File force and motion notes 2010
... The more inertia an object has, the harder it is to start the object moving or slow it down. ...
... The more inertia an object has, the harder it is to start the object moving or slow it down. ...
No Slide Title
... the velocity the object will follow a uniform circular path. The direction of the velocity changes while the magnitude of the velocity remains constant. The acceleration is called the centripetal acceleration which means “center-seeking” and always points toward the center of the circular path. The ...
... the velocity the object will follow a uniform circular path. The direction of the velocity changes while the magnitude of the velocity remains constant. The acceleration is called the centripetal acceleration which means “center-seeking” and always points toward the center of the circular path. The ...
Exploring Motion Introduction
... The first law states that a body in motion will remain in motion unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. The same is true for a body at rest. The second law predicts that when an unbalanced force is applied to a body it will produce acceleration; while the mass of the body (inertia) resists accele ...
... The first law states that a body in motion will remain in motion unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. The same is true for a body at rest. The second law predicts that when an unbalanced force is applied to a body it will produce acceleration; while the mass of the body (inertia) resists accele ...
11-2 Vector Cross Product
... 11-7 The Spinning Top and Gyroscope The angular velocity of the precession is given by: ...
... 11-7 The Spinning Top and Gyroscope The angular velocity of the precession is given by: ...
cm1_sow_med-short_term
... impact, including the case where the bodies coalesce (knowledge of impulse and the coefficient of restitution is not required). Understand the term resultant as applied to two or more forces acting at a point, and use vector addition in solving problems involving resultants and components of forces ...
... impact, including the case where the bodies coalesce (knowledge of impulse and the coefficient of restitution is not required). Understand the term resultant as applied to two or more forces acting at a point, and use vector addition in solving problems involving resultants and components of forces ...
HP Unit 3 - student handout
... Consider a skydiver who steps off a hovering helicopter at high altitude. NOW consider the effect of air resistance (friction) during the fall. Initially at t=0, what forces act on the skydiver? Initially at t=0, what is the acceleration and velocity of the ...
... Consider a skydiver who steps off a hovering helicopter at high altitude. NOW consider the effect of air resistance (friction) during the fall. Initially at t=0, what forces act on the skydiver? Initially at t=0, what is the acceleration and velocity of the ...
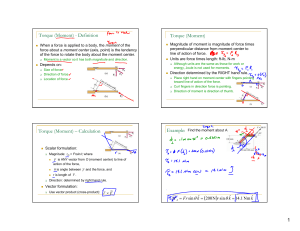
1 Torque (Moment) - Definition Torque (Moment) Torque (Moment
... Given forces and moments including weight. a2) Support reactions (where the body is cut from the rest of the world). b) Add all mass*acceleration terms to the Kinetic Diagram. Add all necessary dimensions. Enforce Newton’s 2nd Law: a) If necessary, set up any required Kinematic equations. b) Solve A ...
... Given forces and moments including weight. a2) Support reactions (where the body is cut from the rest of the world). b) Add all mass*acceleration terms to the Kinetic Diagram. Add all necessary dimensions. Enforce Newton’s 2nd Law: a) If necessary, set up any required Kinematic equations. b) Solve A ...
I. Force, Mass, and Acceleration
... The Law of Gravitation º We’re very attractive people (gravity attracts us to everything). º Law of gravitation says that any two masses exert an attractive force on each other. º Depends on two things – the masses and the distance between them. º So as mass increases gravity increases. º As distanc ...
... The Law of Gravitation º We’re very attractive people (gravity attracts us to everything). º Law of gravitation says that any two masses exert an attractive force on each other. º Depends on two things – the masses and the distance between them. º So as mass increases gravity increases. º As distanc ...
Energy Math
... • Walking a box up a flight of stairs or running a box up a flight of stairs? • You are doing the same amount of work, so why are you more tired? • POWER • Power is the measure of how fast work is done ...
... • Walking a box up a flight of stairs or running a box up a flight of stairs? • You are doing the same amount of work, so why are you more tired? • POWER • Power is the measure of how fast work is done ...
01 Newton`s First Law Notes
... The Newton is defined as the amount of force that, when acting on a 1kg mass, produces an acceleration of 1 m/s2. Therefore, 1N = 1kg*m/s2. The weight of an object is expressed in Newtons with one pound being equal to about 4.448 N. ...
... The Newton is defined as the amount of force that, when acting on a 1kg mass, produces an acceleration of 1 m/s2. Therefore, 1N = 1kg*m/s2. The weight of an object is expressed in Newtons with one pound being equal to about 4.448 N. ...
Newton`s Laws Powerpoint
... Sample Problems • It takes 50 N to pull a 6.0 kg object along a desk at constant speed. What is the coefficient of friction? • The coefficient of friction between two materials is 0.35. A 5.0 kg object made of one material is being pulled along a table made of another material. What is the force of ...
... Sample Problems • It takes 50 N to pull a 6.0 kg object along a desk at constant speed. What is the coefficient of friction? • The coefficient of friction between two materials is 0.35. A 5.0 kg object made of one material is being pulled along a table made of another material. What is the force of ...
Newton`s Laws Powerpoint - pams
... The ladder is in motion because the truck is in motion. When the truck stops, the ladder stays in motion. The truck is stopped by the force of the car, but the ladder is not. What force stops the ladder? ...
... The ladder is in motion because the truck is in motion. When the truck stops, the ladder stays in motion. The truck is stopped by the force of the car, but the ladder is not. What force stops the ladder? ...
Forces
... What general statement can be made concerning the angle of applied force? As the angle of the applied force increases, the horizontal force _____________? Find the component velocities of a helicopter traveling 95km/h at an angle of 350 with the ground. ...
... What general statement can be made concerning the angle of applied force? As the angle of the applied force increases, the horizontal force _____________? Find the component velocities of a helicopter traveling 95km/h at an angle of 350 with the ground. ...
Uniform Circular Motion (UCM)
... Centripetal forces are provided by real forces acting on the object. (FT, Ff, FN, Fg) (The actual force acting on the object that causes it to change direction.) ...
... Centripetal forces are provided by real forces acting on the object. (FT, Ff, FN, Fg) (The actual force acting on the object that causes it to change direction.) ...
Newton`s Laws of Motion
... watch it slide to a rest position. The book comes to a rest because of the presence of a force that force being the force of friction which brings the book to a rest position. ...
... watch it slide to a rest position. The book comes to a rest because of the presence of a force that force being the force of friction which brings the book to a rest position. ...