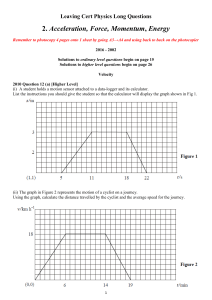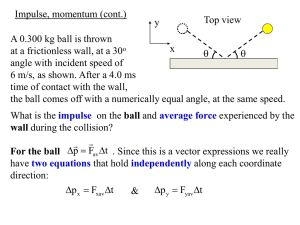
Ch 8 – Oscillation
... from its equilibrium position. It moves as far on one side as it does on the other. • The time that it takes to make one complete repetition or cycle is called the period of the motion. We will usually measure the period in seconds. • Frequency is the number of cycles per second that an oscillator g ...
... from its equilibrium position. It moves as far on one side as it does on the other. • The time that it takes to make one complete repetition or cycle is called the period of the motion. We will usually measure the period in seconds. • Frequency is the number of cycles per second that an oscillator g ...
How Things Work
... On earth due to gravity from the ball 3rd law On ball due to gravity from the earth pair On ball due to support from table 3rd law pair On table due to support from ball Forces 2 and 3 aren’t a Newton’s 3rd law pair! ...
... On earth due to gravity from the ball 3rd law On ball due to gravity from the earth pair On ball due to support from table 3rd law pair On table due to support from ball Forces 2 and 3 aren’t a Newton’s 3rd law pair! ...
TEKS 8.7 A
... the rock is pushing very hard on the rock underneath it. Meanwhile, the rock underneath is pushing back up with exactly the same force and in the opposite direction, so the forces, even though they are very large, are balanced out. If the ...
... the rock is pushing very hard on the rock underneath it. Meanwhile, the rock underneath is pushing back up with exactly the same force and in the opposite direction, so the forces, even though they are very large, are balanced out. If the ...
Lecture 18
... • The sum of all the Forces acting on the system is equal to the total mass of the system times the acceleration of its center of mass. • The center of mass of a system of particles (or objects) with total mass M moves like a single particle of mass M acted upon by the same net external force. ...
... • The sum of all the Forces acting on the system is equal to the total mass of the system times the acceleration of its center of mass. • The center of mass of a system of particles (or objects) with total mass M moves like a single particle of mass M acted upon by the same net external force. ...
Newton`s Law of motion 1
... Gravitational mass is measured by such method, e.g. spring balance. Measuring the mass (inertia mass) Mass can be defined as the ‘ amount of matter’ in an object. But considering Newton’s 2nd Law of motion, m = FN / a, mass has a new meaning – “Inertia”. Inertia is the resistance of an object to a c ...
... Gravitational mass is measured by such method, e.g. spring balance. Measuring the mass (inertia mass) Mass can be defined as the ‘ amount of matter’ in an object. But considering Newton’s 2nd Law of motion, m = FN / a, mass has a new meaning – “Inertia”. Inertia is the resistance of an object to a c ...
Chapter 4- wrap up
... • The magnitude of the frictional force depends on the normal force and the material of the two objects in contact. Wood on wood would have a different frictional force than steel on wood, and so on. Heavy objects have more friction than very light ones, etc. • When an object is at rest, it takes a ...
... • The magnitude of the frictional force depends on the normal force and the material of the two objects in contact. Wood on wood would have a different frictional force than steel on wood, and so on. Heavy objects have more friction than very light ones, etc. • When an object is at rest, it takes a ...
ExamView - S15--Physics Q4 Torque.tst
... 5. A heavy bank-vault door is opened by the application of a force of 3.0 × 10 2 N directed perpendicular to the plane of the door at a distance of 0.80 m from the hinges. What is the torque? a. 240 N•m b. 360 N•m c. 300 N•m d. 120 N•m 6. Where should a force be applied on a lever arm to produce the ...
... 5. A heavy bank-vault door is opened by the application of a force of 3.0 × 10 2 N directed perpendicular to the plane of the door at a distance of 0.80 m from the hinges. What is the torque? a. 240 N•m b. 360 N•m c. 300 N•m d. 120 N•m 6. Where should a force be applied on a lever arm to produce the ...
Chapter 13
... Forces On May 27, 1931, a train called Empire Builder encountered the amazing force of a tornado as it moved across Minnesota. The tornado’s force was so great that as the train moved along the track at 60 miles per hour, five of its 60-ton cars where lifted from the rails! One car was lifted and th ...
... Forces On May 27, 1931, a train called Empire Builder encountered the amazing force of a tornado as it moved across Minnesota. The tornado’s force was so great that as the train moved along the track at 60 miles per hour, five of its 60-ton cars where lifted from the rails! One car was lifted and th ...
PHYS 1443 – Section 501 Lecture #1
... The above condition is sufficient for a point-like particle to be at its static equilibrium. However for object with size this is not sufficient. One more condition is needed. What is it? Let’s consider two forces equal magnitude but opposite direction acting on a rigid object as shown in the figure ...
... The above condition is sufficient for a point-like particle to be at its static equilibrium. However for object with size this is not sufficient. One more condition is needed. What is it? Let’s consider two forces equal magnitude but opposite direction acting on a rigid object as shown in the figure ...
Review Questions
... Follow through on your golf swing means that the golf club is in contact with the ball for more time, which means the golf club will impart a greater impulse to the ball. A greater impulse means that the ball gains more momentum, which is another way of saying that it gets up to higher speed. Of cou ...
... Follow through on your golf swing means that the golf club is in contact with the ball for more time, which means the golf club will impart a greater impulse to the ball. A greater impulse means that the ball gains more momentum, which is another way of saying that it gets up to higher speed. Of cou ...
HW8
... 12. 35. We examine the box when it is about to tip. Since it will rotate about the lower right edge, that is where the normal force of the floor is exerted. This force is labeled FN on the diagram that follows. The force of friction is denoted by f, the applied force by F, and the force of gravity b ...
... 12. 35. We examine the box when it is about to tip. Since it will rotate about the lower right edge, that is where the normal force of the floor is exerted. This force is labeled FN on the diagram that follows. The force of friction is denoted by f, the applied force by F, and the force of gravity b ...