
How Do I Move? - tpsexercisescience12
... Occurs when a body moves along a circular path, through the same angle, in the same direction, and at the same time ...
... Occurs when a body moves along a circular path, through the same angle, in the same direction, and at the same time ...
Regular Note
... While driving down the road, a firefly strikes the windshield of a bus and makes a quite obvious mess in front of the face of the driver. This is a clear case of Newton's third law of motion. The firefly hit the bus and the bus hits the firefly. Which of the two forces is greater: the force on the f ...
... While driving down the road, a firefly strikes the windshield of a bus and makes a quite obvious mess in front of the face of the driver. This is a clear case of Newton's third law of motion. The firefly hit the bus and the bus hits the firefly. Which of the two forces is greater: the force on the f ...
Tutorial 7
... its axis. The centripetal acceleration of another student at Cambridge is ac. What are the magnitudes of the centripetal acceleration for each student? Radius of Earth Angular velocity of Earth about its own axis ...
... its axis. The centripetal acceleration of another student at Cambridge is ac. What are the magnitudes of the centripetal acceleration for each student? Radius of Earth Angular velocity of Earth about its own axis ...
Force and Motion
... _____ opposes motion between touching objects. How is mass different from weight? Define friction. How do we use natural forces everyday? Share with a partner one thing you learned about force and motion. ...
... _____ opposes motion between touching objects. How is mass different from weight? Define friction. How do we use natural forces everyday? Share with a partner one thing you learned about force and motion. ...
Force and Motion
... _____ opposes motion between touching objects. How is mass different from weight? Define friction. How do we use natural forces everyday? Share with a partner one thing you learned about force and motion. ...
... _____ opposes motion between touching objects. How is mass different from weight? Define friction. How do we use natural forces everyday? Share with a partner one thing you learned about force and motion. ...
Chapter 11 Test
... 1. Which of the following is not a factor in calculating momentum? a. mass c. acceleration b. direction d. speed 2. If you divide momentum by velocity, the result is the value of the object’s a. mass. c. energy. b. direction. d. speed. 3. Whenever an object is standing still, the value(s) that is/ar ...
... 1. Which of the following is not a factor in calculating momentum? a. mass c. acceleration b. direction d. speed 2. If you divide momentum by velocity, the result is the value of the object’s a. mass. c. energy. b. direction. d. speed. 3. Whenever an object is standing still, the value(s) that is/ar ...
ASTRONOMY 161
... (2) The acceleration of an object is directly proportional to force, and inversely proportional to mass. (3) For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. Law of Gravity: (4) The gravitational force between masses M and m, separated by distance r, is ...
... (2) The acceleration of an object is directly proportional to force, and inversely proportional to mass. (3) For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. Law of Gravity: (4) The gravitational force between masses M and m, separated by distance r, is ...
Lecture Notes: Chapter 2 Motion
... Scientists at NASA need to consider frames of reference because all objects in space are in constant motion relative to earth. They can’t just send up a satellite or spacecraft and expect it to be at the speed of the other objects. Distance An important part of describing the motion of an object ...
... Scientists at NASA need to consider frames of reference because all objects in space are in constant motion relative to earth. They can’t just send up a satellite or spacecraft and expect it to be at the speed of the other objects. Distance An important part of describing the motion of an object ...
The Force
... of an object with zero net force. • Only a frame of reference (F.O.R) can distinguish between rest and constant velocity. An object at rest in one F.O.R can have constant velocity in another (F.O.R) • It defines the kind of frame of reference, called an inertial frame of reference, in which Newton’s ...
... of an object with zero net force. • Only a frame of reference (F.O.R) can distinguish between rest and constant velocity. An object at rest in one F.O.R can have constant velocity in another (F.O.R) • It defines the kind of frame of reference, called an inertial frame of reference, in which Newton’s ...


















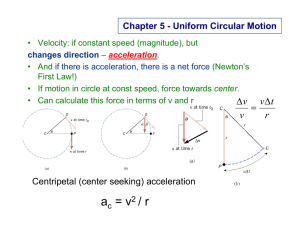



![[force and motion]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/006065207_1-8bff05158caa0c6fdea67b84566f5781-300x300.png)
