CHAPTER THREE NOTES - NEWTON`S SECOND LAW OF
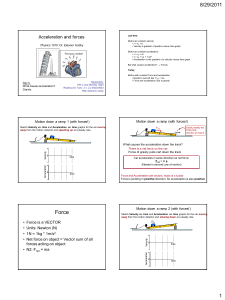
... CONSTANT ACCELERATION happens when an object changes velocity at a predictable, even rate. This would happen with a ball rolling down an incline track or a falling object in free fall. Two formulas can be used for constant acceleration. v=at for finding the speed of a constantly accelerating object ...
... CONSTANT ACCELERATION happens when an object changes velocity at a predictable, even rate. This would happen with a ball rolling down an incline track or a falling object in free fall. Two formulas can be used for constant acceleration. v=at for finding the speed of a constantly accelerating object ...
Physics Presentation
... object to follow a circular path. “Any force that is directed at right angles to the path of the moving body and produces circular motion.” ...
... object to follow a circular path. “Any force that is directed at right angles to the path of the moving body and produces circular motion.” ...
BT109 General Chemistry
... Newton’s First Law @ The motion of an object does not change unless it is acted upon by a net force. * If v = 0, it remains at rest. * If v = C, it till move at that value. @ Another way to say the same thing: ...
... Newton’s First Law @ The motion of an object does not change unless it is acted upon by a net force. * If v = 0, it remains at rest. * If v = C, it till move at that value. @ Another way to say the same thing: ...
ppt
... Before going on: Remember that this all boils down to particles Mass, position, velocity, (linear) momentum, force are fundamental Inertia tensor, orientation, angular velocity, angular momentum, torque are just abstractions Don’t get too puzzled about interpretation of torque for example: ...
... Before going on: Remember that this all boils down to particles Mass, position, velocity, (linear) momentum, force are fundamental Inertia tensor, orientation, angular velocity, angular momentum, torque are just abstractions Don’t get too puzzled about interpretation of torque for example: ...
Document
... This idea is called inertia. Explain why your body feels like it is being pushed back when the car starts back up again: __________________________________________________________ ...
... This idea is called inertia. Explain why your body feels like it is being pushed back when the car starts back up again: __________________________________________________________ ...
Chapter 3 - Mrs. Wiedeman
... How would you throw a long pass with a football? Anything that has mass is attracted by gravity Gravity: attractive force between two objects that depends on masses and distance Stronger force? More mass/closer together ...
... How would you throw a long pass with a football? Anything that has mass is attracted by gravity Gravity: attractive force between two objects that depends on masses and distance Stronger force? More mass/closer together ...
Forces and the Laws of Motion Section 3
... •Objects at rest stay at rest and objects in motion stay in motion with the same speed and in the same direction unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. (also called the law of inertia). ...
... •Objects at rest stay at rest and objects in motion stay in motion with the same speed and in the same direction unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. (also called the law of inertia). ...
Sport Application and Newton`s Laws of Motion
... power impressed, and is made in the direction of the right(straight) line in which the force is impressed. • Or • If a body of mass(m) has an acceleration(a), the force acting on it is (f), defined as the product of its mass and acceleration (F=ma) • Law of Acceleration-the acceleration of an object ...
... power impressed, and is made in the direction of the right(straight) line in which the force is impressed. • Or • If a body of mass(m) has an acceleration(a), the force acting on it is (f), defined as the product of its mass and acceleration (F=ma) • Law of Acceleration-the acceleration of an object ...
File
... Helpful Questions: 1. What are coefficients of friction and how do they affect the motion of an object on a surface? ...
... Helpful Questions: 1. What are coefficients of friction and how do they affect the motion of an object on a surface? ...
Question 1 - BrainMass
... same direction and minimum of 470m if they are in apposite directions. When we find resultant 10m with 530 and x value of x should be 520m or 540m and with 470m it should be 460m and 480m. Hence x could be a minimum of 460m and a maximum value of 540m. Between 460m and 540 meters ...
... same direction and minimum of 470m if they are in apposite directions. When we find resultant 10m with 530 and x value of x should be 520m or 540m and with 470m it should be 460m and 480m. Hence x could be a minimum of 460m and a maximum value of 540m. Between 460m and 540 meters ...