CP-S-HW-ch-8-detailed
... object is in equilibrium if the forces are equal in magnitude and opposite in direction. (b) The object is in equilibrium if the net torque on the object is zero. (c) The object is in equilibrium if the forces act at the same point on the object. (d) The object is in equilibrium if the net force and ...
... object is in equilibrium if the forces are equal in magnitude and opposite in direction. (b) The object is in equilibrium if the net torque on the object is zero. (c) The object is in equilibrium if the forces act at the same point on the object. (d) The object is in equilibrium if the net force and ...
Ph211_CH5_worksheet-f06
... Since the masses are attached their accelerations are equal: a1y = a2x = asystem Solving for asystem: m2gsin – m1asystem - m1g = m2asystem asystem = (m2gsin – m1g)/(m1 + m2) = -1.03 m/s2 (i.e. up the incline!) e. What are the tension forces acting on each mass? Express the tension vectors in compo ...
... Since the masses are attached their accelerations are equal: a1y = a2x = asystem Solving for asystem: m2gsin – m1asystem - m1g = m2asystem asystem = (m2gsin – m1g)/(m1 + m2) = -1.03 m/s2 (i.e. up the incline!) e. What are the tension forces acting on each mass? Express the tension vectors in compo ...
Standard EPS Shell Presentation
... Movement Around the Loop The force that causes an object to move in a circle is called a centripetal force Any type of physical force can be a centripetal force if it results in circular motion The centripetal force is always directed toward the center of the circle that the object’s motion f ...
... Movement Around the Loop The force that causes an object to move in a circle is called a centripetal force Any type of physical force can be a centripetal force if it results in circular motion The centripetal force is always directed toward the center of the circle that the object’s motion f ...
Thursday, June 22, 2006
... When there are more than one force being exerted on certain points of the object, one can sum up the torque generated by each force vectorially. The convention for sign of the torque is positive if rotation is in counter-clockwise and negative if clockwise. ...
... When there are more than one force being exerted on certain points of the object, one can sum up the torque generated by each force vectorially. The convention for sign of the torque is positive if rotation is in counter-clockwise and negative if clockwise. ...
2.Newtons_Laws
... • The Free Body Diagram is a drawing to help us visualize all of the forces acting on an object. • You will use the Free Body Diagram throughout your career in physics. • To draw an FBD: – Draw the object as a point – Draw each force on the object as a vector starting from the object. ...
... • The Free Body Diagram is a drawing to help us visualize all of the forces acting on an object. • You will use the Free Body Diagram throughout your career in physics. • To draw an FBD: – Draw the object as a point – Draw each force on the object as a vector starting from the object. ...
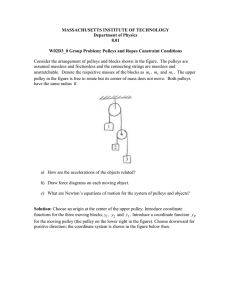
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
... Consider the arrangement of pulleys and blocks shown in the figure. The pulleys are assumed massless and frictionless and the connecting strings are massless and unstretchable. Denote the respective masses of the blocks as m1 , m2 and m3 . The upper pulley in the figure is free to rotate but its cen ...
... Consider the arrangement of pulleys and blocks shown in the figure. The pulleys are assumed massless and frictionless and the connecting strings are massless and unstretchable. Denote the respective masses of the blocks as m1 , m2 and m3 . The upper pulley in the figure is free to rotate but its cen ...
Chapter 4 Dynamics: Newton`s Laws of Motion
... Also, the crate does not accelerate horizontally (steady speed), and so ...
... Also, the crate does not accelerate horizontally (steady speed), and so ...
Chapter 12 ppt
... Imagine that you are trying to push a heavy desk across the floor. There are two opposing forces on the desk: the force you apply, and the force of friction between the desk and the floor. What will happen if the force of friction is the same magnitude as the force that you apply? What will happen i ...
... Imagine that you are trying to push a heavy desk across the floor. There are two opposing forces on the desk: the force you apply, and the force of friction between the desk and the floor. What will happen if the force of friction is the same magnitude as the force that you apply? What will happen i ...
RevfinQans
... Answer: The tension is zero. By the same v v2 v1 argument as in the question above, one can show that the acceleration is straight down when the mass on the extreme right with the string horizontal. Since the acceleration is straight down, the net force must be straight down, so there can be no ...
... Answer: The tension is zero. By the same v v2 v1 argument as in the question above, one can show that the acceleration is straight down when the mass on the extreme right with the string horizontal. Since the acceleration is straight down, the net force must be straight down, so there can be no ...
Fall 2005 MC Final Review
... 48. Two forces act on a hockey puck. For which orientation of the forces will the puck acquire an acceleration with the largest magnitude? (e) The magnitude of the acceleration will be the same in all four cases shown above. 49. A rock is suspended from a string; and it moves downward at constant sp ...
... 48. Two forces act on a hockey puck. For which orientation of the forces will the puck acquire an acceleration with the largest magnitude? (e) The magnitude of the acceleration will be the same in all four cases shown above. 49. A rock is suspended from a string; and it moves downward at constant sp ...
Chapter 12 Forces and Motion
... crumpled ball of paper fell more quickly to the ground and followed a straight-line path. Do not assess students on correctly identifying the two opposing forces on the paper; accept any reasonable response. The two opposing forces are gravity and air resistance. ...
... crumpled ball of paper fell more quickly to the ground and followed a straight-line path. Do not assess students on correctly identifying the two opposing forces on the paper; accept any reasonable response. The two opposing forces are gravity and air resistance. ...
Class 10 Newton’s third law | Friction PHY 231 Fall 2004
... equal and opposite force (somewhere in the universe) balancing it out. This means that the net force of these two forces must be zero. F=ma => there can be no acceleration; nothing accelerates. 1. True, but Newton’s 3rd law only works part of the time 2. False, Newton’s 3rd law is wrong 3. False, Ne ...
... equal and opposite force (somewhere in the universe) balancing it out. This means that the net force of these two forces must be zero. F=ma => there can be no acceleration; nothing accelerates. 1. True, but Newton’s 3rd law only works part of the time 2. False, Newton’s 3rd law is wrong 3. False, Ne ...
Factors That Affect Motion
... Factors That Affect Motion Objective 4.05 Determine factors that affect motion including: Force Friction Inertia Momentum ...
... Factors That Affect Motion Objective 4.05 Determine factors that affect motion including: Force Friction Inertia Momentum ...
1. (a) Torque and moment are to do with `distance multiplied by force
... one mark for one correct moment, one mark for the second correct moment and equated to first moment ...
... one mark for one correct moment, one mark for the second correct moment and equated to first moment ...