Statics-introduction
... the text to indicate which of several forces we are talking about. The letters F and subscript 1,2 etc. are completely arbitrary although often used. Other letters which you find in textbooks to represent forces are P, Q, and R. The arrow above each symbol is a reminder for us that a force is a quan ...
... the text to indicate which of several forces we are talking about. The letters F and subscript 1,2 etc. are completely arbitrary although often used. Other letters which you find in textbooks to represent forces are P, Q, and R. The arrow above each symbol is a reminder for us that a force is a quan ...
Balanced Forces Intro
... • Mr. Heffernan’s Law of Laziness– If something is not moving it will keep not moving unless something makes it move. – If something is moving it will keep moving in the same way unless something makes it change how its moving. ...
... • Mr. Heffernan’s Law of Laziness– If something is not moving it will keep not moving unless something makes it move. – If something is moving it will keep moving in the same way unless something makes it change how its moving. ...
Chapter 6: Forces
... The acceleration of an object as produced by a net force is directly proportional to the magnitude of the net force, in the same direction as the net force, and inversely proportional to the mass of the object. ...
... The acceleration of an object as produced by a net force is directly proportional to the magnitude of the net force, in the same direction as the net force, and inversely proportional to the mass of the object. ...
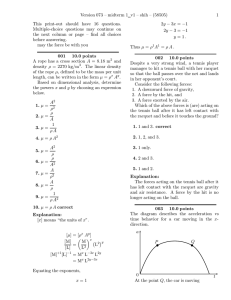
Version 073 – midterm 1 v1 – shih – (58505) 1
... Version 073 – midterm 1 v1 – shih – (58505) 016 10.0 points A particle undergoes two displacements. The first has a magnitude of 161 cm and makes an angle of 138.1◦ with the positive x axis. The resultant of the two displacements is 105 cm directed at an angle of 33.6◦ to the positive x ...
... Version 073 – midterm 1 v1 – shih – (58505) 016 10.0 points A particle undergoes two displacements. The first has a magnitude of 161 cm and makes an angle of 138.1◦ with the positive x axis. The resultant of the two displacements is 105 cm directed at an angle of 33.6◦ to the positive x ...
ch 4 Giancoli
... the use of instructors in teaching their courses and assessing student learning. Dissemination or sale of any part of this work (including on the World Wide Web) will destroy the integrity of the work and is not permitted. The work and materials from it should never be made available to students exc ...
... the use of instructors in teaching their courses and assessing student learning. Dissemination or sale of any part of this work (including on the World Wide Web) will destroy the integrity of the work and is not permitted. The work and materials from it should never be made available to students exc ...
Answers to Sample exam 2004
... A lab cart is set in motion, by hand, on a frictionless incline. Once the cart has been given its motion, only the force of gravity acts on it, and thus gravity controls its velovity on the incline. The three `velocity Vs time` curves presented in the graph below result from three different angles f ...
... A lab cart is set in motion, by hand, on a frictionless incline. Once the cart has been given its motion, only the force of gravity acts on it, and thus gravity controls its velovity on the incline. The three `velocity Vs time` curves presented in the graph below result from three different angles f ...
Uniform Circular Motion
... force, Fc, differently, so the normal force, FN, which provides the difference between Fc and mg varies with position. ...
... force, Fc, differently, so the normal force, FN, which provides the difference between Fc and mg varies with position. ...
Lab Write-Up
... A slanting surface connecting a lower level to a higher level. Things move up or down it. A couple everyday examples where you would find one would be a slide, stairs, ramp, hill or roller coaster. What forces act upon an inclined plane? 1) Normal Force: Any perpendicular force coming from the surfa ...
... A slanting surface connecting a lower level to a higher level. Things move up or down it. A couple everyday examples where you would find one would be a slide, stairs, ramp, hill or roller coaster. What forces act upon an inclined plane? 1) Normal Force: Any perpendicular force coming from the surfa ...
Mit - Massachusetts Institute of Technology
... for the case of an arbitrary direction for the relative velocity ~v of one frame with respect to the other. Assume that the corresponding axes of the two frames remain parallel. (Hint: let ~v have components vx , vy , vz .) The laws of physics (and how to transform from one frame to another) are in ...
... for the case of an arbitrary direction for the relative velocity ~v of one frame with respect to the other. Assume that the corresponding axes of the two frames remain parallel. (Hint: let ~v have components vx , vy , vz .) The laws of physics (and how to transform from one frame to another) are in ...
Wednesday, Feb. 6, 2002
... being exerted on the ball are only T and Fg. The acceleration of the ball is the same as that of the box car and is provided by the x component of the tension force. In the non-inertial frame observer, the forces being exerted on the ball are T, Fg, and Ffic. For some reason the ball is under a forc ...
... being exerted on the ball are only T and Fg. The acceleration of the ball is the same as that of the box car and is provided by the x component of the tension force. In the non-inertial frame observer, the forces being exerted on the ball are T, Fg, and Ffic. For some reason the ball is under a forc ...
1. In the absence of air friction, an object dropped near the surface of
... 15. A conservative force has the potential energy function U(x), shown by the graph above. A particle moving in one dimension under the influence of this force has kinetic energy 1.0 joule when it is at position x1 Which of the following is a correct statement about the motion of the particle? (A) ...
... 15. A conservative force has the potential energy function U(x), shown by the graph above. A particle moving in one dimension under the influence of this force has kinetic energy 1.0 joule when it is at position x1 Which of the following is a correct statement about the motion of the particle? (A) ...
Test hints
... 4. Making or interpreting displacement vs time graphs or velocity vs time graphs. A. Displacement vs time graphs: (1) Slope is the velocity. (2) Flat areas on the curve represent places where the object is at rest and its velocity is zero. (3) Positive slope means object is moving away from origin. ...
... 4. Making or interpreting displacement vs time graphs or velocity vs time graphs. A. Displacement vs time graphs: (1) Slope is the velocity. (2) Flat areas on the curve represent places where the object is at rest and its velocity is zero. (3) Positive slope means object is moving away from origin. ...
Force and Motion in Two Dimensions - juan-roldan
... You will need to apply Newton’s laws once in the xdirection and once in the y-direction. Because the weight does not point in either of these directions, you will need to break this vector into its xand y-components before you can sum your forces in these two directions. ...
... You will need to apply Newton’s laws once in the xdirection and once in the y-direction. Because the weight does not point in either of these directions, you will need to break this vector into its xand y-components before you can sum your forces in these two directions. ...