Lecture 5 - McMaster Physics and Astronomy
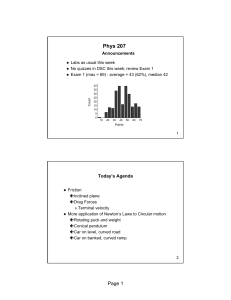
... coefficient of static friction μs=0.50. What minimum force F is needed to pull the block? ...
... coefficient of static friction μs=0.50. What minimum force F is needed to pull the block? ...
Chapter 5: Using Newton`s Laws
... where µk is the coefficient of kinetic friction and N is the magnitude of the normal force. Therefore, during the sliding, a kinetic frictional force of magnitude fk opposes the motion. 4. When several agents push in different directions on an object, the frictional force opposes the component of t ...
... where µk is the coefficient of kinetic friction and N is the magnitude of the normal force. Therefore, during the sliding, a kinetic frictional force of magnitude fk opposes the motion. 4. When several agents push in different directions on an object, the frictional force opposes the component of t ...
Lecture 13 - UD Physics
... ÍIf a similar block (same µ) of mass 2m were placed on the same incline and given a brief push, it would: (a) stop (b) accelerate (c) move with constant speed m ...
... ÍIf a similar block (same µ) of mass 2m were placed on the same incline and given a brief push, it would: (a) stop (b) accelerate (c) move with constant speed m ...
Chapter 5
... reached the critical value at which motion is about to start. When T is less than this value, the inequality sign holds. In that case we have to use the equilibrium conditions (∑F = 0) to find fs. If there is no applied force (T = 0), then there is not static friction force either (fs = 0). ...
... reached the critical value at which motion is about to start. When T is less than this value, the inequality sign holds. In that case we have to use the equilibrium conditions (∑F = 0) to find fs. If there is no applied force (T = 0), then there is not static friction force either (fs = 0). ...
quote - AgriSETA
... Apply symbols and abbreviations used on electrical circuits for schematic and wiring diagrams, connection schedules, cables schedules, layouts and single-line drawings. Compile material lists from electrical, engineering and electronic drawings. Set up AC and/or DC welding machines, equipment includ ...
... Apply symbols and abbreviations used on electrical circuits for schematic and wiring diagrams, connection schedules, cables schedules, layouts and single-line drawings. Compile material lists from electrical, engineering and electronic drawings. Set up AC and/or DC welding machines, equipment includ ...
Centripetal Force (Chapter Section 6.5)
... - HW 4 given out due in a next Wednesday ( in one week) Recap: friction For a block on an incline plane we learned last lecture that the block will only start to slide down the inline when the angle of the incline with the horizontal is large enough. We decided that there must be some force preventi ...
... - HW 4 given out due in a next Wednesday ( in one week) Recap: friction For a block on an incline plane we learned last lecture that the block will only start to slide down the inline when the angle of the incline with the horizontal is large enough. We decided that there must be some force preventi ...
Everyday_Forcesfor_moodle
... Normal Force-Fn • Force exerted by one object on another in a direction perpendicular to the surface of contact. ...
... Normal Force-Fn • Force exerted by one object on another in a direction perpendicular to the surface of contact. ...
Chap. 8 Friction
... kg) and is held in position off the side of a ship by the spars at A and B. A man having a weight of 650 N ( 65 kg) gets in the boat, wraps a rope around an overhead boom at C, and ties it to the end of the boat as shown. If the boat is disconnected from the spars, determine the minimum number of ha ...
... kg) and is held in position off the side of a ship by the spars at A and B. A man having a weight of 650 N ( 65 kg) gets in the boat, wraps a rope around an overhead boom at C, and ties it to the end of the boat as shown. If the boat is disconnected from the spars, determine the minimum number of ha ...
Doris williams - HCC Learning Web
... This exists when the object is at rest relative to the surface. This force must be overcome in order to make the object start moving. It is given by fs = µs n. b) Kinetic friction ( fk) This exists when the object is in motion and is given by fk = µk n. where µs and µk are the coefficient of static ...
... This exists when the object is at rest relative to the surface. This force must be overcome in order to make the object start moving. It is given by fs = µs n. b) Kinetic friction ( fk) This exists when the object is in motion and is given by fk = µk n. where µs and µk are the coefficient of static ...
PPTX - University of Toronto Physics
... you to walk! Walking certainly involves speeding up, and this would not be possible if the floor were frictionless or covered in marbles! ...
... you to walk! Walking certainly involves speeding up, and this would not be possible if the floor were frictionless or covered in marbles! ...
International Space Station - University of Toronto Physics
... you to walk! Walking certainly involves speeding up, and this would not be possible if the floor were frictionless or covered in marbles! ...
... you to walk! Walking certainly involves speeding up, and this would not be possible if the floor were frictionless or covered in marbles! ...
Exp 04 - Coefficient of Friction
... This exists when the object is at rest relative to the surface. This force must be overcome in order to make the object start moving. It is given by fs = µs n. b) Kinetic friction ( fk) This exists when the object is in motion and is given by fk = µk n. where µs and µk are the coefficient of static ...
... This exists when the object is at rest relative to the surface. This force must be overcome in order to make the object start moving. It is given by fs = µs n. b) Kinetic friction ( fk) This exists when the object is in motion and is given by fk = µk n. where µs and µk are the coefficient of static ...
Chapter 5: Forces in Two DImensions
... Equilibrium- when all forces balance/cancel each other out Net force is zero Acceleration is zero Velocity is constant (even if it’s zero) ...
... Equilibrium- when all forces balance/cancel each other out Net force is zero Acceleration is zero Velocity is constant (even if it’s zero) ...
Doris williams - HCC Learning Web
... This exists when the object is at rest relative to the surface. This force must be overcome in order to make the object start moving. It is given by fs = µs n. b) Kinetic friction ( fk) This exists when the object is in motion and is given by fk = µk n. where µs and µk are the coefficient of static ...
... This exists when the object is at rest relative to the surface. This force must be overcome in order to make the object start moving. It is given by fs = µs n. b) Kinetic friction ( fk) This exists when the object is in motion and is given by fk = µk n. where µs and µk are the coefficient of static ...
04_friction
... This exists when the object is at rest relative to the surface. This force must be overcome in order to make the object start moving. It is given by fs = µs n. b) Kinetic friction ( fk) This exists when the object is in motion and is given by fk = µk n. ...
... This exists when the object is at rest relative to the surface. This force must be overcome in order to make the object start moving. It is given by fs = µs n. b) Kinetic friction ( fk) This exists when the object is in motion and is given by fk = µk n. ...
Section 1: Measuring Motion
... Negative acceleration – negative number with a negative slope on a velocity-time graph Constant velocity – zero slope – flat line ...
... Negative acceleration – negative number with a negative slope on a velocity-time graph Constant velocity – zero slope – flat line ...
Checkpoint Chapter 1 – Force Review
... 16. The friction of an object at rest is called STATIC friction. 17. The friction of two solid surfaces moving over each other is called SLIDING friction. 18. The friction of wheels is an example ROLLING friction. 19. The friction caused by moving through liquids and gases is called FLUID friction. ...
... 16. The friction of an object at rest is called STATIC friction. 17. The friction of two solid surfaces moving over each other is called SLIDING friction. 18. The friction of wheels is an example ROLLING friction. 19. The friction caused by moving through liquids and gases is called FLUID friction. ...
Unit 1 exercises - Tick ( ) in front of true sentence, And Tick ( ) in
... b. The friction force depends on the shape of the surface of two touching objects. c. Ball bearings are used to increase the friction force. d. The pushing of an object forward is opposed by a friction force at the same direction. e. Oil is used to decrease the friction force. f. When the affecting ...
... b. The friction force depends on the shape of the surface of two touching objects. c. Ball bearings are used to increase the friction force. d. The pushing of an object forward is opposed by a friction force at the same direction. e. Oil is used to decrease the friction force. f. When the affecting ...
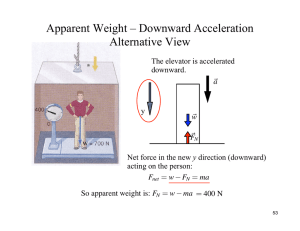
Apparent Weight – Downward Acceleration Alternative View
... A crate is being pushed across the floor at constant velocity by applying a downward force at an angle θ to the horizontal. Show that θ if is greater than a certain value, then it is impossible to push the crate, no matter how large the force. ...
... A crate is being pushed across the floor at constant velocity by applying a downward force at an angle θ to the horizontal. Show that θ if is greater than a certain value, then it is impossible to push the crate, no matter how large the force. ...
lecture_11 - Lyle School of Engineering
... Forces and energy dissipated Temperature rise Tolerances of workpiece after machining Surface finish of workpiece after machining • Wear and failure of tool • Type of chip produced ...
... Forces and energy dissipated Temperature rise Tolerances of workpiece after machining Surface finish of workpiece after machining • Wear and failure of tool • Type of chip produced ...
Motion Velocity Net Force Sliding Friction Speed Rolling Friction
... the actual amount of length traveled or ground covered during a motion ...
... the actual amount of length traveled or ground covered during a motion ...
Everyday Forces
... • the type of sliding motion – starting or moving. • Does not depend on any other factor. • It is a constant. ...
... • the type of sliding motion – starting or moving. • Does not depend on any other factor. • It is a constant. ...
Friction stir welding

Friction-stir welding (FSW) is a solid-state joining process (the metal is not melted) that uses a third body tool to join two facing surfaces. Heat is generated between the tool and material which leads to a very soft region near the FSW tool. It then mechanically intermixes the two pieces of metal at the place of the joint, then the softened metal (due to the elevated temperature) can be joined using mechanical pressure (which is applied by the tool), much like joining clay, or dough. It is primarily used on aluminium, and most often on extruded aluminium (non-heat treatable alloys), and on structures which need superior weld strength without a post weld heat treatment.It was invented and experimentally proven at The Welding Institute UK in December 1991. TWI holds patents on the process, the first being the most descriptive.