1. In the absence of air friction, an object dropped near the surface of
... 15. A conservative force has the potential energy function U(x), shown by the graph above. A particle moving in one dimension under the influence of this force has kinetic energy 1.0 joule when it is at position x1 Which of the following is a correct statement about the motion of the particle? (A) ...
... 15. A conservative force has the potential energy function U(x), shown by the graph above. A particle moving in one dimension under the influence of this force has kinetic energy 1.0 joule when it is at position x1 Which of the following is a correct statement about the motion of the particle? (A) ...
Chapter_10
... 1. What is the magnitude 2. Through what angle does 3. Through what angle does of the angular the wheel rotate in these the wheel rotate between acceleration of the wheel 3 sec (in rad)? 2 and 3 sec (in rad)? (in rad/s2)? A. 18 A. 5 A. 0 ...
... 1. What is the magnitude 2. Through what angle does 3. Through what angle does of the angular the wheel rotate in these the wheel rotate between acceleration of the wheel 3 sec (in rad)? 2 and 3 sec (in rad)? (in rad/s2)? A. 18 A. 5 A. 0 ...
Chapter 4 forces - student practice notes
... What is the formula for force? What are the units for force? What’s the difference between a force diagram and a free body diagram? What is the difference between mass and weight? What is Fg? ...
... What is the formula for force? What are the units for force? What’s the difference between a force diagram and a free body diagram? What is the difference between mass and weight? What is Fg? ...
chapter4
... separate free body diagrams for each object Choose a convenient coordinate system for each object The x- and y-components should be taken from the vector equation and written separately ...
... separate free body diagrams for each object Choose a convenient coordinate system for each object The x- and y-components should be taken from the vector equation and written separately ...
Slide 1
... it fall. Describe the motion of the paper. • Hold a sheet of notebook paper that has been crumpled into a tight ball at eye level. Release the crumpled paper and watch it fall. Describe the motion of the paper. • How do the motions of the flat sheet of paper and crumpled ball of paper compare? What ...
... it fall. Describe the motion of the paper. • Hold a sheet of notebook paper that has been crumpled into a tight ball at eye level. Release the crumpled paper and watch it fall. Describe the motion of the paper. • How do the motions of the flat sheet of paper and crumpled ball of paper compare? What ...
Solutions to Mechanics Problems
... Newton’s 3rd law states that for every action (force), there is an equal and opposite reaction (force). Thus, if I push on a block, the block will push back on me with an equal and opposite force. Note that the two forces act on different objects. I push on the block, the block pushes on me. Many pe ...
... Newton’s 3rd law states that for every action (force), there is an equal and opposite reaction (force). Thus, if I push on a block, the block will push back on me with an equal and opposite force. Note that the two forces act on different objects. I push on the block, the block pushes on me. Many pe ...
Slide 1
... When a moving train stops, you continue moving forward. When the stopped train starts moving again, you remain stationary and are thrown backwards. In both cases, it’s due to your inertia. ...
... When a moving train stops, you continue moving forward. When the stopped train starts moving again, you remain stationary and are thrown backwards. In both cases, it’s due to your inertia. ...
Introductory Physics
... every force that is applied to anything, there is an equal and opposite reaction at that exact same point. For example, if you lean up against a wall, the wall is pushing up against you to keep you from falling over. ...
... every force that is applied to anything, there is an equal and opposite reaction at that exact same point. For example, if you lean up against a wall, the wall is pushing up against you to keep you from falling over. ...
Forces
... Resistive Force on a Falling Object Air resistance creates a resistive force opposite to the force of gravity. The faster an object falls, the bigger the resistive force. Eventually the upwards resistive force becomes as big as the downwards gravitational force. The two forces are equal and opposite ...
... Resistive Force on a Falling Object Air resistance creates a resistive force opposite to the force of gravity. The faster an object falls, the bigger the resistive force. Eventually the upwards resistive force becomes as big as the downwards gravitational force. The two forces are equal and opposite ...
Expedition 3: Fundamental Forces
... • All objects with mass are attracted to each other by a type of force called gravitationalforce. ...
... • All objects with mass are attracted to each other by a type of force called gravitationalforce. ...
09 Newtons Second Law
... How does a cart change its motion when you push and pull on it? You might think that the harder you push on a cart, the faster it goes. Is the cart’s velocity related to the force you apply? Or does the force just change the velocity? Also, what does the mass of the cart have to do with how the moti ...
... How does a cart change its motion when you push and pull on it? You might think that the harder you push on a cart, the faster it goes. Is the cart’s velocity related to the force you apply? Or does the force just change the velocity? Also, what does the mass of the cart have to do with how the moti ...
11.4B The Rides At The Park - Texarkana Independent School
... For students requiring accommodations, they should be allowed to work with a peer tutor for the Lab Worksheet since it requires a lot of reading. For Greased Lightnin and Texas Cyclone, it is suggested that they need only one answer per block unless they do these worksheets with a peer tutor. ...
... For students requiring accommodations, they should be allowed to work with a peer tutor for the Lab Worksheet since it requires a lot of reading. For Greased Lightnin and Texas Cyclone, it is suggested that they need only one answer per block unless they do these worksheets with a peer tutor. ...
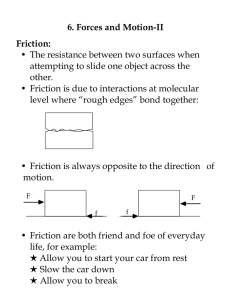
6. Forces and Motion-II Friction: • The resistance between two surfaces when
... but neither objects are moving with respect to each other. • The friction is always equal to the net force parallel to the surface. • If one net force increases or decreases, the friction force will also increase or decrease to compensate. • Experimentally, the maximum magnitude of static friction i ...
... but neither objects are moving with respect to each other. • The friction is always equal to the net force parallel to the surface. • If one net force increases or decreases, the friction force will also increase or decrease to compensate. • Experimentally, the maximum magnitude of static friction i ...
Forces and Motion
... Forces Force: a Push or a Pull on an object. SI Unit of Force: One Newton (N) is the force that causes a 1-kilogram mass to accelerate at a rate of 1 meter per second each second (1 m/s2). 1 N = 1 kg•m/s2 Combining Forces Representing Force Arrows can represent a force. The lengths of the arrows sho ...
... Forces Force: a Push or a Pull on an object. SI Unit of Force: One Newton (N) is the force that causes a 1-kilogram mass to accelerate at a rate of 1 meter per second each second (1 m/s2). 1 N = 1 kg•m/s2 Combining Forces Representing Force Arrows can represent a force. The lengths of the arrows sho ...
Chapter 2 Lessons 1 - 3 slides
... A particle moves in a straight line from O to A with a constant acceleration of 2ms-2. Its velocity at A is 30ms-1 and it takes 12 seconds to travel from O to A. Find the particle’s velocity at O and the distance OA. A train starts from rest at a station S and moves with constant acceleration. It p ...
... A particle moves in a straight line from O to A with a constant acceleration of 2ms-2. Its velocity at A is 30ms-1 and it takes 12 seconds to travel from O to A. Find the particle’s velocity at O and the distance OA. A train starts from rest at a station S and moves with constant acceleration. It p ...
force
... she falls faster and faster through the air, does her acceleration increase, decrease, or remain the same? A: Acceleration decreases because the net force acting on her decreases. Net force is equal to her weight minus her air drag, and being that air drag, increases with speed, net force and hence ...
... she falls faster and faster through the air, does her acceleration increase, decrease, or remain the same? A: Acceleration decreases because the net force acting on her decreases. Net force is equal to her weight minus her air drag, and being that air drag, increases with speed, net force and hence ...
Newton`s Laws of Motion
... discovery of the law of gravity also discovered the three laws of motion. He published them in his book Philosophiae Naturalis Principia Mathematica (mathematic principles of natural philosophy) in 1687. Today these laws are known as Newton’s Laws of Motion and describe the motion of all objects on ...
... discovery of the law of gravity also discovered the three laws of motion. He published them in his book Philosophiae Naturalis Principia Mathematica (mathematic principles of natural philosophy) in 1687. Today these laws are known as Newton’s Laws of Motion and describe the motion of all objects on ...