equilibrium
... pivoting about an axis under influence of two forces of equal magnitude act in opposite directions along parallel lines of action (a couple) ...
... pivoting about an axis under influence of two forces of equal magnitude act in opposite directions along parallel lines of action (a couple) ...
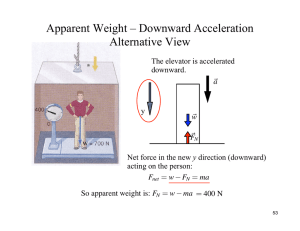
Apparent Weight – Downward Acceleration Alternative View
... much like a tread of a tire. Its strength comes from tough fibers called collagen. The joint surface cartilage is well lubricated - more slippery than well-manufactured ball bearings... Its living cells are nourished by joint fluid, called synovial fluid which is also extremely good lubrication. ...
... much like a tread of a tire. Its strength comes from tough fibers called collagen. The joint surface cartilage is well lubricated - more slippery than well-manufactured ball bearings... Its living cells are nourished by joint fluid, called synovial fluid which is also extremely good lubrication. ...
Physics - Newton`s Laws
... Friction A force that resists the motion between two objects in contact with one another The First Law: Newton’s First Law: An object at rest remains at rest, and an object in motion remains in motion with constant velocity unless it is acted upon by an outside force. This law really deals with in ...
... Friction A force that resists the motion between two objects in contact with one another The First Law: Newton’s First Law: An object at rest remains at rest, and an object in motion remains in motion with constant velocity unless it is acted upon by an outside force. This law really deals with in ...
Newton`s Second Law of Motion
... II. Force Causes Acceleration A. Acceleration is caused by applying a force B. Net Force- combination of all forces that act on an object C. Acceleration is directly proportional to the net force: if net force is doubled acceleration is doubled D. Direction of acceleration is in direction of net fo ...
... II. Force Causes Acceleration A. Acceleration is caused by applying a force B. Net Force- combination of all forces that act on an object C. Acceleration is directly proportional to the net force: if net force is doubled acceleration is doubled D. Direction of acceleration is in direction of net fo ...
= ∑ = ∫ - dps allahabad
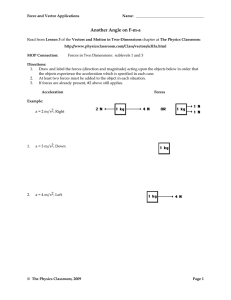
... A 2kg particle starts at the origin and moves along the positive x-axis. The net force acting on it measured at intervals of 1 m is: 27.9, 28.3, 30.9, 34.0, 34.5, 46.9, 48.2, 50.0, 63.5, 13.6, 12.2, 32.7, 46.6 and 27.0 (in Newton’s). What is the total work done on the particle in this interval? ...
... A 2kg particle starts at the origin and moves along the positive x-axis. The net force acting on it measured at intervals of 1 m is: 27.9, 28.3, 30.9, 34.0, 34.5, 46.9, 48.2, 50.0, 63.5, 13.6, 12.2, 32.7, 46.6 and 27.0 (in Newton’s). What is the total work done on the particle in this interval? ...
HOLLENBECK MIDDLE SCHOOL 8TH GRADE SCIENCE, MR. E
... Which statement describes the motion of the robotic car? A The car accelerates away from its storage area for 15 seconds. It moves at a constant speed for 10 seconds. Then it decelerates for 15 seconds. B The car moves away from its storage area at a constant speed for 15 seconds. It remains still f ...
... Which statement describes the motion of the robotic car? A The car accelerates away from its storage area for 15 seconds. It moves at a constant speed for 10 seconds. Then it decelerates for 15 seconds. B The car moves away from its storage area at a constant speed for 15 seconds. It remains still f ...
Newton`s 3rd Law Notes
... the exhaust gas pushes the rocket upward with equal force. The force of the rocket pushing on the gas does not balance or counter the upward force of the exhaust gas because the downward force is acting on the exhaust gas not the rocket. The motion of the rocket is determined by the forces acting on ...
... the exhaust gas pushes the rocket upward with equal force. The force of the rocket pushing on the gas does not balance or counter the upward force of the exhaust gas because the downward force is acting on the exhaust gas not the rocket. The motion of the rocket is determined by the forces acting on ...
Newton`s Laws of Motion Units of Force
... (magnitude and direction) as long as no net force acts on it. The key to this statement is “no net force”. There are always forces acting on an object, but all of these forces, when added together must equal zero. We call this state ‘equilibrium’. Equilibrium: Sum of Forces in the x-direction = 0 Su ...
... (magnitude and direction) as long as no net force acts on it. The key to this statement is “no net force”. There are always forces acting on an object, but all of these forces, when added together must equal zero. We call this state ‘equilibrium’. Equilibrium: Sum of Forces in the x-direction = 0 Su ...
Slide 1
... string Y and then hung from a beam using string X. String X is burned through using a candle. Neglecting the mass of each string, what is the tension in string Y I Before string X is burned through & II After string X is burned through? ...
... string Y and then hung from a beam using string X. String X is burned through using a candle. Neglecting the mass of each string, what is the tension in string Y I Before string X is burned through & II After string X is burned through? ...
Forces Worksheet
... 2. What are unbalanced forces and give an example? 3. What are balanced forces and give an example? Calculate the net force on the object described in each situation. Draw a free body diagram for each and show the directions of forces as well as the total net force and direction of net force. Exampl ...
... 2. What are unbalanced forces and give an example? 3. What are balanced forces and give an example? Calculate the net force on the object described in each situation. Draw a free body diagram for each and show the directions of forces as well as the total net force and direction of net force. Exampl ...
brief push
... When you first learned how to roller skate, you may have gotten started by pushing off the wall at the skating rink. Draw a force diagram for yourself as you accelerate. Using agent-object notation, clearly label all the forces acting on you. ...
... When you first learned how to roller skate, you may have gotten started by pushing off the wall at the skating rink. Draw a force diagram for yourself as you accelerate. Using agent-object notation, clearly label all the forces acting on you. ...