PHY820 Homework Set 5
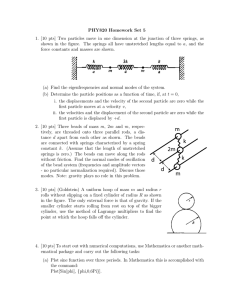
... first particle moves at a velocity v, ii. the velocities and the displacement of the second particle are zero while the first particle is displaced by +d. 2. [10 pts] Three beads of mass m, 2m and m, respectively, are threaded onto three parallel rods, a distance d apart from each other as shown. Th ...
... first particle moves at a velocity v, ii. the velocities and the displacement of the second particle are zero while the first particle is displaced by +d. 2. [10 pts] Three beads of mass m, 2m and m, respectively, are threaded onto three parallel rods, a distance d apart from each other as shown. Th ...
No questions like this on midterm exam
... 31. You are in outer space and you throw the 2 kilogram mass away from your spacecraft; describe the motion of the object. It will travel in a constant direction and with a constant speed. Law of INERTIA 32. What is the weight of the 2 kilogram object in Newtons? Weight = mg = 2 kg (9.8 m/s2) = 19.6 ...
... 31. You are in outer space and you throw the 2 kilogram mass away from your spacecraft; describe the motion of the object. It will travel in a constant direction and with a constant speed. Law of INERTIA 32. What is the weight of the 2 kilogram object in Newtons? Weight = mg = 2 kg (9.8 m/s2) = 19.6 ...
Physics Stations
... Station 11; Newton’s Laws/Speed graph Background Information: Newton's First Law of Motion is often stated as: An object at rest tends to stay at rest and an object in motion tends to stay in motion with the same speed and in the same direction unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. Put another w ...
... Station 11; Newton’s Laws/Speed graph Background Information: Newton's First Law of Motion is often stated as: An object at rest tends to stay at rest and an object in motion tends to stay in motion with the same speed and in the same direction unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. Put another w ...
topic 2
... kilograms (kg), and weight is calculated from W = mg. If the gravitational acceleration (g) is specified in units of m/s2, then the weight is expressed in newtons (N). On the earth’s surface, g can be taken as g = 9.81 m/s2. W (N) = m (kg) g (m/s2) => N = kg·m/s2 FPS System: In the FPS system of uni ...
... kilograms (kg), and weight is calculated from W = mg. If the gravitational acceleration (g) is specified in units of m/s2, then the weight is expressed in newtons (N). On the earth’s surface, g can be taken as g = 9.81 m/s2. W (N) = m (kg) g (m/s2) => N = kg·m/s2 FPS System: In the FPS system of uni ...
Drawing Force Diagrams
... You drop your doll from the top of the Eifel Tower. Ignore air resistance! ...
... You drop your doll from the top of the Eifel Tower. Ignore air resistance! ...
P4 – Explaining Motion
... Work and Kinetic Energy • If friction and air resistance can be ignored, an object’s kinetic energy increases by an amount equal to the work done on it by an applied force • Air resistance or friction will cause the gain in an object’s kinetic energy to be less than the work done on it by an applie ...
... Work and Kinetic Energy • If friction and air resistance can be ignored, an object’s kinetic energy increases by an amount equal to the work done on it by an applied force • Air resistance or friction will cause the gain in an object’s kinetic energy to be less than the work done on it by an applie ...
PowerPoint Presentation - ABOUT TEAL
... Friction acts exactly at the one point of contact and is tangential, i.e. perpendicular to the radius One peculiarity: Sliding along a surface, friction does negative work Rolling without slipping, friction does zero work 8.01L IAP 2007 ...
... Friction acts exactly at the one point of contact and is tangential, i.e. perpendicular to the radius One peculiarity: Sliding along a surface, friction does negative work Rolling without slipping, friction does zero work 8.01L IAP 2007 ...
CTNewtonLawsa
... each must have the same size mass acceleration. If mass is big, acceleration must be small; if mass is small, acceleration must be big: M a = m A. Because of its small mass, the car experiences a much greater acceleration during the collision, and it is this sudden change in velocity which injures ...
... each must have the same size mass acceleration. If mass is big, acceleration must be small; if mass is small, acceleration must be big: M a = m A. Because of its small mass, the car experiences a much greater acceleration during the collision, and it is this sudden change in velocity which injures ...
NEWTON`S LAWS OF MOTION CARTOON TIME! Newton`s First Law
... For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. The statement means that in every interaction, there is a pair of forces acting on the two interacting objects. The size of the forces on the first object equals the size of the force on the second object. The direction of the force on the f ...
... For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. The statement means that in every interaction, there is a pair of forces acting on the two interacting objects. The size of the forces on the first object equals the size of the force on the second object. The direction of the force on the f ...
Newton`s second law of motion
... Looking at the results Discuss your students’ results: Do they find that acceleration is proportional to force, and inversely proportional to mass? Numerically, are their results consistent with the equation F = ma? You may wish to point out that the experiment can only show proportionality. In othe ...
... Looking at the results Discuss your students’ results: Do they find that acceleration is proportional to force, and inversely proportional to mass? Numerically, are their results consistent with the equation F = ma? You may wish to point out that the experiment can only show proportionality. In othe ...
Force Mass Motion
... the object won’t accelerate. Acceleration is not the same as motion…it is a change in motion! ...
... the object won’t accelerate. Acceleration is not the same as motion…it is a change in motion! ...
PSC1121Chap2-4
... Objects at rest tend to remain at rest unless a force is applied to set them in motion When an object is moving its tendency is to remain moving along a straight line path if no friction acts against it. ...
... Objects at rest tend to remain at rest unless a force is applied to set them in motion When an object is moving its tendency is to remain moving along a straight line path if no friction acts against it. ...
Coriolis Force
... the absolute frame of reference. FM is some arbitrary “mystery” force (per unit mass) acting on the parcel to maintain its position over the same spot on the earth’s surface. ...
... the absolute frame of reference. FM is some arbitrary “mystery” force (per unit mass) acting on the parcel to maintain its position over the same spot on the earth’s surface. ...
Document
... Example 5: The Effect of Speed on Centripetal Force The model airplane has a mass of 0.90 kg and moves at constant speed on a circle that is parallel to the ground. The path of the airplane and the guideline lie in the same horizontal plane because the weight of the plane is balanced by the lift gen ...
... Example 5: The Effect of Speed on Centripetal Force The model airplane has a mass of 0.90 kg and moves at constant speed on a circle that is parallel to the ground. The path of the airplane and the guideline lie in the same horizontal plane because the weight of the plane is balanced by the lift gen ...
CPO Chapter 3 Notes
... • An object at rest will remain at rest unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. An object in motion will continue with constant speed and direction, unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. • Unless you apply a force, things tend to keep doing what they were already doing. ...
... • An object at rest will remain at rest unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. An object in motion will continue with constant speed and direction, unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. • Unless you apply a force, things tend to keep doing what they were already doing. ...























