measuring the value of q for the surroundings, and qsys = - qsur. If we know the energy of combustion for a compound, in units of kJ/g, then we can say q = m Ucom m = mass of compound burned Ucom = energy of combustion (in kJ/g) Note th ...
... The negative sign in the above equation occurs because we are measuring the value of q for the surroundings, and qsys = - qsur. If we know the energy of combustion for a compound, in units of kJ/g, then we can say q = m Ucom m = mass of compound burned Ucom = energy of combustion (in kJ/g) Note th ...
E2 and E11 Acid Deposition Past Paper Questions
... NH4 + 2 O2 2 H + NO3 + H2O Plus any THREE of the following: adding NH3 to soil makes it less acidic salt particles formed are acidic/have pH lower than 7 salts are washed into the ground; in earth they can be nitrified; nitrification acidifies the soil ...
... NH4 + 2 O2 2 H + NO3 + H2O Plus any THREE of the following: adding NH3 to soil makes it less acidic salt particles formed are acidic/have pH lower than 7 salts are washed into the ground; in earth they can be nitrified; nitrification acidifies the soil ...
Subject Materials for Chemistry
... Glycerol decreases the rate of reaction. So glycerol is –ve catalyst. No, Catalyst doesn’t undergo any change chemically. A Catalyst may be recovered in mass and composition at the end of the chemical reaction. 6. What is the effect of temperature on the following? i) Dissociation of an electrolyte ...
... Glycerol decreases the rate of reaction. So glycerol is –ve catalyst. No, Catalyst doesn’t undergo any change chemically. A Catalyst may be recovered in mass and composition at the end of the chemical reaction. 6. What is the effect of temperature on the following? i) Dissociation of an electrolyte ...
Preparation of KOH/CaO/C Supported Biodiesel Catalyst and
... was 4 h. The effects of C/CaO mass ratio on biodiesel yield were investigated and the results were listed in Figure 1. Clearly, the biodiesel yield first increases and then declines with the rising C/CaO ratio, and is maximized to be 93.0% at the ratio of 4:6 (Figure 1). This is because the carrier ...
... was 4 h. The effects of C/CaO mass ratio on biodiesel yield were investigated and the results were listed in Figure 1. Clearly, the biodiesel yield first increases and then declines with the rising C/CaO ratio, and is maximized to be 93.0% at the ratio of 4:6 (Figure 1). This is because the carrier ...
Ch. 3 Sections 3.9-3.10 Notes
... • We don’t however, have to carry out the reaction with these actual numbers of moles. • Whatever quantities we choose must be in the proportions set by the coefficients. • Regardless of the scale of the reaction, the coefficients of a chemical equation give the ratio in which the moles of one subst ...
... • We don’t however, have to carry out the reaction with these actual numbers of moles. • Whatever quantities we choose must be in the proportions set by the coefficients. • Regardless of the scale of the reaction, the coefficients of a chemical equation give the ratio in which the moles of one subst ...
Sample Problems
... 5. 56 grams of nitrogen gas reacts with hydrogen to produce ammonia (NH3). How many grams of ammonia are produced? Assignment: Page 311, 1- 5 ...
... 5. 56 grams of nitrogen gas reacts with hydrogen to produce ammonia (NH3). How many grams of ammonia are produced? Assignment: Page 311, 1- 5 ...
avogadro exam 2001 - University of Waterloo
... 15 What is the total pressure in a 4.55-L container if it contains 0.0410 mol O2, 0.173 mol N2 and 0.056 mol He, at a temperature of 167oC? ...
... 15 What is the total pressure in a 4.55-L container if it contains 0.0410 mol O2, 0.173 mol N2 and 0.056 mol He, at a temperature of 167oC? ...
No Slide Title
... Energy is the capacity to do work or transfer heat. In principal any kind of energy can be converted into an equivalent amount of work or heat. We divide energy into two general types: kinetic energy (due to motion in a particular direction) ...
... Energy is the capacity to do work or transfer heat. In principal any kind of energy can be converted into an equivalent amount of work or heat. We divide energy into two general types: kinetic energy (due to motion in a particular direction) ...
Mechanical Engineering and Aeronautics
... liquids at normal atmospheric conditions, while those with less than 5 atoms in the molecule are gaseous. Alcohols are an exception to the above rule. All alcohols are liquids at normal atmospheric conditions. ...
... liquids at normal atmospheric conditions, while those with less than 5 atoms in the molecule are gaseous. Alcohols are an exception to the above rule. All alcohols are liquids at normal atmospheric conditions. ...
Document
... 8. The numbers preceding the formulas in chemical equations are referred to as the ________ coefficients. a) theoretical ...
... 8. The numbers preceding the formulas in chemical equations are referred to as the ________ coefficients. a) theoretical ...
The 100% Mineral Alternative for Micropollutants Removal
... unit combined with the injection of a dry sorbent. The treatment takes place in the duct and on the surface of the filter bags. This process has low investment costs and can be adapted easily to any existing installation. Minsorb® is delivered in bulk or in big bags and can easily substitute carbon- ...
... unit combined with the injection of a dry sorbent. The treatment takes place in the duct and on the surface of the filter bags. This process has low investment costs and can be adapted easily to any existing installation. Minsorb® is delivered in bulk or in big bags and can easily substitute carbon- ...
2 C2H6 (g)
... The Ostwald process is used commercially to produce nitric acid, which is, in turn, used in many modern chemical processes. In the first step of the Ostwald process, ammonia is reacted with oxygen gas to produce nitric oxide and water. 4 NH3 (g) + 5 O2 (g) 4 NO g + 6 H2O (g) What is the maximum ma ...
... The Ostwald process is used commercially to produce nitric acid, which is, in turn, used in many modern chemical processes. In the first step of the Ostwald process, ammonia is reacted with oxygen gas to produce nitric oxide and water. 4 NH3 (g) + 5 O2 (g) 4 NO g + 6 H2O (g) What is the maximum ma ...
Unit 6 Chemical Equations and Reactions Balancing Equations
... 6. Aluminum metal is oxidized by oxygen (from the air) to form aluminum oxide. 4 Al (s) + 3 O2 → 2 Al2O3 7. Sodium oxide reacts with carbon dioxide to form sodium carbonate. Na2O + CO2 → Na2 CO3 8. Calcium metal reacts with water to form calcium hydroxide and hydrogen gas. Ca (s) + 2H2O → Ca(OH)2 + ...
... 6. Aluminum metal is oxidized by oxygen (from the air) to form aluminum oxide. 4 Al (s) + 3 O2 → 2 Al2O3 7. Sodium oxide reacts with carbon dioxide to form sodium carbonate. Na2O + CO2 → Na2 CO3 8. Calcium metal reacts with water to form calcium hydroxide and hydrogen gas. Ca (s) + 2H2O → Ca(OH)2 + ...