Part23 - FacStaff Home Page for CBU
... Air Resistance and Gravity -mg + bv2 = m (dv/dt) The first step is to calculate the forces based on initial conditions. Let’s say we drop an object that has a mass of 2 kg and an air resistance coefficient 0.03 Nt-s2/m2 from a helicopter 1,000 meters above the ground. Fgravity = mg = 2 kg * 9.8 m/s ...
... Air Resistance and Gravity -mg + bv2 = m (dv/dt) The first step is to calculate the forces based on initial conditions. Let’s say we drop an object that has a mass of 2 kg and an air resistance coefficient 0.03 Nt-s2/m2 from a helicopter 1,000 meters above the ground. Fgravity = mg = 2 kg * 9.8 m/s ...
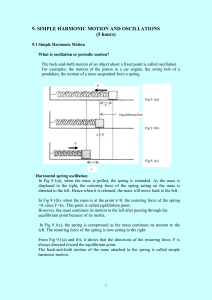
simple harmonic motion and oscilation
... The negative sign indicates that F is always in the opposite direction to the displacement. From Newton’s second Law of motion, equation 9.18 can be written as ...
... The negative sign indicates that F is always in the opposite direction to the displacement. From Newton’s second Law of motion, equation 9.18 can be written as ...
ODU-Mechanics-Questions
... Balanced and unbalanced forces .................................................... 17 Resolution of forces ...................................................................... 22 Work done, kinetic and potential energy ........................................ 25 Section 3: Collisions and explosio ...
... Balanced and unbalanced forces .................................................... 17 Resolution of forces ...................................................................... 22 Work done, kinetic and potential energy ........................................ 25 Section 3: Collisions and explosio ...
Document
... Newton’s Law of Gravitation Gravitational force: an attractive force that exists between all objects with mass; an object with mass attracts another object with mass; the magnitude of the force is directly proportional to the masses of the two objects and inversely proportional to the square of the ...
... Newton’s Law of Gravitation Gravitational force: an attractive force that exists between all objects with mass; an object with mass attracts another object with mass; the magnitude of the force is directly proportional to the masses of the two objects and inversely proportional to the square of the ...
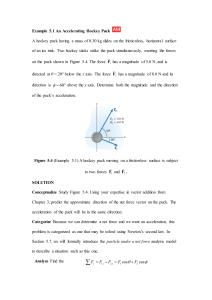
Example 5.1 An Accelerating Hockey Puck A hockey puck having a
... hands together and push against each other so that they move apart. (A) Who moves away with the higher speed? SOLUTION This situation is similar to what we saw in Quick Quiz 5.5. According to Newton’s third law, the force exerted by the man on the boy and the force exerted by the boy on the man are ...
... hands together and push against each other so that they move apart. (A) Who moves away with the higher speed? SOLUTION This situation is similar to what we saw in Quick Quiz 5.5. According to Newton’s third law, the force exerted by the man on the boy and the force exerted by the boy on the man are ...
MAE 241 –Statics Fall 2006 Jacky C. Prucz
... The motion of a particle is governed by Newton’s three laws of motion. First Law: A particle originally at rest, or moving in a straight line at constant velocity, will remain in this state if the resultant force acting on the particle is zero. Second Law: If the resultant force on the particle ...
... The motion of a particle is governed by Newton’s three laws of motion. First Law: A particle originally at rest, or moving in a straight line at constant velocity, will remain in this state if the resultant force acting on the particle is zero. Second Law: If the resultant force on the particle ...
0BJECTIVES 7
... 4. A man pushes a crate along a factory floor by exerting a force of 55 N. If the crate moves a distance of 4.0 m, how much work does the man perform? a. 165 J c. zero b. 220 J d. 145 J ...
... 4. A man pushes a crate along a factory floor by exerting a force of 55 N. If the crate moves a distance of 4.0 m, how much work does the man perform? a. 165 J c. zero b. 220 J d. 145 J ...
Tuesday, June 26, 2007 - UTA High Energy Physics page.
... the infinitesimal distance ds=rdq is dW F ds F cos( 2 f ) rdq F sin f rdq What is Fsinf? ...
... the infinitesimal distance ds=rdq is dW F ds F cos( 2 f ) rdq F sin f rdq What is Fsinf? ...
PHYS 1443 – Section 501 Lecture #1
... Consider a system with two particles that does not have any external forces exerting on it. What is the impact of Newton’s 3rd Law? If particle#1 exerts force on particle #2, there must be another force that the particle #2 exerts on #1 as the reaction force. Both the forces are internal forces and ...
... Consider a system with two particles that does not have any external forces exerting on it. What is the impact of Newton’s 3rd Law? If particle#1 exerts force on particle #2, there must be another force that the particle #2 exerts on #1 as the reaction force. Both the forces are internal forces and ...
Mechanical Systems - University of KwaZulu
... •What class lever is used in the example above? (1) •What is the output force required to lift the car? (5) The handles of the wheelbarrow are 2.00m long from the front wheel. A 95kg load is placed 25cm behind the wheel. ...
... •What class lever is used in the example above? (1) •What is the output force required to lift the car? (5) The handles of the wheelbarrow are 2.00m long from the front wheel. A 95kg load is placed 25cm behind the wheel. ...