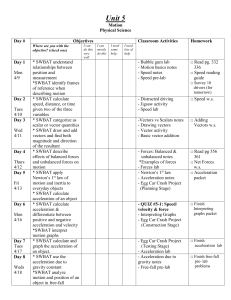
Unit 5 plan motion
... * SWBAT categorize as scalar or vector quantities * SWBAT draw and add vectors and find both magnitude and direction of the resultant * SWBAT describe effects of balanced forces and unbalanced forces on motion * SWBAT apply Newton’s 1st law of motion and inertia to everyday objects * SWBAT calculate ...
... * SWBAT categorize as scalar or vector quantities * SWBAT draw and add vectors and find both magnitude and direction of the resultant * SWBAT describe effects of balanced forces and unbalanced forces on motion * SWBAT apply Newton’s 1st law of motion and inertia to everyday objects * SWBAT calculate ...
AP1 Ch. 8 Review w/answers
... 1. In a spin cycle of a clothes washer, the drum turns at 635 rev/min. If the lid of the washer is opened, the motor is turned off. It takes 8.0 s for the drum to slow to a stop. a.) What is the initial angular velocity of the drum? ...
... 1. In a spin cycle of a clothes washer, the drum turns at 635 rev/min. If the lid of the washer is opened, the motor is turned off. It takes 8.0 s for the drum to slow to a stop. a.) What is the initial angular velocity of the drum? ...
Chapter 4: Forces and the Laws of Motion Name Use Chapter 4 in
... Definition The vector sum of all the forces acting on an object. An applied force on an object like a push or pull. The force due to gravity on an object. The resistance to motion that occurs whenever 2 materials or media are in contact. A tension force transmitted through a string or rope when it i ...
... Definition The vector sum of all the forces acting on an object. An applied force on an object like a push or pull. The force due to gravity on an object. The resistance to motion that occurs whenever 2 materials or media are in contact. A tension force transmitted through a string or rope when it i ...
Document
... Example: Consider two objects of mass m and 2m are accelerated from rest. Compare the work done on them, their final kinetic energies and their final speeds if they are under the influence of identical forces acting over the same distances. Compare the work done on them, their final kinetic energie ...
... Example: Consider two objects of mass m and 2m are accelerated from rest. Compare the work done on them, their final kinetic energies and their final speeds if they are under the influence of identical forces acting over the same distances. Compare the work done on them, their final kinetic energie ...
Describing Motion - Science
... First we need to define the word FORCE: • The cause of motion (what causes objects to move) • Two types of forces – Pushes – Pulls ...
... First we need to define the word FORCE: • The cause of motion (what causes objects to move) • Two types of forces – Pushes – Pulls ...
3 newton`s laws of motion notes
... object to resist changing its state of motion. • An object with a lot of inertia takes a lot of force to stop • Mass is a measure of the inertia of an object • The more mass an object has the greater the inertia and the greater the force needed to change the object’s motion. ...
... object to resist changing its state of motion. • An object with a lot of inertia takes a lot of force to stop • Mass is a measure of the inertia of an object • The more mass an object has the greater the inertia and the greater the force needed to change the object’s motion. ...
Measurement and Kinematics
... 36. How do the angular and linear speed for an object near the center of a merry go round compare to one towards the edge? 37. What is the force called which causes an object to move in a circle? 38. If an object is traveling in a circle, what is the direction is the force acting upon it? 39. How ca ...
... 36. How do the angular and linear speed for an object near the center of a merry go round compare to one towards the edge? 37. What is the force called which causes an object to move in a circle? 38. If an object is traveling in a circle, what is the direction is the force acting upon it? 39. How ca ...
lecture03
... Application of Newton’s Laws (Ropes and tension) Example 1: You tie a rope to a tree and you pull on the rope with a force of 100 N. What is the tension in the rope? The tension in the rope is the force that the rope “feels” across any section of it (or that you would feel if you replaced a piece o ...
... Application of Newton’s Laws (Ropes and tension) Example 1: You tie a rope to a tree and you pull on the rope with a force of 100 N. What is the tension in the rope? The tension in the rope is the force that the rope “feels” across any section of it (or that you would feel if you replaced a piece o ...
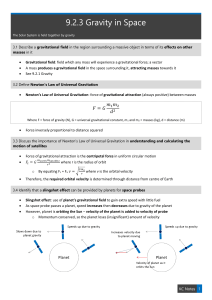
Chapter 6 Notes Circular Motion and Gravity
... A curved path requires an inward pull. centripetal force: the force needed to make an object follow a curved path Centripetal force is the force perpendicular to the velocity of an object moving along a curved path. The centripetal force is the force directed toward the center of the curvature of th ...
... A curved path requires an inward pull. centripetal force: the force needed to make an object follow a curved path Centripetal force is the force perpendicular to the velocity of an object moving along a curved path. The centripetal force is the force directed toward the center of the curvature of th ...
TEST 2 (96-97) Laws of Motion/5-7
... Understanding the relationship between weight, mass, and inertia. ...
... Understanding the relationship between weight, mass, and inertia. ...
Circular Motion PowerPoint
... • We usually think of acceleration as a change in speed. • Because velocity includes both speed and direction, acceleration can also be a change in the direction of motion. ...
... • We usually think of acceleration as a change in speed. • Because velocity includes both speed and direction, acceleration can also be a change in the direction of motion. ...
Exam Name___________________________________
... 25) If the velocity of the roller coaster car is sufficiently large at the top of the loop, the person (and car) will remain on the track. For lower speeds, the normal force on the person goes to 0 before she reaches the top, meaning that she comes out of the seat. mV2 (This follows from N = r - m ...
... 25) If the velocity of the roller coaster car is sufficiently large at the top of the loop, the person (and car) will remain on the track. For lower speeds, the normal force on the person goes to 0 before she reaches the top, meaning that she comes out of the seat. mV2 (This follows from N = r - m ...
Introduction to Forces and Newton*s Laws of Motion
... A thrown ball and dropped ball will hit the ground at the same time. Both balls travel the same vertical distance in the same amount of time. The thrown ball travels a greater horizontal ...
... A thrown ball and dropped ball will hit the ground at the same time. Both balls travel the same vertical distance in the same amount of time. The thrown ball travels a greater horizontal ...