Units, Metric System and Conversions - bba-npreiser
... • So how can they start moving, or accelerate? ...
... • So how can they start moving, or accelerate? ...
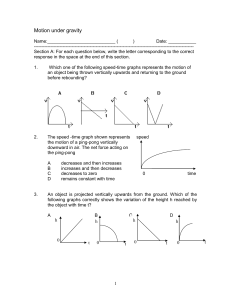
Quiz on Motion under gravity
... Which one of the following speed-time graphs represents the motion of an object being thrown vertically upwards and returning to the ground ...
... Which one of the following speed-time graphs represents the motion of an object being thrown vertically upwards and returning to the ground ...
P2a Forces and Their Effects
... Car safety: The force on a passenger will be large if there is a large change in momentum in a short time. The key to safety is to extend the time of impact to reduce the force. This is done by: seat belts stretch a little, crumple zones at the front and rear, air bags to cushion the impact. ...
... Car safety: The force on a passenger will be large if there is a large change in momentum in a short time. The key to safety is to extend the time of impact to reduce the force. This is done by: seat belts stretch a little, crumple zones at the front and rear, air bags to cushion the impact. ...
Motion & Forces
... Any passenger not wearing a safety belt continues to move forward at the same speed the car was traveling. Within about 0.02 s (1/50 of a second) after the car stops, unbelted passengers slam into the dashboard, steering wheel, windshield, or the backs of the front seats. The force needed to slow a ...
... Any passenger not wearing a safety belt continues to move forward at the same speed the car was traveling. Within about 0.02 s (1/50 of a second) after the car stops, unbelted passengers slam into the dashboard, steering wheel, windshield, or the backs of the front seats. The force needed to slow a ...
Unit 3 - Forces
... If you stop pushing an object, does it stop moving? Newton’s First Law - In the absence of any net external force, an object will keep moving at a constant speed in a straight line, or remain at rest. This is also known as the law of inertia. ...
... If you stop pushing an object, does it stop moving? Newton’s First Law - In the absence of any net external force, an object will keep moving at a constant speed in a straight line, or remain at rest. This is also known as the law of inertia. ...
Matching - Hauserphysics
... 53. T/F, The Law of Inertia says that if an object has a zero net force, its motion will not change. 54. If more force is applied to an object, its acceleration will _______________. A) increase B) decrease 55. A force of 100 N is applied to objects A and B. Object A’s mass is 6 kg and object B’s ma ...
... 53. T/F, The Law of Inertia says that if an object has a zero net force, its motion will not change. 54. If more force is applied to an object, its acceleration will _______________. A) increase B) decrease 55. A force of 100 N is applied to objects A and B. Object A’s mass is 6 kg and object B’s ma ...
Part I
... • Fr is NOT a new kind of force. Exactly what it is depends on the problem. It could be string tension, gravity, etc. It is the right side of ∑F = ma, not the left side! (It is the form of ma for circular motion) ...
... • Fr is NOT a new kind of force. Exactly what it is depends on the problem. It could be string tension, gravity, etc. It is the right side of ∑F = ma, not the left side! (It is the form of ma for circular motion) ...
Forces 6 - Cobb Learning
... force is zero and the horse cannot pull the cart." What is wrong about this set of particulars? [I.e., why can the horse pull the cart?] ...
... force is zero and the horse cannot pull the cart." What is wrong about this set of particulars? [I.e., why can the horse pull the cart?] ...
17.5 Acceleration and Newton`s 2nd law of motion
... About 100 years later, Newton’s second law explained why. A heavy object experiences a stronger pull from gravity than a light object, but it also has more inertia which makes it harder to get moving! The two effects cancel out, so all objects fall to Earth a = F1/m1 = F2/m2 with the same accelerati ...
... About 100 years later, Newton’s second law explained why. A heavy object experiences a stronger pull from gravity than a light object, but it also has more inertia which makes it harder to get moving! The two effects cancel out, so all objects fall to Earth a = F1/m1 = F2/m2 with the same accelerati ...
Document
... •Motion = Event that involves a change in the position or location of something •Distance is the total length traveled from motion…distance traveled depends on the path you take •Displacement is a straight line distance between 2 points •Reference point is a location to which you compare other locat ...
... •Motion = Event that involves a change in the position or location of something •Distance is the total length traveled from motion…distance traveled depends on the path you take •Displacement is a straight line distance between 2 points •Reference point is a location to which you compare other locat ...
... Reaction forces does not appear since it acts on There are four fundamental forces in the “The acceleration a of an object is directly a different object. nature, but we will discuss the fundamental proportional to the net force acting on it and Drawing a free body diagram. forces later time. invers ...
Day 1 Notes: Dealing with projectiles in two dimensions. There are
... D. Diagonal forces can be split into x axis and y axis. Then, using trig functions, a student simply can plug the net force value in to Newton’s second law formula. E. When a student is encountered with an off centered plane questions, simply make diagonal lines x and y axis. Then, the original hori ...
... D. Diagonal forces can be split into x axis and y axis. Then, using trig functions, a student simply can plug the net force value in to Newton’s second law formula. E. When a student is encountered with an off centered plane questions, simply make diagonal lines x and y axis. Then, the original hori ...
MOTION, FORCES, AND WORK
... 11. Work: Force exerted on an object that causes it to move. 12. Joule: a unit of work equal to one Newton-meter 13. Machine: a device that changes that amount of force exerted or the direction in which force is exerted 14. Fulcrum: the fixed point around which a lever rotates 15. Compound machine: ...
... 11. Work: Force exerted on an object that causes it to move. 12. Joule: a unit of work equal to one Newton-meter 13. Machine: a device that changes that amount of force exerted or the direction in which force is exerted 14. Fulcrum: the fixed point around which a lever rotates 15. Compound machine: ...
Roller Coasters and Science??
... An object at rest remains at rest and an object in motion maintains its velocity unless it experiences an unbalanced force. What does this mean? When the roller coaster is going it will keep going unless something stops it ...
... An object at rest remains at rest and an object in motion maintains its velocity unless it experiences an unbalanced force. What does this mean? When the roller coaster is going it will keep going unless something stops it ...
speed
... unbalanced forces cause objects to accelerate with an acceleration which is directly proportional to the net force and inversely proportional to the mass. This one is telling us that big heavy objects don’t move as fast or as easily as smaller lighter objects. It takes more to slow down a charging b ...
... unbalanced forces cause objects to accelerate with an acceleration which is directly proportional to the net force and inversely proportional to the mass. This one is telling us that big heavy objects don’t move as fast or as easily as smaller lighter objects. It takes more to slow down a charging b ...
practice for midterm, part 3 - West Windsor
... b) Determine the direction of acceleration using a motion diagram. c) Interpret x vs t and v vs t graphs in terms of position, velocity, displacement, and acceleration. 1. Are you moving while sitting on a train that is leaving the station? 2. Describe the point-like model of a real object. Explain ...
... b) Determine the direction of acceleration using a motion diagram. c) Interpret x vs t and v vs t graphs in terms of position, velocity, displacement, and acceleration. 1. Are you moving while sitting on a train that is leaving the station? 2. Describe the point-like model of a real object. Explain ...
When the Acceleration is g
... If v is antiparallel to F, speed decreases. If v perpendicular to F, direction of v changes. See Check Yourself questions page 59, ...
... If v is antiparallel to F, speed decreases. If v perpendicular to F, direction of v changes. See Check Yourself questions page 59, ...
HP Unit 2 vectors & newton 1D - student handout
... A person stands on a bathroom scale in an elevator at rest on the ground floor of a building. The scale reads 836N. As the elevator begins to move upward, the scale reading briefly increases to 935N but then returns to 836N after reaching a constant speed. a) Determine the acceleration of the elevat ...
... A person stands on a bathroom scale in an elevator at rest on the ground floor of a building. The scale reads 836N. As the elevator begins to move upward, the scale reading briefly increases to 935N but then returns to 836N after reaching a constant speed. a) Determine the acceleration of the elevat ...