Vectors: Motion and Forces in Two Dimensions
... • Free-body diagrams are used to show the relative magnitude and direction of all forces acting upon an object in a given situation. • The size of the arrow in a free-body diagram reflects the magnitude of the force. The arrow shows the direction that the force is acting. • Each force arrow in the d ...
... • Free-body diagrams are used to show the relative magnitude and direction of all forces acting upon an object in a given situation. • The size of the arrow in a free-body diagram reflects the magnitude of the force. The arrow shows the direction that the force is acting. • Each force arrow in the d ...
Powerpoint for today
... A. If you park on a hill with a 10 degree slope with the car held by the parking brake, what is the magnitude of the frictional force that holds your car in place? B. The coefficient of static friction between your car's wheels and the road when wet is 0.30. What is the largest angle slope on which ...
... A. If you park on a hill with a 10 degree slope with the car held by the parking brake, what is the magnitude of the frictional force that holds your car in place? B. The coefficient of static friction between your car's wheels and the road when wet is 0.30. What is the largest angle slope on which ...
Ch33 - Wells College
... 2. draw force arrows, length to scale if you can, either tip or tail on the body, in accurate directions [At this stage in the course all forces act at a single point]. 3. choose a 2d Cartesian coordinate system with origin at that point, oriented with one + coordinate along the acceleration directi ...
... 2. draw force arrows, length to scale if you can, either tip or tail on the body, in accurate directions [At this stage in the course all forces act at a single point]. 3. choose a 2d Cartesian coordinate system with origin at that point, oriented with one + coordinate along the acceleration directi ...
Final Exam Practice questions
... 10) A 100 N traffic light is suspended by two wires of length L1 and L2 as shown in the figure. If L1 = 3.0 m and L2 = 5.0 m and the distance x = 2.0 m, then the tension in the wire of length L1 is, a) 125 N b) 101 N c) 90 N d) 82 N e) 75 N 11) You are designing a soap-box derby race car that will r ...
... 10) A 100 N traffic light is suspended by two wires of length L1 and L2 as shown in the figure. If L1 = 3.0 m and L2 = 5.0 m and the distance x = 2.0 m, then the tension in the wire of length L1 is, a) 125 N b) 101 N c) 90 N d) 82 N e) 75 N 11) You are designing a soap-box derby race car that will r ...
Free Body Diagram
... Forces always come in pairs!! If we take the entire universe as our system then the sum of these forces always adds up to zero!!! Thus, the total motion of the universe is always ...
... Forces always come in pairs!! If we take the entire universe as our system then the sum of these forces always adds up to zero!!! Thus, the total motion of the universe is always ...
Friction
... drag a 200 kg safe up a ramp at an angle of θ=20°. The safe is currently not moving while he pulls on the rope with a force of 400 N. What is the magnitude and direction of the force of friction on the safe? ...
... drag a 200 kg safe up a ramp at an angle of θ=20°. The safe is currently not moving while he pulls on the rope with a force of 400 N. What is the magnitude and direction of the force of friction on the safe? ...
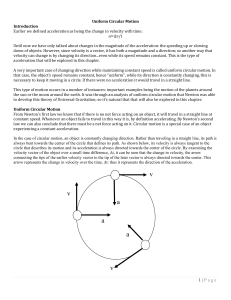
Acceleration Characteristics for Circular Motion
... In that case, you treat this case the same way you did in any dynamics problem, the sum of the forces matters...not any one force. So for instance, if we changed the prior example by having the object moving in a vertical circle, rather than a horizontal one, we have two forces acting on the object ...
... In that case, you treat this case the same way you did in any dynamics problem, the sum of the forces matters...not any one force. So for instance, if we changed the prior example by having the object moving in a vertical circle, rather than a horizontal one, we have two forces acting on the object ...
A simplified human birth model: Translation of a Rigid - Tulane-Math
... Here, µ is viscosity, xk are points on discretized tube and rod, fk is the force at that point, and ε is a regularization parameter. [3] R. Cortez (2001). Method of Regularized Stokeslets, SIAM Journal of Scientific Computing. [4] R. Cortez, L. Fauci, A. Medovikov (2005). The method of regularized S ...
... Here, µ is viscosity, xk are points on discretized tube and rod, fk is the force at that point, and ε is a regularization parameter. [3] R. Cortez (2001). Method of Regularized Stokeslets, SIAM Journal of Scientific Computing. [4] R. Cortez, L. Fauci, A. Medovikov (2005). The method of regularized S ...
Lecture4_Work_Proportions
... Lifting weights is definitely work even by this physics definition! What about lowering weights back down? When lowering an object, the force you apply to support it (and keep it from dropping too fast) is NOT in the same direction as its motion. In fact it is OPPOSITE. Instead we think in terms of ...
... Lifting weights is definitely work even by this physics definition! What about lowering weights back down? When lowering an object, the force you apply to support it (and keep it from dropping too fast) is NOT in the same direction as its motion. In fact it is OPPOSITE. Instead we think in terms of ...
fall04-term1-exercise
... this observation we can conclude that a. k > tan b. k < tan c. s < tan d.s > tan 73. A block is released at the top of a plane inclined at 60ø with the horizontal. The block travels 1 m in 2 s. What is the coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the plane? a. 0.3 b. 0.4 c. ...
... this observation we can conclude that a. k > tan b. k < tan c. s < tan d.s > tan 73. A block is released at the top of a plane inclined at 60ø with the horizontal. The block travels 1 m in 2 s. What is the coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the plane? a. 0.3 b. 0.4 c. ...
PHYS 1443 * Section 501 Lecture #1
... proton #2 initially at rest. After the collision, proton #1 moves at an angle of 37o to the horizontal axis and proton #2 deflects at an angle to the same axis. Find the final speeds of the two protons and the scattering angle of proton #2, . This must be done in much more detail than the book o ...
... proton #2 initially at rest. After the collision, proton #1 moves at an angle of 37o to the horizontal axis and proton #2 deflects at an angle to the same axis. Find the final speeds of the two protons and the scattering angle of proton #2, . This must be done in much more detail than the book o ...