Document
... angle θ above the horizontal. The block moves at a constant horizontal acceleration a. Express all the results in terms of m, θ, F, a, and fundamental constants. a. Below show and label a free-body diagram with all forces acting on the block. b. Write an expression for the normal force applied by th ...
... angle θ above the horizontal. The block moves at a constant horizontal acceleration a. Express all the results in terms of m, θ, F, a, and fundamental constants. a. Below show and label a free-body diagram with all forces acting on the block. b. Write an expression for the normal force applied by th ...
Laws of Motion Conservation Laws Gravity
... Vertical & Horizontal motion independent • All objects accelerate at the same rate, regardless of whether – they fall straight down, or – are moving horizontally C2-21 C2-22 ...
... Vertical & Horizontal motion independent • All objects accelerate at the same rate, regardless of whether – they fall straight down, or – are moving horizontally C2-21 C2-22 ...
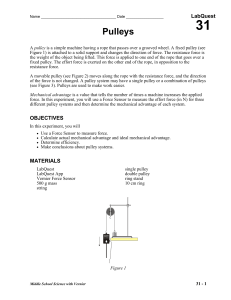
31 Pulleys
... A pulley is a simple machine having a rope that passes over a grooved wheel. A fixed pulley (see Figure 1) is attached to a solid support and changes the direction of force. The resistance force is the weight of the object being lifted. This force is applied to one end of the rope that goes over a f ...
... A pulley is a simple machine having a rope that passes over a grooved wheel. A fixed pulley (see Figure 1) is attached to a solid support and changes the direction of force. The resistance force is the weight of the object being lifted. This force is applied to one end of the rope that goes over a f ...
Preview Sample 1
... b. Maximum and minimum kinetic energy. ANS: The maximum kinetic energy occurs at the point where the ball is moving fastest, namely right after it leaves Larissa’s hand and right before she catches it. The minimum kinetic energy will occur when the ball is moving slowest – right at the top of the p ...
... b. Maximum and minimum kinetic energy. ANS: The maximum kinetic energy occurs at the point where the ball is moving fastest, namely right after it leaves Larissa’s hand and right before she catches it. The minimum kinetic energy will occur when the ball is moving slowest – right at the top of the p ...
Terminal velocity - School
... a) Describe the forces when the skydiver falls at a constant velocity ...
... a) Describe the forces when the skydiver falls at a constant velocity ...
Ch. 6 Newton`s Second law of Motion Force and Acceleration
... Both liquids and gases are called fluids because they flow. • Fluid friction occurs as an object pushes aside the fluid it is moving through. • The friction of liquids is appreciable, even at low speeds. • Air resistance is the friction acting on something moving through air. ...
... Both liquids and gases are called fluids because they flow. • Fluid friction occurs as an object pushes aside the fluid it is moving through. • The friction of liquids is appreciable, even at low speeds. • Air resistance is the friction acting on something moving through air. ...
An object accelerates when a net force acts on it.
... Both liquids and gases are called fluids because they flow. • Fluid friction occurs as an object pushes aside the fluid it is moving through. • The friction of liquids is appreciable, even at low speeds. • Air resistance is the friction acting on something moving through air. ...
... Both liquids and gases are called fluids because they flow. • Fluid friction occurs as an object pushes aside the fluid it is moving through. • The friction of liquids is appreciable, even at low speeds. • Air resistance is the friction acting on something moving through air. ...
6 Newton`s Second Law of Motion–Force and Acceleration
... Both liquids and gases are called fluids because they flow. • Fluid friction occurs as an object pushes aside the fluid it is moving through. • The friction of liquids is appreciable, even at low speeds. • Air resistance is the friction acting on something moving through air. ...
... Both liquids and gases are called fluids because they flow. • Fluid friction occurs as an object pushes aside the fluid it is moving through. • The friction of liquids is appreciable, even at low speeds. • Air resistance is the friction acting on something moving through air. ...
Document
... pieces impart equal and opposite forces on each other (Newton’s third law) these internal forces cannot provide a net change in momentum so momentum must be conserved in explosions ...
... pieces impart equal and opposite forces on each other (Newton’s third law) these internal forces cannot provide a net change in momentum so momentum must be conserved in explosions ...
momentum - SFSU Physics & Astronomy
... (a) it is a vector (b) it is a product of mass times velocity (c) impulses are required to change it (d) all of the above ...
... (a) it is a vector (b) it is a product of mass times velocity (c) impulses are required to change it (d) all of the above ...
Motion - leitl
... In a car the driver’s head is moving horizontally at 8.0 ms-1 and collides with an air bag as shown. The time taken for the driver’s head to come to a complete stop is 1.6 x 10-1 s. This collision may be modelled as a simple horizontal collision between the head of mass 7.0 kg and the air bag. ...
... In a car the driver’s head is moving horizontally at 8.0 ms-1 and collides with an air bag as shown. The time taken for the driver’s head to come to a complete stop is 1.6 x 10-1 s. This collision may be modelled as a simple horizontal collision between the head of mass 7.0 kg and the air bag. ...