chapter02posta
... so you might think that if the mass were twice as big, the acceleration would be half as big. Which of the following resolves this contradiction with Galileo’s experiments in a logical way? A.Newton’s 2nd law does not apply. B.The acceleration is different but the time for the drop is not. C.The gra ...
... so you might think that if the mass were twice as big, the acceleration would be half as big. Which of the following resolves this contradiction with Galileo’s experiments in a logical way? A.Newton’s 2nd law does not apply. B.The acceleration is different but the time for the drop is not. C.The gra ...
5.Rotational_P9sim_09
... Linear velocity is proportional to rotational velocity v~rω r = distance from axis of rotation. ...
... Linear velocity is proportional to rotational velocity v~rω r = distance from axis of rotation. ...
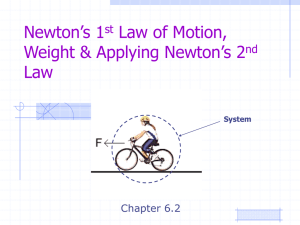
Newton`s Laws of Motion
... Think about it . . . What happens if you are standing on a skateboard or a slippery floor and push against a wall? You slide in the opposite direction (away from the wall), because you pushed on the wall but the wall pushed back on you with equal and opposite force. Why does it hurt so much when yo ...
... Think about it . . . What happens if you are standing on a skateboard or a slippery floor and push against a wall? You slide in the opposite direction (away from the wall), because you pushed on the wall but the wall pushed back on you with equal and opposite force. Why does it hurt so much when yo ...
38. REASONING It is the static friction force that accelerates the cup
... enough. In part a of the drawing the bucket is hanging stationary and, therefore, is in equilibrium. The forces acting on it are its weight and the two tension forces from the rope. There are two tension forces from the rope, because the rope is attached to the bucket handle at two places. These thr ...
... enough. In part a of the drawing the bucket is hanging stationary and, therefore, is in equilibrium. The forces acting on it are its weight and the two tension forces from the rope. There are two tension forces from the rope, because the rope is attached to the bucket handle at two places. These thr ...
WYSIWYG - DiMaggio
... Inclined planes, screws, and wedges all allow you to apply less force, but you have to apply the force over a greater distance. (MA > 1) They are also all related (all have a slanted surface (inclined plane) part). o To increase the MA, make the inclined plane part longer. Levers are classified base ...
... Inclined planes, screws, and wedges all allow you to apply less force, but you have to apply the force over a greater distance. (MA > 1) They are also all related (all have a slanted surface (inclined plane) part). o To increase the MA, make the inclined plane part longer. Levers are classified base ...
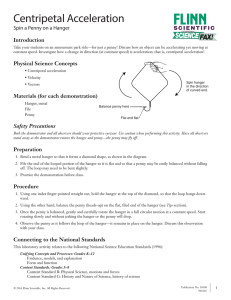
RG 6 - mine
... acting on it. This means that, as the net force acting on the object decreases, the acceleration of the object ...
... acting on it. This means that, as the net force acting on the object decreases, the acceleration of the object ...
Motion Forces and Work rvw pak 13.14
... 7.P.1 Understand motion, the effects of forces on motion and the graphical representations of motion. 7.P.1.1 Explain how the motion of an object can be described by its position, direction of motion, and speed with respect to some other object. 7.P.1.2 Explain the effects of balanced and unbalanced ...
... 7.P.1 Understand motion, the effects of forces on motion and the graphical representations of motion. 7.P.1.1 Explain how the motion of an object can be described by its position, direction of motion, and speed with respect to some other object. 7.P.1.2 Explain the effects of balanced and unbalanced ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Newton’s Laws of Motion
... Imagine a ball of a certain mass moving at a certain acceleration. This ball has a certain force. Now imagine we make the ball twice as big (double the mass) but keep the acceleration constant. F = ma says that this new ball has twice the force of the old ball. Now imagine the original ball moving a ...
... Imagine a ball of a certain mass moving at a certain acceleration. This ball has a certain force. Now imagine we make the ball twice as big (double the mass) but keep the acceleration constant. F = ma says that this new ball has twice the force of the old ball. Now imagine the original ball moving a ...
Exp Physics review Problems
... 1. From 0 to 40 s what was the average velocity? 2. At 20 s what is the instantaneous velocity? 3. From 0 to 70 s what was the average velocity? 4. From 70 to 90 s what was the average velocity? 5. At 80 s what is the instantaneous velocity? 6. For the whole trip 0 to 100 seconds what was the averag ...
... 1. From 0 to 40 s what was the average velocity? 2. At 20 s what is the instantaneous velocity? 3. From 0 to 70 s what was the average velocity? 4. From 70 to 90 s what was the average velocity? 5. At 80 s what is the instantaneous velocity? 6. For the whole trip 0 to 100 seconds what was the averag ...
Physics 123/5 - UConn Physics
... The coefficient of static friction between steel train wheels and Steel rails is 0.58. The engineer of a train moving at 140 km/h spots a stalled car on the tracks 150 m ahead. If he applies the brakes so that the wheels don’t slip, will the train stop in time? ...
... The coefficient of static friction between steel train wheels and Steel rails is 0.58. The engineer of a train moving at 140 km/h spots a stalled car on the tracks 150 m ahead. If he applies the brakes so that the wheels don’t slip, will the train stop in time? ...
2-11. Third Law of Motion
... 2-10. Mass and Weight • Weight Definition: The force with which an object is attracted by the earth’s gravitational pull • Example: A person weighing 160 lbs is being pulled towards the earth with a force of 160 lbs (712 N). ...
... 2-10. Mass and Weight • Weight Definition: The force with which an object is attracted by the earth’s gravitational pull • Example: A person weighing 160 lbs is being pulled towards the earth with a force of 160 lbs (712 N). ...
UNIFORM CIRCULAR MOTION Rotational Motion
... • Yo-yo swings in a circle it accelerates, because its velocity is constantly changing direction • In order to have centripetal acceleration there must be a force present on the Yo-yo • Force that causes centripetal acceleration points in the same direction as the centripetal acceleration Toward ...
... • Yo-yo swings in a circle it accelerates, because its velocity is constantly changing direction • In order to have centripetal acceleration there must be a force present on the Yo-yo • Force that causes centripetal acceleration points in the same direction as the centripetal acceleration Toward ...
momentum
... -1686, Sir Issac Newton publishes his book Principia in which he describes 3 laws relating forces to motion of objects -did not discover all 3 laws himself, but combined previous discoveries by other scientists and explained them in a way that people could understand -as a result, the 3 laws are com ...
... -1686, Sir Issac Newton publishes his book Principia in which he describes 3 laws relating forces to motion of objects -did not discover all 3 laws himself, but combined previous discoveries by other scientists and explained them in a way that people could understand -as a result, the 3 laws are com ...
Test 2 Review Test 2 Review_9
... (C) The force of motion is proportional to the speed of the puck. (D) The force to the right must be equal to the force from friction. (26) ___________ True or False: A force is required to keep objects moving. (27) Using Newton’s 1st Law, explain why it is important for students to wear seat belts. ...
... (C) The force of motion is proportional to the speed of the puck. (D) The force to the right must be equal to the force from friction. (26) ___________ True or False: A force is required to keep objects moving. (27) Using Newton’s 1st Law, explain why it is important for students to wear seat belts. ...
How many laws did Newton create?
... 2. Which law explains why we need to wear seatbelts? 3. Which law says that force is equal to mass times acceleration (F=MA)? 4. Which law explains how rockets are launched into space? 5. Which law says that heavier objects require more force than lighter objects to move or accelerate them (Throwing ...
... 2. Which law explains why we need to wear seatbelts? 3. Which law says that force is equal to mass times acceleration (F=MA)? 4. Which law explains how rockets are launched into space? 5. Which law says that heavier objects require more force than lighter objects to move or accelerate them (Throwing ...