Thursday, Sept. 18, 2014
... Free-body diagram: A diagram of vector forces acting on an object A great tool to solve a problem using forces or using dynamics Select a point on an object in the problem Identify all the forces acting only on the selected object Define a reference frame with positive and negative axes specified Dr ...
... Free-body diagram: A diagram of vector forces acting on an object A great tool to solve a problem using forces or using dynamics Select a point on an object in the problem Identify all the forces acting only on the selected object Define a reference frame with positive and negative axes specified Dr ...
W = (1/2)
... horsepower motor that can be used to save the ship? 2.2lb = (1kg)(9.81 m/s2) = 9.81 N Force applied to water = 10 lb = (10 lb)(9.81 N)/(2.2 lb) =44.6 N Velocity of water = (2.00 m) / (1.0sec) = 2.00 m/s Power = F· v = (44.6 N) (2.0 m/s) = 89.2 W ...
... horsepower motor that can be used to save the ship? 2.2lb = (1kg)(9.81 m/s2) = 9.81 N Force applied to water = 10 lb = (10 lb)(9.81 N)/(2.2 lb) =44.6 N Velocity of water = (2.00 m) / (1.0sec) = 2.00 m/s Power = F· v = (44.6 N) (2.0 m/s) = 89.2 W ...
Document
... An important example of linear motion is:: motion under the effect of the Earth’s gravitational field. This field produces an acceleration of ...
... An important example of linear motion is:: motion under the effect of the Earth’s gravitational field. This field produces an acceleration of ...
Slide 1
... but it is falling around Earth, rather than straight downward. Everything in the orbiting space shuttle is falling around Earth at the same rate, in the same way you and the scale were falling in the elevator. Objects in the shuttle seem to be floating because they are all falling with the same ...
... but it is falling around Earth, rather than straight downward. Everything in the orbiting space shuttle is falling around Earth at the same rate, in the same way you and the scale were falling in the elevator. Objects in the shuttle seem to be floating because they are all falling with the same ...
Newton`s 3rd Law
... the windshield of a bus and makes a quite obvious mess in front of the face of the driver. This is a clear case of Newton's third law of motion. The firefly hit the bus and the bus hits the firefly. Which of the two forces is greater: the force on the firefly or the force on the ...
... the windshield of a bus and makes a quite obvious mess in front of the face of the driver. This is a clear case of Newton's third law of motion. The firefly hit the bus and the bus hits the firefly. Which of the two forces is greater: the force on the firefly or the force on the ...
Forces & the Laws of Motion
... 1. Describe acceleration of an object in terms of its mass and the net external force acting on it 2. Predict direction & magnitude of acceleration caused by a known net external force 3. Identify action-reaction force pairs ...
... 1. Describe acceleration of an object in terms of its mass and the net external force acting on it 2. Predict direction & magnitude of acceleration caused by a known net external force 3. Identify action-reaction force pairs ...
Gravity and Outer Space
... If the mass increases, what happens to the required net force if the acceleration is to be kept the same? Increased net force ...
... If the mass increases, what happens to the required net force if the acceleration is to be kept the same? Increased net force ...
Slide 1
... • Velocity changes when one or both of the following change: 1) speed 2) direction • Velocity is measured in m/s or km/hr plus direction. v = d/t + direction • d = distance t= time • Reference point is something that a moving object’s position is compared to. ...
... • Velocity changes when one or both of the following change: 1) speed 2) direction • Velocity is measured in m/s or km/hr plus direction. v = d/t + direction • d = distance t= time • Reference point is something that a moving object’s position is compared to. ...
Dynamics What causes motion? What causes changes in motion? Mass
... propelling it stops its action” Galileo – Newton: “ ...
... propelling it stops its action” Galileo – Newton: “ ...
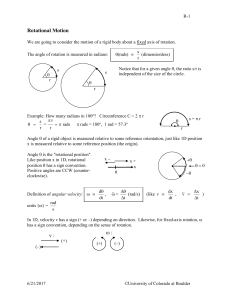
RotationalMotion - University of Colorado Boulder
... Aside: Torque, like force, is a vector quantity. Torque has a direction. Definition of vector torque : r F = cross product of r and F: "r cross F" Vector Math interlude: The cross-product of two vectors is a third vector A B C defined like this: The magnitude of A B is A B sin . The dir ...
... Aside: Torque, like force, is a vector quantity. Torque has a direction. Definition of vector torque : r F = cross product of r and F: "r cross F" Vector Math interlude: The cross-product of two vectors is a third vector A B C defined like this: The magnitude of A B is A B sin . The dir ...
Forces & the Laws of Motion
... A 24 kg crate initially at rest on a horizontal floor requires 75 N horizontal force to set it in motion. Find the coefficient of static friction between the crate and the floor. A student moves a box of books by attaching a rope to the box and pulling with a force of 90.0 N at an angle of 30.0o. Th ...
... A 24 kg crate initially at rest on a horizontal floor requires 75 N horizontal force to set it in motion. Find the coefficient of static friction between the crate and the floor. A student moves a box of books by attaching a rope to the box and pulling with a force of 90.0 N at an angle of 30.0o. Th ...
23Motion - NMSU Astronomy
... – Acceleration: change in velocity, either speed OR direction OR both ...
... – Acceleration: change in velocity, either speed OR direction OR both ...
Centripetal Force
... The “Real” Force required to turn a car • The car wants to continue its current motion. • At location 1, the car wants to continue to move forward (up). • The force required to make a turn (or circle) must be directed toward the center of the turn. ...
... The “Real” Force required to turn a car • The car wants to continue its current motion. • At location 1, the car wants to continue to move forward (up). • The force required to make a turn (or circle) must be directed toward the center of the turn. ...
- St. Aidan School
... two objects with different masses fall at exactly the same rate. P. 346) *Near the surface of Earth, the acceleration due to gravity is 9.8m/s2 ...
... two objects with different masses fall at exactly the same rate. P. 346) *Near the surface of Earth, the acceleration due to gravity is 9.8m/s2 ...
Document
... where I is the moment of inertia about axis O. Note the similarity to NSL for translation in one dimension, ...
... where I is the moment of inertia about axis O. Note the similarity to NSL for translation in one dimension, ...
Word
... The first cannon is set at an angle of 53 degrees and has an initial velocity of 5 m/s. As show in the picture, that means that the vertical component of the velocity is 4 m/s and the horizontal velocity is 3 m/s. The second cannon has an initial velocity of 5.7 m/s and a launch angle of 45 degrees. ...
... The first cannon is set at an angle of 53 degrees and has an initial velocity of 5 m/s. As show in the picture, that means that the vertical component of the velocity is 4 m/s and the horizontal velocity is 3 m/s. The second cannon has an initial velocity of 5.7 m/s and a launch angle of 45 degrees. ...