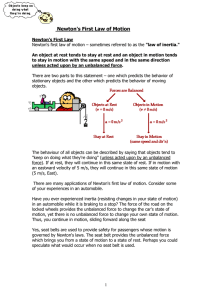
Lesson 1: Newton`s First Law of Motion
... A force is a push or a pull upon an object which results from its interaction with another object. Forces result from interactions! Some forces result from contact interactions (normal, frictional, tensional, and applied forces are examples of contact forces) and other forces result from action-at-a ...
... A force is a push or a pull upon an object which results from its interaction with another object. Forces result from interactions! Some forces result from contact interactions (normal, frictional, tensional, and applied forces are examples of contact forces) and other forces result from action-at-a ...
Preview as PDF - Pearson Higher Education
... object. For each force, make sure that you can answer the question “What other object interacts with the chosen object to cause that force?” If you can’t answer that question, you may be imagining a force that isn’t there. c. Label each force as a vector using a symbol that represents the magnitud ...
... object. For each force, make sure that you can answer the question “What other object interacts with the chosen object to cause that force?” If you can’t answer that question, you may be imagining a force that isn’t there. c. Label each force as a vector using a symbol that represents the magnitud ...
Rotational Dynamics
... Earth is an example of a rotating, rigid object. Even though different points on Earth rotate different distances in each revolution, all points rotate through the same angle. The Sun, on the other hand, is not a rigid body. Different parts of the Sun rotate at different rates. ...
... Earth is an example of a rotating, rigid object. Even though different points on Earth rotate different distances in each revolution, all points rotate through the same angle. The Sun, on the other hand, is not a rigid body. Different parts of the Sun rotate at different rates. ...
Worked Examples from Introductory Physics Vol. I: Basic Mechanics
... required in a general physics course is not very great. Any student who has difficulty solving the equations we derive in working these problems really needs to re–take some math courses! Physics is all about finding the right equations to solve. The rest of it ought to be easy. My two purposes in c ...
... required in a general physics course is not very great. Any student who has difficulty solving the equations we derive in working these problems really needs to re–take some math courses! Physics is all about finding the right equations to solve. The rest of it ought to be easy. My two purposes in c ...
Unit 5 Part 1 Simple Harmonic Motion Notes
... No force is acting on the mass when the spring is at equilibrium. If you pulled the mass to the right and then released it (Figure 1a), the spring will apply a leftward force on the object to pull it back to the left. This leftward F on the object will give it a leftward acceleration. This leftward ...
... No force is acting on the mass when the spring is at equilibrium. If you pulled the mass to the right and then released it (Figure 1a), the spring will apply a leftward force on the object to pull it back to the left. This leftward F on the object will give it a leftward acceleration. This leftward ...
MCQ For XI - auroraclasses.org
... A 150 m long train is moving north at a speed of 20m/s. A bird flying south at a speed of 5m/s cross the train. What is the time taken by the bird to cross the train (a) 30s (b) 10s (c) 7.5s (d) 6s From a 20 m high tower one ball is thrown upwards with speed of 10m/s and another is thrown vertically ...
... A 150 m long train is moving north at a speed of 20m/s. A bird flying south at a speed of 5m/s cross the train. What is the time taken by the bird to cross the train (a) 30s (b) 10s (c) 7.5s (d) 6s From a 20 m high tower one ball is thrown upwards with speed of 10m/s and another is thrown vertically ...
Stacey Carpenter
... a difference how long you apply the force? Descartes (Need to check this.) took the equation from Newton's 2nd Law, F = ma, and looked at what would happen if the force was applied for a period of time. Ft = ?. Applying the force for a longer time will result in the same acceleration, but a greate ...
... a difference how long you apply the force? Descartes (Need to check this.) took the equation from Newton's 2nd Law, F = ma, and looked at what would happen if the force was applied for a period of time. Ft = ?. Applying the force for a longer time will result in the same acceleration, but a greate ...
Date
... In order to catch a ball, a baseball player moves his or her hand backward in the direction of the ball's motion. Doing this reduces the force of impact on the player's hand principally because __________. A) the time of impact is increased. B) the time of impact is decreased. C) the momentum of imp ...
... In order to catch a ball, a baseball player moves his or her hand backward in the direction of the ball's motion. Doing this reduces the force of impact on the player's hand principally because __________. A) the time of impact is increased. B) the time of impact is decreased. C) the momentum of imp ...
further questions
... (b) State the expression for the angular momentum of an object in terms of its moment of inertia. (c) State the equation for the rotational kinetic energy of a rigid object. 2. A bicycle wheel has a moment of inertia of 0.25 kg m2 about its hub. Calculate the angular momentum of the wheel when rotat ...
... (b) State the expression for the angular momentum of an object in terms of its moment of inertia. (c) State the equation for the rotational kinetic energy of a rigid object. 2. A bicycle wheel has a moment of inertia of 0.25 kg m2 about its hub. Calculate the angular momentum of the wheel when rotat ...
Physics 106P: Lecture 6 Notes
... The Free Body Diagram The tools we have for making & solving problems: » Ropes & Pulleys (tension) » Hooke’s Law (springs) ...
... The Free Body Diagram The tools we have for making & solving problems: » Ropes & Pulleys (tension) » Hooke’s Law (springs) ...
4. Weighty Arguments - The University of Arizona – The Atlas Project
... off tangentially away from the Earth, but the force of gravity is modifying its velocity by adding GM/R2 ft/sec toward the Earth each second, which causes the Moon to turn continually in a roughly circular orbit around the Earth. The centripetal acceleration of an object revolving in a circle is v2/ ...
... off tangentially away from the Earth, but the force of gravity is modifying its velocity by adding GM/R2 ft/sec toward the Earth each second, which causes the Moon to turn continually in a roughly circular orbit around the Earth. The centripetal acceleration of an object revolving in a circle is v2/ ...
CHAPTER 7 Kinetic Energy and Work UPI Photo/Dilip Vishwanat
... A force does positive work when it has a vector component in the same direction displacement, and it does negative work when it has a vector component in the opposite direction. It does zero work when it has no such vector component. ...
... A force does positive work when it has a vector component in the same direction displacement, and it does negative work when it has a vector component in the opposite direction. It does zero work when it has no such vector component. ...
PROBLEMS
... 13.21. A tuning fork labeled 392 Hz has the tip of each of its two prongs vibrating with an amplitude of 0.600 mm. (a) What is the maximum speed of the tip of a prong? (b) A housefly (Musc a domestica) with mass 0.0270 g is holding on to the tip of one of Section 13,4 Applications of Simple Harmonic ...
... 13.21. A tuning fork labeled 392 Hz has the tip of each of its two prongs vibrating with an amplitude of 0.600 mm. (a) What is the maximum speed of the tip of a prong? (b) A housefly (Musc a domestica) with mass 0.0270 g is holding on to the tip of one of Section 13,4 Applications of Simple Harmonic ...