7-1-work - High Point University
... The momentum principle tells us that the net force times the time interval during which it acts is equal to the change in the momentum of an object. The quantity, net force times time interval, is called impulse. What about net force times displacement? If the net force on an object acts through a c ...
... The momentum principle tells us that the net force times the time interval during which it acts is equal to the change in the momentum of an object. The quantity, net force times time interval, is called impulse. What about net force times displacement? If the net force on an object acts through a c ...
ISNS4371_011107_bw - The University of Texas at Dallas
... - opposes gravity and prevents us falling to the center of the Earth - what is measured by a weighing scale. For a body supported in a stationary position, normal force exactly balances earth's gravitational force - apparent weight has the same magnitude as actual weight. If no contact with any surf ...
... - opposes gravity and prevents us falling to the center of the Earth - what is measured by a weighing scale. For a body supported in a stationary position, normal force exactly balances earth's gravitational force - apparent weight has the same magnitude as actual weight. If no contact with any surf ...
Friction Problems
... concrete floor. What is the coefficient of static friction between the box and the floor? 12. If the 40.0 n force from problem 11 continues, the box accelerates at 0.70 m/s2. What is the coefficient of sliding friction? ...
... concrete floor. What is the coefficient of static friction between the box and the floor? 12. If the 40.0 n force from problem 11 continues, the box accelerates at 0.70 m/s2. What is the coefficient of sliding friction? ...
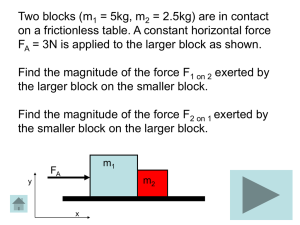
Tutorial_blocks
... This is not the only correct choice. This is true according to Newton’s third law. Since block 1 exerts a force (action) on block 2 by being pushed into it, block two must exert a force (reaction) on block 1. This pair of forces, as with all action-reaction pairs, act in opposite directions, and hav ...
... This is not the only correct choice. This is true according to Newton’s third law. Since block 1 exerts a force (action) on block 2 by being pushed into it, block two must exert a force (reaction) on block 1. This pair of forces, as with all action-reaction pairs, act in opposite directions, and hav ...
Mechanics:
... The baggage at the airport is delivered on a horizontal circular conveyor belt that is moving at constant speed. The radius of the circular belt is 7.0 m. (a) Draw an arrow in the diagram below to show the direction of the velocity of the suitcase that is on the moving circular belt. [A] (b) Explain ...
... The baggage at the airport is delivered on a horizontal circular conveyor belt that is moving at constant speed. The radius of the circular belt is 7.0 m. (a) Draw an arrow in the diagram below to show the direction of the velocity of the suitcase that is on the moving circular belt. [A] (b) Explain ...
Document
... Force is zero at equilibrium. For many systems, the net force takes this form near equilibrium, provided equilibrium is stable ...
... Force is zero at equilibrium. For many systems, the net force takes this form near equilibrium, provided equilibrium is stable ...
File
... x(t ) 2.17m (4.80m / s 2 )t 2 (0.100m / s 6 )t 6 . Find it’s a) position and acceleration at the instants when the car has zero velocity. b) Draw x-t, v-t, and a-t graphs for the motion of the bumper between t=o and t=2 s. 4. A car is stopped at a traffic light. It then travels along a straigh ...
... x(t ) 2.17m (4.80m / s 2 )t 2 (0.100m / s 6 )t 6 . Find it’s a) position and acceleration at the instants when the car has zero velocity. b) Draw x-t, v-t, and a-t graphs for the motion of the bumper between t=o and t=2 s. 4. A car is stopped at a traffic light. It then travels along a straigh ...
Force Motion Pasco Lab
... For this activity, a motion sensor measures the motion of a cart that is pulled by a string. The string is attached to a mass and suspended over a pulley. A force sensor mounted on the cart measures the force that accelerates the cart. The Science Workshop program calculates the velocity of the movi ...
... For this activity, a motion sensor measures the motion of a cart that is pulled by a string. The string is attached to a mass and suspended over a pulley. A force sensor mounted on the cart measures the force that accelerates the cart. The Science Workshop program calculates the velocity of the movi ...
Dynamic Universe Forces Energy Power 2015 (10.4MB PowerPoint)
... In 1609, Galileo heard about the invention of the telescope in Holland. Without having seen an example, he constructed a superior version and made many astronomical discoveries. These included mountains and valleys on the surface of the moon, sunspots, the four largest moons of the planet Jupiter an ...
... In 1609, Galileo heard about the invention of the telescope in Holland. Without having seen an example, he constructed a superior version and made many astronomical discoveries. These included mountains and valleys on the surface of the moon, sunspots, the four largest moons of the planet Jupiter an ...
Lesson 1 - SchoolRack
... Lesson 3: Newton’s Laws of Motion • Inertia is the tendency of an object to resist a change of motion Newton’s first law of motion states that an object will remain at rest or in constant straight-line motion unless unbalanced forces act on the object. • Newton’s second law of motion states that th ...
... Lesson 3: Newton’s Laws of Motion • Inertia is the tendency of an object to resist a change of motion Newton’s first law of motion states that an object will remain at rest or in constant straight-line motion unless unbalanced forces act on the object. • Newton’s second law of motion states that th ...
1 PHYSICS 231 Lecture 13: Keeping momentum
... is very much reduced. The wall does not move, although the force on the ball is the same as the force on the wall (Newton’s 3rd law: Fwall-bullet=-Fbullet-wall). ...
... is very much reduced. The wall does not move, although the force on the ball is the same as the force on the wall (Newton’s 3rd law: Fwall-bullet=-Fbullet-wall). ...
The Modern Galileo Experiment
... to begin data collection. Within the limits of the spring, move the Force Sensor and slowly stretch the spring about 50 cm over several seconds. Hold the sensor still until data collection stops. Do not get any closer than 40 cm to the Motion Detector 16. Examine the graphs. Identify when you starte ...
... to begin data collection. Within the limits of the spring, move the Force Sensor and slowly stretch the spring about 50 cm over several seconds. Hold the sensor still until data collection stops. Do not get any closer than 40 cm to the Motion Detector 16. Examine the graphs. Identify when you starte ...
Chapter 5
... In this chapter, we use light ropes, which means that we are using massless ropes, which we refer to as “ideal” ropes. A nice connection to the previous page: Consider a rope whose mass is not negligible compared with the other masses in the system. If we pull on one end of this rope and there are n ...
... In this chapter, we use light ropes, which means that we are using massless ropes, which we refer to as “ideal” ropes. A nice connection to the previous page: Consider a rope whose mass is not negligible compared with the other masses in the system. If we pull on one end of this rope and there are n ...
CSS - CBSE Guess
... Q.9> A force F = 4i + 7j – 2k acts on a particle whose position vector is r = 6i – j + 3k. The particle is free to rotate about an axis passing through the origin. Find the torque produced by the force. Q.10> To maintain a fan at a constant speed of 10rad/sec the motor has to provide a torque of 100 ...
... Q.9> A force F = 4i + 7j – 2k acts on a particle whose position vector is r = 6i – j + 3k. The particle is free to rotate about an axis passing through the origin. Find the torque produced by the force. Q.10> To maintain a fan at a constant speed of 10rad/sec the motor has to provide a torque of 100 ...
Phys_21_N7_WORK_and_ENERGY
... to begin data collection. Within the limits of the spring, move the Force Sensor and slowly stretch the spring about 50 cm over several seconds. Hold the sensor still until data collection stops. Do not get any closer than 40 cm to the Motion Detector 16. Examine the graphs. Identify when you starte ...
... to begin data collection. Within the limits of the spring, move the Force Sensor and slowly stretch the spring about 50 cm over several seconds. Hold the sensor still until data collection stops. Do not get any closer than 40 cm to the Motion Detector 16. Examine the graphs. Identify when you starte ...
1 - Net Start Class
... Like most problems, this problem begins with a free-body diagram (as shown at right). Note that there is no rightwards applied force (a common mistake). Note also that the force of friction is the only force responsible for the acceleration (deceleration) of the car. The Ffrict value is the net forc ...
... Like most problems, this problem begins with a free-body diagram (as shown at right). Note that there is no rightwards applied force (a common mistake). Note also that the force of friction is the only force responsible for the acceleration (deceleration) of the car. The Ffrict value is the net forc ...