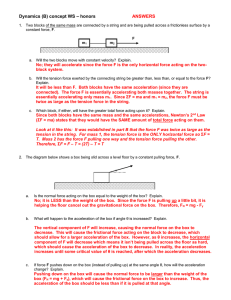
Physics 106a/196a – Problem Set 1 – Due Oct 6,... v. 2: updated Oct 1, 2006
... of the lecture notes. Problems 1, 2 are for 106a students only, 3-6 for 106a and 196a students, and 7, 8 for 196a students only. Problem sets will typically only have 4 problems, but this is relatively easy review material. However, 106a students ought to be able to do problems 7 and 8 – they’re not ...
... of the lecture notes. Problems 1, 2 are for 106a students only, 3-6 for 106a and 196a students, and 7, 8 for 196a students only. Problem sets will typically only have 4 problems, but this is relatively easy review material. However, 106a students ought to be able to do problems 7 and 8 – they’re not ...
Force and Motion
... An object is in EQULIBRIUM when the sum of all of the forces acting on it is zero. An object in EQUILIBRIUM will either be (and remain) at rest (no motion), or Will move with CONSTANT VELOCITY ...
... An object is in EQULIBRIUM when the sum of all of the forces acting on it is zero. An object in EQUILIBRIUM will either be (and remain) at rest (no motion), or Will move with CONSTANT VELOCITY ...
No Slide Title
... motion; if it was at rest, it remains at rest. If it was moving with a certain velocity, it will keep on moving with the same velocity. Second Law: The acceleration of an object is proportional to the net force acting on it, and inversely proportional to its mass: F=ma If two objects interact, t ...
... motion; if it was at rest, it remains at rest. If it was moving with a certain velocity, it will keep on moving with the same velocity. Second Law: The acceleration of an object is proportional to the net force acting on it, and inversely proportional to its mass: F=ma If two objects interact, t ...
Slide 1 - Phy 2048-0002
... body’s velocity cannot change; the body cannot accelerate v = constant in magnitude and direction. Principle of superposition: when two or more forces act on a body, the net force can be obtained by adding the individual forces vectorially. Inertial reference frame: where Newton’s laws hold. ...
... body’s velocity cannot change; the body cannot accelerate v = constant in magnitude and direction. Principle of superposition: when two or more forces act on a body, the net force can be obtained by adding the individual forces vectorially. Inertial reference frame: where Newton’s laws hold. ...
Newton`s Second Law of Motion
... the force just change the velocity? Also, what does the mass of the cart have to do with how the motion changes? We know that it takes a much harder push to get a heavy cart moving than a lighter one. A Force Sensor and an Accelerometer will let you measure the force on a cart simultaneously with th ...
... the force just change the velocity? Also, what does the mass of the cart have to do with how the motion changes? We know that it takes a much harder push to get a heavy cart moving than a lighter one. A Force Sensor and an Accelerometer will let you measure the force on a cart simultaneously with th ...
AP PHYSICS C: MECHANICS
... motion. Determine the rotational inertia for a system of particles and for particular shapes of objects. Compare the rotational inertia of various shaped objects, and how it is affected by changes in the object’s dimensions. State and apply the parallel-axis theorem. Determine the magnitude and dire ...
... motion. Determine the rotational inertia for a system of particles and for particular shapes of objects. Compare the rotational inertia of various shaped objects, and how it is affected by changes in the object’s dimensions. State and apply the parallel-axis theorem. Determine the magnitude and dire ...
Simple harmonic motion
... A TRAMPOLINE exerts a restoring force on the jumper that is directly proportional to the average force required to displace the mat. Such restoring forces provide the driving forces necessary for objects that oscillate with simple harmonic motion. ...
... A TRAMPOLINE exerts a restoring force on the jumper that is directly proportional to the average force required to displace the mat. Such restoring forces provide the driving forces necessary for objects that oscillate with simple harmonic motion. ...
Homework Answers pg 98-101
... A force is needed to bounce the ball back up, because the ball changes direction, so the ball accelerates. If the ball accelerates, there must be a force. ...
... A force is needed to bounce the ball back up, because the ball changes direction, so the ball accelerates. If the ball accelerates, there must be a force. ...
Circular Motion - juan
... Rather than labeling this axis x or y, call it c, for centripetal acceleration. The other axis is in the direction of the velocity, tangent to the circle. It is labeled tang for tangential. Centripetal force is just another name for the net force in the centripetal direction. It is the sum of all th ...
... Rather than labeling this axis x or y, call it c, for centripetal acceleration. The other axis is in the direction of the velocity, tangent to the circle. It is labeled tang for tangential. Centripetal force is just another name for the net force in the centripetal direction. It is the sum of all th ...
Chapter AA
... Look at the minus sign (“ – “ ). Well this is interesting, because we have velocity v on the right hand side of this formula. So if v is positive (ie the car is moving to the right) then v , the change in speed is negative (to the left), so the speed decreases. That makes sense, since that’s what f ...
... Look at the minus sign (“ – “ ). Well this is interesting, because we have velocity v on the right hand side of this formula. So if v is positive (ie the car is moving to the right) then v , the change in speed is negative (to the left), so the speed decreases. That makes sense, since that’s what f ...
AP Physics – Centripetal Acceleration
... A record is rotating with an angular velocity of 45 rpm. If it rotates for 35 seconds, how many rotations does it make? ...
... A record is rotating with an angular velocity of 45 rpm. If it rotates for 35 seconds, how many rotations does it make? ...
d. all of the above.
... Which has more mass, a kilogram of feathers or a kilogram of iron? a. The feathers b. The iron c. Neither—they both have the same mass. ...
... Which has more mass, a kilogram of feathers or a kilogram of iron? a. The feathers b. The iron c. Neither—they both have the same mass. ...
balanced forces flight
... 2. Convert the mass of the airplane into kilograms. 3. Now calculate the force due to weight on the Wright brothers' airplane. 4. In order for their airplane to fly, the lift force must have exceeded: _______. 5. The Wright Brothers' airplane flew 120 feet in 12 seconds. Calculate its speed in feet ...
... 2. Convert the mass of the airplane into kilograms. 3. Now calculate the force due to weight on the Wright brothers' airplane. 4. In order for their airplane to fly, the lift force must have exceeded: _______. 5. The Wright Brothers' airplane flew 120 feet in 12 seconds. Calculate its speed in feet ...
A Force - Cloudfront.net
... • We know that objects with different masses accelerate to the ground at the same rate. (Gravity = 9.8 m/s) • However, because of the 2nd Law we know that they don’t hit the ground with the same force. F = ma ...
... • We know that objects with different masses accelerate to the ground at the same rate. (Gravity = 9.8 m/s) • However, because of the 2nd Law we know that they don’t hit the ground with the same force. F = ma ...
Solution - Georgia Tech
... • Show all the steps of your calculation and provide explanations when necessary. If you need more space continue working on the back of the test form sheet. • Explain the physical meaning of your results. ...
... • Show all the steps of your calculation and provide explanations when necessary. If you need more space continue working on the back of the test form sheet. • Explain the physical meaning of your results. ...