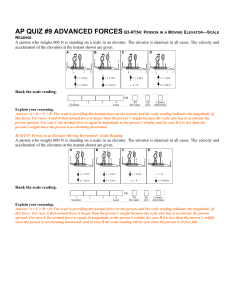
ACTIVITY 1: Forces and Motion
... scientists have concluded that it is a force that acts in the opposite direction as an object’s motion. In the case of friction force (F Friction), the force diagram is always drawn ...
... scientists have concluded that it is a force that acts in the opposite direction as an object’s motion. In the case of friction force (F Friction), the force diagram is always drawn ...
Physics_files/Unit 5 Review Part 1
... Unit 5: Forces & Momentum When objects interact, like forces are exchanged and momentum is transferred. ...
... Unit 5: Forces & Momentum When objects interact, like forces are exchanged and momentum is transferred. ...
Introductory Physics Laboratory Manual Course 20300
... No measuring device can be read to an unlimited number of digits. In addition when we repeat a measurement we often obtain a different value because of changes in conditions that we cannot control. We are therefore uncertain as to the exact values of measurements. These uncertainties make quantities ...
... No measuring device can be read to an unlimited number of digits. In addition when we repeat a measurement we often obtain a different value because of changes in conditions that we cannot control. We are therefore uncertain as to the exact values of measurements. These uncertainties make quantities ...
7thMotionfinal_Oct
... Gravity is a universal force that causes objects to be attracted to each other. When no other outside force, such as friction or air resistance, acts upon a falling object, its speed increases. An object constantly gains speed for every second it falls until it reaches a maximum speed, which differs ...
... Gravity is a universal force that causes objects to be attracted to each other. When no other outside force, such as friction or air resistance, acts upon a falling object, its speed increases. An object constantly gains speed for every second it falls until it reaches a maximum speed, which differs ...
JP`s Physics 101 Test Bank 1
... ____ 68. To report the ____ of an object, we must specify both its speed and its direction . A. acceleration B. position C. mass D. velocity E. length ____ 69. Assuming level ground and no air resistance, a projectile fired at an angle of 30° will have the same range as another projectile fired with ...
... ____ 68. To report the ____ of an object, we must specify both its speed and its direction . A. acceleration B. position C. mass D. velocity E. length ____ 69. Assuming level ground and no air resistance, a projectile fired at an angle of 30° will have the same range as another projectile fired with ...
Experiment P09: Acceleration of a Dynamics Cart I (Smart Pulley)
... For this activity, a Smart Pulley will measure the motion of a cart as it is pulled by a string that is attached to an object suspended over the pulley. The Science Workshop program calculates the changing speed of the cart as it moves. A graph of speed and time can give the acceleration of the cart ...
... For this activity, a Smart Pulley will measure the motion of a cart as it is pulled by a string that is attached to an object suspended over the pulley. The Science Workshop program calculates the changing speed of the cart as it moves. A graph of speed and time can give the acceleration of the cart ...
Turntables PPT - Physics of Theatre Home
... r = radius from axis to force (ft) q = angle between r and F (will be 90o for turntable drives) ...
... r = radius from axis to force (ft) q = angle between r and F (will be 90o for turntable drives) ...
Review the study notes and homework for the hour tests and
... Know how to find the proper banking angle for banked curves (Equation 5.4). Be able to recognize Equations (5.5) and (5.6) as formulas for the speed and period, respectively of an object in a circular orbit. Chapter 6 Work and Energy Summary is on p.186. Know how to find the work done by a constant ...
... Know how to find the proper banking angle for banked curves (Equation 5.4). Be able to recognize Equations (5.5) and (5.6) as formulas for the speed and period, respectively of an object in a circular orbit. Chapter 6 Work and Energy Summary is on p.186. Know how to find the work done by a constant ...