Pre-Lecture 4
... Summary of Newton’s Three Laws • An object tends to remain at rest, or, if moving, to continue moving at constant speed in a straight line (1st Law). Objects tend to resist changes in motion (inertia) – mass measures this. • (2nd Law) When there is a net force on an object, it will accelerate: a = ...
... Summary of Newton’s Three Laws • An object tends to remain at rest, or, if moving, to continue moving at constant speed in a straight line (1st Law). Objects tend to resist changes in motion (inertia) – mass measures this. • (2nd Law) When there is a net force on an object, it will accelerate: a = ...
Mechanics I basic forces FBD
... Balanced and Unbalanced Forces • Sometimes all the forces on an object will cancel out. We say that object is in equilibrium or a state of balance • Sometimes all the forces will not cancel out and we say there is a Net Force acting on the object. • The Net Force is the Force that causes accelerati ...
... Balanced and Unbalanced Forces • Sometimes all the forces on an object will cancel out. We say that object is in equilibrium or a state of balance • Sometimes all the forces will not cancel out and we say there is a Net Force acting on the object. • The Net Force is the Force that causes accelerati ...
Click here for a short consolidation presentation on the basics of
... The moment can be calculate using the following equation. ...
... The moment can be calculate using the following equation. ...
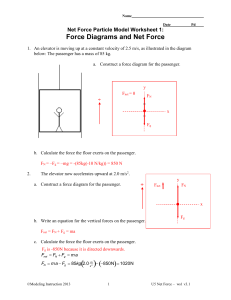
Name
... Free Response - Solve each problem using one or more of these equations. Show all work. ∑F=ma ...
... Free Response - Solve each problem using one or more of these equations. Show all work. ∑F=ma ...
Chapter 7 – Rotational Motion and the Law of Gravity
... Rotational motion – the motion of an object that is spinning 1. The object spins about an axis. 2. The axis of rotation is the line about which the rotation occurs. 3. Circular motion is defined as a point on an object that moves (rotates) around an axis. Since the direction of the motion is constan ...
... Rotational motion – the motion of an object that is spinning 1. The object spins about an axis. 2. The axis of rotation is the line about which the rotation occurs. 3. Circular motion is defined as a point on an object that moves (rotates) around an axis. Since the direction of the motion is constan ...
Laws of Motion - SCHOOLinSITES
... All objects in universe attract each other through gravitational force Sir Isaac Newton (1642–1727) Universal Gravitation Equation ...
... All objects in universe attract each other through gravitational force Sir Isaac Newton (1642–1727) Universal Gravitation Equation ...
Intro Forces and Newton`s 3 Laws
... An object at rest has a natural tendency to stay at rest, or an object in motion will stay in motion, unless a force is acting upon it. This is also known as the law of INERTIA. INERTIA is an objects resistance to change in motion. ...
... An object at rest has a natural tendency to stay at rest, or an object in motion will stay in motion, unless a force is acting upon it. This is also known as the law of INERTIA. INERTIA is an objects resistance to change in motion. ...
r - TTU Physics
... of “mass” μ) is not an inertial frame! – Its not a force in the Newtonian sense! (It doesn’t come from any interaction of the “mass” μ with its environment!) It’s a part of the “μa” (right!) of Newton’s 2nd Law, rewritten to appear on the “F” (left) side. For more discussion, see Ch. 10. ...
... of “mass” μ) is not an inertial frame! – Its not a force in the Newtonian sense! (It doesn’t come from any interaction of the “mass” μ with its environment!) It’s a part of the “μa” (right!) of Newton’s 2nd Law, rewritten to appear on the “F” (left) side. For more discussion, see Ch. 10. ...
College Physics
... Note: Newton’s third law : the force exerted by the man on the boy and the force exerted by the boy on the man are an action–reaction pair, and so they must be equal in magnitude the boy, having the lesser mass, experiences the greater acceleration. Both individuals accelerate for the same amount ...
... Note: Newton’s third law : the force exerted by the man on the boy and the force exerted by the boy on the man are an action–reaction pair, and so they must be equal in magnitude the boy, having the lesser mass, experiences the greater acceleration. Both individuals accelerate for the same amount ...
Laws of Motion Powerpoint
... between two objects. • The strength of gravity depends on an object’s mass and distance. • For example, the moon’s gravity is 1/6 of the Earth’s gravity because it is much smaller. • Where would gravity be less, at sea level or on top of a mountain? ...
... between two objects. • The strength of gravity depends on an object’s mass and distance. • For example, the moon’s gravity is 1/6 of the Earth’s gravity because it is much smaller. • Where would gravity be less, at sea level or on top of a mountain? ...
PPA6_Lecture_Ch_05
... 5-6 Newton’s Law of Universal Gravitation Therefore, the gravitational force must be proportional to both masses. By observing planetary orbits, Newton also concluded that the gravitational force must decrease as the inverse of the square of the distance between the masses. In its final form, the L ...
... 5-6 Newton’s Law of Universal Gravitation Therefore, the gravitational force must be proportional to both masses. By observing planetary orbits, Newton also concluded that the gravitational force must decrease as the inverse of the square of the distance between the masses. In its final form, the L ...
Force Diagrams and Net Force Key
... 6. a. Draw a force diagram for a 900 kg car that exerts 5000 N of traction force on a level road while being opposed by 1000 newtons of friction and drag forces combined. y Fnet FN Fg ...
... 6. a. Draw a force diagram for a 900 kg car that exerts 5000 N of traction force on a level road while being opposed by 1000 newtons of friction and drag forces combined. y Fnet FN Fg ...
Contact forces - Uplift Education
... Forces are usually divided into two types. 1. Contact forces occur because of physical contact between objects. Examples: pushing open a door pulling on a rope ...
... Forces are usually divided into two types. 1. Contact forces occur because of physical contact between objects. Examples: pushing open a door pulling on a rope ...
force and motion
... Is a single force that represents the combined effect of 2 or more forces in magnitude and direction. ...
... Is a single force that represents the combined effect of 2 or more forces in magnitude and direction. ...
document
... skateboard but missed it by a centimeter. The board goes flying across the pavement, but Robert magically lands on his feet. Which of Newton’s laws does this demonstrate? ...
... skateboard but missed it by a centimeter. The board goes flying across the pavement, but Robert magically lands on his feet. Which of Newton’s laws does this demonstrate? ...
Forces Reivew
... c) is the same for both. 16. A sheet of paper can be withdrawn from under a container of milk without falling over if the paper is jerked quickly. The reason this can be done is that ___. a) the milk carton has no acceleration. c) the gravitational field pulls on the milk carton. b) there is an acti ...
... c) is the same for both. 16. A sheet of paper can be withdrawn from under a container of milk without falling over if the paper is jerked quickly. The reason this can be done is that ___. a) the milk carton has no acceleration. c) the gravitational field pulls on the milk carton. b) there is an acti ...