Example - mrdsample
... stops after 10 min, while Bubba is able to push for 5 minutes longer. Compare the work against the wall they each do. ...
... stops after 10 min, while Bubba is able to push for 5 minutes longer. Compare the work against the wall they each do. ...
Luna Park Physics
... That is, the only force acting on us is gravity (apart from our possibly clutching at the safety bar!). This means that while the cage is dropping we are experiencing a zero g-force (but 1g of acceleration). Then the cage motion has to be arrested and we slow down with considerable acceleration, and ...
... That is, the only force acting on us is gravity (apart from our possibly clutching at the safety bar!). This means that while the cage is dropping we are experiencing a zero g-force (but 1g of acceleration). Then the cage motion has to be arrested and we slow down with considerable acceleration, and ...
Document
... Gravity acts on objects in water as it does on ground. Buoyant force - the upward force a fluid exerts on any object in the fluid It acts against the downward force of gravity. Buoyancy exists because of pressure differences in fluids acts on all objects in a fluid, but floats only if bu ...
... Gravity acts on objects in water as it does on ground. Buoyant force - the upward force a fluid exerts on any object in the fluid It acts against the downward force of gravity. Buoyancy exists because of pressure differences in fluids acts on all objects in a fluid, but floats only if bu ...
Uniform Circular Motion - K
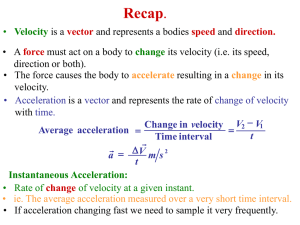
... together, Δv is directed more and more toward the exact center of the circular path. Since when we have the instantaneous acceleration, v1 and v2 should be about a fraction of a second apart, at that moment the direction is in fact directed directly toward the center of the circle. ...
... together, Δv is directed more and more toward the exact center of the circular path. Since when we have the instantaneous acceleration, v1 and v2 should be about a fraction of a second apart, at that moment the direction is in fact directed directly toward the center of the circle. ...
Document
... constant speed A. has a net force acting upon it in the direction of motion. B. has zero acceleration. C. has no forces acting on it. D. both B & C E. None of these. ...
... constant speed A. has a net force acting upon it in the direction of motion. B. has zero acceleration. C. has no forces acting on it. D. both B & C E. None of these. ...
FORCE_AND_MOTION - Effingham County Schools
... between the application of a force and the resulting change in position and motion on an object. a. Identify simple machines b. Using different size objects, observe how force affects speed and motion. c. Explain what happens to the speed or direction of an object when a greater force than the initi ...
... between the application of a force and the resulting change in position and motion on an object. a. Identify simple machines b. Using different size objects, observe how force affects speed and motion. c. Explain what happens to the speed or direction of an object when a greater force than the initi ...
Lecture 14ba
... Section 8-4: Torque • Newton’s 1st Law (rotational language version): “A rotating body will continue to rotate at a constant angular velocity unless an external TORQUE acts.” • Clearly, to understand this, we need to define the concept of TORQUE. • Newton’s 2nd Law (rotational language version): Al ...
... Section 8-4: Torque • Newton’s 1st Law (rotational language version): “A rotating body will continue to rotate at a constant angular velocity unless an external TORQUE acts.” • Clearly, to understand this, we need to define the concept of TORQUE. • Newton’s 2nd Law (rotational language version): Al ...
V - USU Physics
... • Car moved at a constant speed but its direction continuously changed – thus its velocity was changing. • But we now know that velocity changes are produced by an acceleration. • Thus when the car rounds the bend at a constant speed it is accelerating!! • Direction of acceleration is given by DV di ...
... • Car moved at a constant speed but its direction continuously changed – thus its velocity was changing. • But we now know that velocity changes are produced by an acceleration. • Thus when the car rounds the bend at a constant speed it is accelerating!! • Direction of acceleration is given by DV di ...
Slide 1
... 19. Describe the velocity of the ball in question 18 as viewed by a pedestrian standing at the side of the road as your car passes. ...
... 19. Describe the velocity of the ball in question 18 as viewed by a pedestrian standing at the side of the road as your car passes. ...
press the brake to apply a force in the opposite direction, so that the
... If the resultant force acting on a stationary body is not zero, the body will accelerate in the direction of the resultant force. A car accelerates when the driving force is greater than the frictional forces. A greater driving force will produce a greater acceleration. ...
... If the resultant force acting on a stationary body is not zero, the body will accelerate in the direction of the resultant force. A car accelerates when the driving force is greater than the frictional forces. A greater driving force will produce a greater acceleration. ...
Solutions Guide - Blue Valley Schools
... bottom of a “bungee” cord plunge also has an instantaneous velocity of zero but a non-zero (upward) acceleration at the same time. 20. An object moving with a constant velocity has a non-zero velocity and a zero acceleration at the same time. So a car driving at constant speed on a straight, level r ...
... bottom of a “bungee” cord plunge also has an instantaneous velocity of zero but a non-zero (upward) acceleration at the same time. 20. An object moving with a constant velocity has a non-zero velocity and a zero acceleration at the same time. So a car driving at constant speed on a straight, level r ...
Newton`s Laws PPT for HTML
... which it rests. Static friction is always opposite to the direction the object would move if there was no friction. Static friction must be overcome before an object can begin moving. Static friction equals the net applied force up to its maximum value which depends on the mass of the object and the ...
... which it rests. Static friction is always opposite to the direction the object would move if there was no friction. Static friction must be overcome before an object can begin moving. Static friction equals the net applied force up to its maximum value which depends on the mass of the object and the ...