ppt - Physics
... • Another frictional force, called the static frictional force, acts even when there is no motion between the surfaces of two objects. • The magnitude of the static frictional force, fs , can have any value from zero up to a maximum value that depends on the applied force. ...
... • Another frictional force, called the static frictional force, acts even when there is no motion between the surfaces of two objects. • The magnitude of the static frictional force, fs , can have any value from zero up to a maximum value that depends on the applied force. ...
Sects. 12.3 through 12.4
... horizontal force of 20.0 N is required to hold the object at rest when it is pulled 0.200 m from its equilibrium position (the origin of the x axis). The object is now released from rest with an initial position of xi = 0.200 m, and it subsequently undergoes simple harmonic oscillations. Find (a) th ...
... horizontal force of 20.0 N is required to hold the object at rest when it is pulled 0.200 m from its equilibrium position (the origin of the x axis). The object is now released from rest with an initial position of xi = 0.200 m, and it subsequently undergoes simple harmonic oscillations. Find (a) th ...
Test #4 - Wando High School
... currently blowing due north at 12.0 m/s. By the time it travels 150.0 m due west using its engines power, how far will it have flown due north due to the air current? Non-900 problems ...
... currently blowing due north at 12.0 m/s. By the time it travels 150.0 m due west using its engines power, how far will it have flown due north due to the air current? Non-900 problems ...
Circular Motion & Gravity
... • Fc could take any form…. • It could be frictional force, tension force, gravitational force, etc. ...
... • Fc could take any form…. • It could be frictional force, tension force, gravitational force, etc. ...
Assignment of Laws of Motion
... Q1. What is the purpose of using shockers in vehicles? Q2. Wheels are made circular why? Q3.calculate impulse necessary to stop a 1500kg car moving with a velocity 25m/s. Q4. what is the inertial frame of reference? Q5. A 50gm bullet is fired from 10kg gun with velocity of 500m/s what is the speed o ...
... Q1. What is the purpose of using shockers in vehicles? Q2. Wheels are made circular why? Q3.calculate impulse necessary to stop a 1500kg car moving with a velocity 25m/s. Q4. what is the inertial frame of reference? Q5. A 50gm bullet is fired from 10kg gun with velocity of 500m/s what is the speed o ...
53 - Angelfire
... 2.55. The speed of a bullet as it travels down the barrel of a rifle toward the opening is given by the expression v = (-5.0 x 107)t2 + (3.0 x 105)t, where v is in meters per second and t is in seconds. The acceleration of the bullet just as it leaves the barrel is zero. (a) Determine the accelerati ...
... 2.55. The speed of a bullet as it travels down the barrel of a rifle toward the opening is given by the expression v = (-5.0 x 107)t2 + (3.0 x 105)t, where v is in meters per second and t is in seconds. The acceleration of the bullet just as it leaves the barrel is zero. (a) Determine the accelerati ...
Chapter 8 Motion and Forces - Mrs. Cavanaugh's PbWiki
... What is the difference between balanced and unbalanced forces? Balanced forces: equal amount of force exerted so net force is zero No movement…..cancel each other Unbalanced forces: forces acting on object do not have same strength, so greatest force will cause the object to accelerate in that dire ...
... What is the difference between balanced and unbalanced forces? Balanced forces: equal amount of force exerted so net force is zero No movement…..cancel each other Unbalanced forces: forces acting on object do not have same strength, so greatest force will cause the object to accelerate in that dire ...
Chapter 3 Notes
... forward, you will go backward. The heavier the ball or the faster you throw it, the quicker you will go backward. P = m x v, P = momentum (kgm/s), m = mass (kg), v = velocity (m/s) Law of Conservation of Momentummomentum cannot be created or destroyed in a group of objects NOT effected by an outsid ...
... forward, you will go backward. The heavier the ball or the faster you throw it, the quicker you will go backward. P = m x v, P = momentum (kgm/s), m = mass (kg), v = velocity (m/s) Law of Conservation of Momentummomentum cannot be created or destroyed in a group of objects NOT effected by an outsid ...
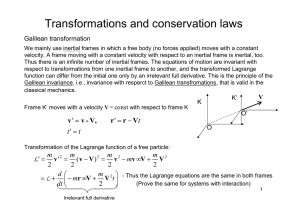
Transformations and conservation laws
... Galilean transformation We mainly use inertial frames in which a free body (no forces applied) moves with a constant velocity. A frame moving with a constant velocity with respect to an inertial frame is inertial, too. Thus there is an infinite number of inertial frames. The equations of motion are ...
... Galilean transformation We mainly use inertial frames in which a free body (no forces applied) moves with a constant velocity. A frame moving with a constant velocity with respect to an inertial frame is inertial, too. Thus there is an infinite number of inertial frames. The equations of motion are ...
22Sept_2014
... • a. The ball bounces because the court floor pushes up on it every time it hits; • b. The floor experiences no acceleration due to the dribbling ball because its mass is so large compared to that of the ball. • c. The ball exerts a force on the player's hand each time the two connect; • d. The play ...
... • a. The ball bounces because the court floor pushes up on it every time it hits; • b. The floor experiences no acceleration due to the dribbling ball because its mass is so large compared to that of the ball. • c. The ball exerts a force on the player's hand each time the two connect; • d. The play ...
1) 200 km/hr 2) 100 km/hr 3) 90 km/hr 4) 70 km/hr 5) 50 km/hr From
... accelerating upward. What is ...
... accelerating upward. What is ...
Motion and Forces Jeopardy
... 24. Formula Daily Double: What is the formula for momentum? P= M X V 25. Which Newton’s Law that states the force acting on an object is equal to the mass X the acceleration. second law 26. The force that opposes the motion when surfaces are in contact with one another. friction 27. Motion under the ...
... 24. Formula Daily Double: What is the formula for momentum? P= M X V 25. Which Newton’s Law that states the force acting on an object is equal to the mass X the acceleration. second law 26. The force that opposes the motion when surfaces are in contact with one another. friction 27. Motion under the ...
26a Dynamics Review A - stpats-sph3u-sem1-2013
... Provide a complete description of the sensations one feels as a result of the ride and an explanation of these sensations using Newton’s laws of motion. 3. Newton’s first law states that objects will remain at rest or in uniform motion provided no external unbalanced force acts on them. Newton’s thi ...
... Provide a complete description of the sensations one feels as a result of the ride and an explanation of these sensations using Newton’s laws of motion. 3. Newton’s first law states that objects will remain at rest or in uniform motion provided no external unbalanced force acts on them. Newton’s thi ...