force - the SASPhysics.com
... on it so resultant force is just its weight. Remember F = ma? Acceleration of 10m/s2 is constant for all objects. ...
... on it so resultant force is just its weight. Remember F = ma? Acceleration of 10m/s2 is constant for all objects. ...
Newton`s 3rd Law of Motion
... obviously, this is a case of Newton's third law of motion. The bug hit the windshield and the windshield hit the bug. Which of the two forces is greater: the force on the bug or the force on the bus? ...
... obviously, this is a case of Newton's third law of motion. The bug hit the windshield and the windshield hit the bug. Which of the two forces is greater: the force on the bug or the force on the bus? ...
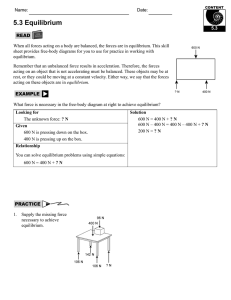
notes 5.3
... For an object to be in equilibrium, all the forces acting on the object must add up to zero. Is this object in ...
... For an object to be in equilibrium, all the forces acting on the object must add up to zero. Is this object in ...
Forces
... • Mass and weight are NOT the same thing. – Mass is a scalar measurement of how much matter an object is made of. An object’s mass does not change because it’s location has changed. – Weight is a vector measurement of the force gravity exerts on an object. If you take an object from the surface of t ...
... • Mass and weight are NOT the same thing. – Mass is a scalar measurement of how much matter an object is made of. An object’s mass does not change because it’s location has changed. – Weight is a vector measurement of the force gravity exerts on an object. If you take an object from the surface of t ...
Getting Into Orbit
... Newtons 1st Law: obj in motion stays in motion, object rest stays at rest, unless acted upon by an outside force. An object will continue to stay in a straight path unless a force acts upon it. If you apply a force, you get an acceleration, which changes the velocity. Therefore, acceleration is the ...
... Newtons 1st Law: obj in motion stays in motion, object rest stays at rest, unless acted upon by an outside force. An object will continue to stay in a straight path unless a force acts upon it. If you apply a force, you get an acceleration, which changes the velocity. Therefore, acceleration is the ...
Universal Gravitation
... 4. If a gravitational force exists between two bodies of different masses, which one feels the stronger force? ____________________________________________ 5. If a gravitational force exists between two bodies of different masses, which one experiences more acceleration? ____________________________ ...
... 4. If a gravitational force exists between two bodies of different masses, which one feels the stronger force? ____________________________________________ 5. If a gravitational force exists between two bodies of different masses, which one experiences more acceleration? ____________________________ ...
forces - Humble ISD
... defined to be the force, W, with which it is attracted to the Earth. On Earth, W = mg, where g is the acceleration due to gravity. (g ≈ 9.81 m/ s2 on Earth). • Weight depends on what planet you’re on. It doesn’t stay the same, like mass does. ...
... defined to be the force, W, with which it is attracted to the Earth. On Earth, W = mg, where g is the acceleration due to gravity. (g ≈ 9.81 m/ s2 on Earth). • Weight depends on what planet you’re on. It doesn’t stay the same, like mass does. ...
Chapter 3 lecture notes pdf
... Falling without air resistance ∑F=ma Gravity is the only force acting upon the object causing the object to change it’s velocity Acceleration (change in velocity) due to gravity on earth is 9.8 m/sec/sec for all objects That means . . . When an object is in free fall it will be increasing its v ...
... Falling without air resistance ∑F=ma Gravity is the only force acting upon the object causing the object to change it’s velocity Acceleration (change in velocity) due to gravity on earth is 9.8 m/sec/sec for all objects That means . . . When an object is in free fall it will be increasing its v ...
The Work-Energy Theorem
... Mechanical Energy The total mechanical energy (E = KE + PE) of an object remains constant as the object moves, provided that the net work done by external nonconservative forces is zero. ...
... Mechanical Energy The total mechanical energy (E = KE + PE) of an object remains constant as the object moves, provided that the net work done by external nonconservative forces is zero. ...
1 PHYSICS 231 Lecture 7: Newton`s Laws
... A ball is rolling from a slope. If the angle is decreased: a) the normal force on the ball increases b) the normal force gets closer to the gravitational force c) the ball rolls slower d) all of the above ...
... A ball is rolling from a slope. If the angle is decreased: a) the normal force on the ball increases b) the normal force gets closer to the gravitational force c) the ball rolls slower d) all of the above ...
Force and Motion
... Acceleration happens when a force acts on a mass. The greater the mass (of the object being accelerated) the greater the amount of force needed (to accelerate the object). ...
... Acceleration happens when a force acts on a mass. The greater the mass (of the object being accelerated) the greater the amount of force needed (to accelerate the object). ...
force - Coosa High School
... toward the outside of the turn. So why does it FEEL like you’re being pushed. Because of _______________________________ Your body wants to continue on its original path as the car turns, you will continue to move straight. ...
... toward the outside of the turn. So why does it FEEL like you’re being pushed. Because of _______________________________ Your body wants to continue on its original path as the car turns, you will continue to move straight. ...
Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that
... 3) A rocket moves through empty space in a straight line with constant speed. It is far from the gravitational effect of any star or planet. Under these conditions, the force that must be applied to the rocket in order to sustain its motion is A) dependent on how fast it is moving. ...
... 3) A rocket moves through empty space in a straight line with constant speed. It is far from the gravitational effect of any star or planet. Under these conditions, the force that must be applied to the rocket in order to sustain its motion is A) dependent on how fast it is moving. ...
Force, Work, & Simple Machines
... Work problem example: If you lifted an object weighing 200 N through a distance of 0.5 m, how much work would you do? W = F x D W = 200 N x 0.5 m W = 100 J ...
... Work problem example: If you lifted an object weighing 200 N through a distance of 0.5 m, how much work would you do? W = F x D W = 200 N x 0.5 m W = 100 J ...
Name Date ______ Block ___ Physics Mid
... at the highest point of its trajectory? 12. An airplane traveling at constant velocity drops a bomb. Where is the airplane when the bomb hits the ground? 13. Which hits the ground first if they start at the same height: a dropped ball or a ball launched with a horizontal velocity? 14. For projectile ...
... at the highest point of its trajectory? 12. An airplane traveling at constant velocity drops a bomb. Where is the airplane when the bomb hits the ground? 13. Which hits the ground first if they start at the same height: a dropped ball or a ball launched with a horizontal velocity? 14. For projectile ...