Theory of Vision: What We Can Easily See
... The goal is to always to get a visual target in the vicinity of the eye’s detection field. From there, it becomes eligible for the next fixation. The bigger something is, the more it takes up in the ...
... The goal is to always to get a visual target in the vicinity of the eye’s detection field. From there, it becomes eligible for the next fixation. The bigger something is, the more it takes up in the ...
Visual pathways cortical and sub
... electrophysiological recordings from dorsal stream neurons neurons that fire during reaching neurons firing during saccades towards stationary objects neurons responding to moving objects if followed by gaze ...
... electrophysiological recordings from dorsal stream neurons neurons that fire during reaching neurons firing during saccades towards stationary objects neurons responding to moving objects if followed by gaze ...
MCB105 QUIZ 5 2016 wA
... visual field as juveniles exhibit neuronal plasticity as adults. a) In which neurons was this plasticity shown? [1] OT neurons with both auditory and visual responses b) How is this change measured (explain or draw)? [1] Measure the same OT neuron before and after prism fitting. Compare the visual r ...
... visual field as juveniles exhibit neuronal plasticity as adults. a) In which neurons was this plasticity shown? [1] OT neurons with both auditory and visual responses b) How is this change measured (explain or draw)? [1] Measure the same OT neuron before and after prism fitting. Compare the visual r ...
Visual vs. Language-based Thinking
... by the mirror neuron system. From a cognitive load perspective, this might benefit learning by leaving more working memory capacity available for processes such as elaboration or reflection on intentions of actions, compared to static visualizations. However, we do not know whether and how the mirro ...
... by the mirror neuron system. From a cognitive load perspective, this might benefit learning by leaving more working memory capacity available for processes such as elaboration or reflection on intentions of actions, compared to static visualizations. However, we do not know whether and how the mirro ...
MIND: The Cognitive Side of Mind and Brain
... assess aspects of perception, attention, and memory. Models of mental structures and processes of human perception, attention, memory, etc. based on data obtained from solid experimental procedures ...
... assess aspects of perception, attention, and memory. Models of mental structures and processes of human perception, attention, memory, etc. based on data obtained from solid experimental procedures ...
Inner music and brain connectivity
... How will the weak top-down connections in visual modality manifest? Attention problems? Only if they are very weak, then object recognition in poor lighting conditions may be impaired. Otherwise: poor visual imagination, memory for visual features, inability to draw from memory, recall and describe ...
... How will the weak top-down connections in visual modality manifest? Attention problems? Only if they are very weak, then object recognition in poor lighting conditions may be impaired. Otherwise: poor visual imagination, memory for visual features, inability to draw from memory, recall and describe ...
Association Cortex, Consciousness, and other topics that Embarrass
... • The concept that different parts of the brain did different things started with Spurzheim and Gall, whose phrenology became quite fashionable: • The phrenologist said that a given area of the brain increases in size, as does the overlying skull, when its function is exercised, and a good clinician ...
... • The concept that different parts of the brain did different things started with Spurzheim and Gall, whose phrenology became quite fashionable: • The phrenologist said that a given area of the brain increases in size, as does the overlying skull, when its function is exercised, and a good clinician ...
Memory for Everyday Activities
... Short-Term Memory (STM): the set of processes that we use to hold and rehearse information that occupies our current awareness ...
... Short-Term Memory (STM): the set of processes that we use to hold and rehearse information that occupies our current awareness ...
A1984TF19600002
... lateral extent of what was recognized as ‘visual’ cortex: its medial and lateral parts had independent subcortical projections. We therefore made small lesions restricted to the medial or lateral visual cortex, and even in the auditory, somatosensory, and motor 4cortex. The 1965 paper of Hubel and W ...
... lateral extent of what was recognized as ‘visual’ cortex: its medial and lateral parts had independent subcortical projections. We therefore made small lesions restricted to the medial or lateral visual cortex, and even in the auditory, somatosensory, and motor 4cortex. The 1965 paper of Hubel and W ...
Cognitive
... This is the speed at which your brain processes information. Faster processing speed means more efficient thinking and learning. Processing speed declines consistently across the adult lifespan, thus compromising higher cognitive performance. It is possible that by challenging your cognitive abiliti ...
... This is the speed at which your brain processes information. Faster processing speed means more efficient thinking and learning. Processing speed declines consistently across the adult lifespan, thus compromising higher cognitive performance. It is possible that by challenging your cognitive abiliti ...
Chap 5: The Cognitive Approach II
... Memory is the capacity to retain information over time. Memory allows us to learn from previous experiences. Memory systems can be characterized by duration, capacity, and coding. ...
... Memory is the capacity to retain information over time. Memory allows us to learn from previous experiences. Memory systems can be characterized by duration, capacity, and coding. ...
Session 4
... Mapping of Visual Areas This map shows a flattened cortex with the known visual areas mapped onto it. There are a large number of distinct visual areas (probably at least 20). Each area appears to have a specific function. The areas show a roughly hierarchical organization (although most areas have ...
... Mapping of Visual Areas This map shows a flattened cortex with the known visual areas mapped onto it. There are a large number of distinct visual areas (probably at least 20). Each area appears to have a specific function. The areas show a roughly hierarchical organization (although most areas have ...
Moran Furman
... based coordinates (“spatial stability”). Whereas early visual areas, such as V1, encode information in purely retinal coordinates, higher association areas of the cortex, such as the LIP in the parietal lobe and the FEF in the frontal lobe, adjust their responses during eye movements to compensate f ...
... based coordinates (“spatial stability”). Whereas early visual areas, such as V1, encode information in purely retinal coordinates, higher association areas of the cortex, such as the LIP in the parietal lobe and the FEF in the frontal lobe, adjust their responses during eye movements to compensate f ...
primary visual cortex
... Friday, December 3: 3:30-4:30 Thursday, December 9: 10:00-12:00, 1:00-3:00 Friday, December 10: 10:00-1:00 ...
... Friday, December 3: 3:30-4:30 Thursday, December 9: 10:00-12:00, 1:00-3:00 Friday, December 10: 10:00-1:00 ...
Jay_21Mar2013
... I. Distinguish 3-D structure from connectivity II. Keep in mind that not all structures have (known) functions – biological structures are evolved, not designed. III. Mind your Greek/Latin ...
... I. Distinguish 3-D structure from connectivity II. Keep in mind that not all structures have (known) functions – biological structures are evolved, not designed. III. Mind your Greek/Latin ...
The effect of visual experience on the development of the mirror
... sulcus and the inferior parietal lobule. These same areas showed significant activations also during the tactile and visual angle discrimination conditions. As expected, auditory, visual and tactile primary sensory regions also were activated during the respective conditions. Ventral occipital brain ...
... sulcus and the inferior parietal lobule. These same areas showed significant activations also during the tactile and visual angle discrimination conditions. As expected, auditory, visual and tactile primary sensory regions also were activated during the respective conditions. Ventral occipital brain ...
Shipp Visual memory Notes
... can be recreated subsequently from just a subset of those inputs. Thus, theoretically, the general basis of the hippocampus in memory encoding is that it receives highly processed sensory ‘concepts’ from all other cortical areas, & can form rapid associations amongst any arbitrary set of such concep ...
... can be recreated subsequently from just a subset of those inputs. Thus, theoretically, the general basis of the hippocampus in memory encoding is that it receives highly processed sensory ‘concepts’ from all other cortical areas, & can form rapid associations amongst any arbitrary set of such concep ...
05powerpoint
... Memory is the capacity to retain information over time. Memory allows us to learn from previous experiences. Memory systems can be characterized by duration, capacity, and coding. ...
... Memory is the capacity to retain information over time. Memory allows us to learn from previous experiences. Memory systems can be characterized by duration, capacity, and coding. ...
From Vision to Movement
... To answer this seemingly basic question, one needs a variety of techniques. Computational models can help us understand how visual signals are transformed into motor signals within artificial networks that are designed to emulate some part(s) of the brain. Studies of patients with damage to specific ...
... To answer this seemingly basic question, one needs a variety of techniques. Computational models can help us understand how visual signals are transformed into motor signals within artificial networks that are designed to emulate some part(s) of the brain. Studies of patients with damage to specific ...
Chapter 5. The Sensual and Perceptual Theories of Visual
... Memory Is basically our personal link with all the images we have ever seen mnemonics ...
... Memory Is basically our personal link with all the images we have ever seen mnemonics ...
Exam - UBC Psychology`s Research Labs
... segregated into distinct pathways that project to areas of the secondary visual cortex and, then, the association visual cortex. • Two main pathways from the primary visual cortex have been identified: The ventral stream is associated with identification (“what”); the dorsal stream is associated wit ...
... segregated into distinct pathways that project to areas of the secondary visual cortex and, then, the association visual cortex. • Two main pathways from the primary visual cortex have been identified: The ventral stream is associated with identification (“what”); the dorsal stream is associated wit ...
New clues to the location of visual consciousness
... control,” says Randolph Blake, professor of psychology at Vanderbilt. He, Hugh R. Wilson, a mathematician from York University in Toronto, and Vanderbilt graduate student Sang-Hun Lee devised the new test. In normal binocular vision, sensory information from the two eyes is fused into a single, thre ...
... control,” says Randolph Blake, professor of psychology at Vanderbilt. He, Hugh R. Wilson, a mathematician from York University in Toronto, and Vanderbilt graduate student Sang-Hun Lee devised the new test. In normal binocular vision, sensory information from the two eyes is fused into a single, thre ...
Slide ()
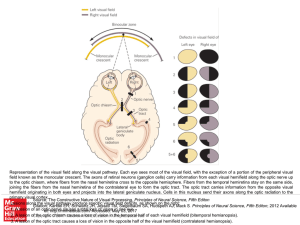
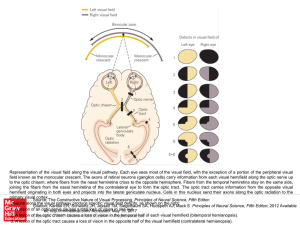
... field known as the monocular crescent. The axons of retinal neurons (ganglion cells) carry information from each visual hemifield along the optic nerve up to the optic chiasm, where fibers from the nasal hemiretina cross to the opposite hemisphere. Fibers from the temporal hemiretina stay on the sam ...
... field known as the monocular crescent. The axons of retinal neurons (ganglion cells) carry information from each visual hemifield along the optic nerve up to the optic chiasm, where fibers from the nasal hemiretina cross to the opposite hemisphere. Fibers from the temporal hemiretina stay on the sam ...
Slide ()
... field known as the monocular crescent. The axons of retinal neurons (ganglion cells) carry information from each visual hemifield along the optic nerve up to the optic chiasm, where fibers from the nasal hemiretina cross to the opposite hemisphere. Fibers from the temporal hemiretina stay on the sam ...
... field known as the monocular crescent. The axons of retinal neurons (ganglion cells) carry information from each visual hemifield along the optic nerve up to the optic chiasm, where fibers from the nasal hemiretina cross to the opposite hemisphere. Fibers from the temporal hemiretina stay on the sam ...
Visual memory

Visual memory describes the relationship between perceptual processing and the encoding, storage and retrieval of the resulting neural representations. Visual memory occurs over a broad time range spanning from eye movements to years in order to visually navigate to a previously visited location. Visual memory is a form of memory which preserves some characteristics of our senses pertaining to visual experience. We are able to place in memory visual information which resembles objects, places, animals or people in a mental image. The experience of visual memory is also referred to as the mind's eye through which we can retrieve from our memory a mental image of original objects, places, animals or people. Visual memory is one of several cognitive systems, which are all interconnected parts that combine to form the human memory. Types of palinopsia, the persistence or recurrence of a visual image after the stimulus has been removed, is a dysfunction of visual memory.