Type Ia Supernovae in the SDSS Strip 82
... Part of the SDSS-II project Aim to discover SN Ia in “redshift desert” from z=0.05 to 0.4 Well-calibrated photometry in multi-band. ...
... Part of the SDSS-II project Aim to discover SN Ia in “redshift desert” from z=0.05 to 0.4 Well-calibrated photometry in multi-band. ...
Star Systems and Galaxies
... Smaller than other galaxies Many bright, young stars Lots of gas and dust to form new stars ...
... Smaller than other galaxies Many bright, young stars Lots of gas and dust to form new stars ...
20.2 The Milky Way and Other Galaxies
... -RECOGNIZE THAT AT THE CENTER OF THE MILKY WAY THERE IS A BULGE STARS, FROM WHICH ARE SPIRAL ARMS OF GAS, DUST AND MOST OF THE YOUNG STARS. -RECOGNIZE THAT THE SOLAR SYSTEM IS PART OF THE MILKY WAY GALAXY. K -DEMONSTRATE THAT HUBBLE’S LAW THAT GALAXIES THAT ARE FARTHER AWAY HAVE A GREATER RED SHIFT, ...
... -RECOGNIZE THAT AT THE CENTER OF THE MILKY WAY THERE IS A BULGE STARS, FROM WHICH ARE SPIRAL ARMS OF GAS, DUST AND MOST OF THE YOUNG STARS. -RECOGNIZE THAT THE SOLAR SYSTEM IS PART OF THE MILKY WAY GALAXY. K -DEMONSTRATE THAT HUBBLE’S LAW THAT GALAXIES THAT ARE FARTHER AWAY HAVE A GREATER RED SHIFT, ...
Kinematics of the galaxies
... Evidence: mainly optical characteristics (tails, counter-rotating cores, dust lanes) ...
... Evidence: mainly optical characteristics (tails, counter-rotating cores, dust lanes) ...
Document
... • Some quasar spectra not only show broad emission lines but also broad absorption lines • (BAL) Quasars: normal quasars viewed at angle along the line-of-sight of intervening, fast-moving material. ...
... • Some quasar spectra not only show broad emission lines but also broad absorption lines • (BAL) Quasars: normal quasars viewed at angle along the line-of-sight of intervening, fast-moving material. ...
The Universe - greenslime.info
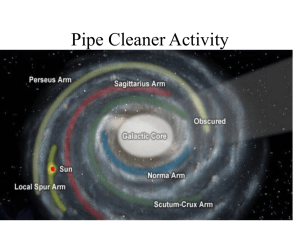
... 100,000 light-years in diameter. contains about 200 billion stars Home to Our Sun the Sun and Earth are located 2/3 away from center in one of the outer spiral arms ● Sun orbits central Milky Way at about 235 km/s around the center of the galaxy You are here! ...
... 100,000 light-years in diameter. contains about 200 billion stars Home to Our Sun the Sun and Earth are located 2/3 away from center in one of the outer spiral arms ● Sun orbits central Milky Way at about 235 km/s around the center of the galaxy You are here! ...
Quasars, Active Galaxies, and Gamma
... • Short, intense bursts of gamma rays are observed at random times coming from random parts of the sky • The origin of short-duration gamma-ray bursters is unknown ...
... • Short, intense bursts of gamma rays are observed at random times coming from random parts of the sky • The origin of short-duration gamma-ray bursters is unknown ...
File - The World of Astronomy
... dust and gas. They usually contain several million to over a trillion stars and can range in size from a few thousand to several hundred thousand light-years across. There are hundreds of billions of galaxies in the universe. Galaxies come in many different sizes, shapes and brightnesses and, like s ...
... dust and gas. They usually contain several million to over a trillion stars and can range in size from a few thousand to several hundred thousand light-years across. There are hundreds of billions of galaxies in the universe. Galaxies come in many different sizes, shapes and brightnesses and, like s ...
Star Systems and Galaxies
... Smaller than other galaxies Many bright, young stars Lots of gas and dust to form new stars ...
... Smaller than other galaxies Many bright, young stars Lots of gas and dust to form new stars ...
Irregular Galaxies
... 1) Globular stars clusters are found in the halos of spiral galaxies and in elliptical galaxies. ...
... 1) Globular stars clusters are found in the halos of spiral galaxies and in elliptical galaxies. ...
Galaxies: 33.1
... the orbital data of the Sun (including our solar system) about the center of the Galaxy. Assume that most of the mass of the Galaxy can be approximated as a uniform sphere of mass (the center bulge). ...
... the orbital data of the Sun (including our solar system) about the center of the Galaxy. Assume that most of the mass of the Galaxy can be approximated as a uniform sphere of mass (the center bulge). ...
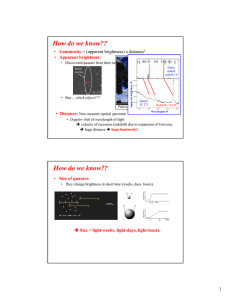
How do we know?? = (apparent brightness) x distance Luminosity Apparent brightness:
... • Luminosity = (apparent brightness) x distance2 • Apparent brightness: • Discovered quasars from their radio emission. Orion nebula ...
... • Luminosity = (apparent brightness) x distance2 • Apparent brightness: • Discovered quasars from their radio emission. Orion nebula ...
ppt - UCL
... and also from inner spiral arms. These extend up to about 15’’ from the nucleus, and fainter arms can be observed further out at about 30’’. We also see (top left) UV emission from the non-interacting companion galaxy IC 5283 (z=0.016024), 1.3’ away. Some of the non-AGN emission from NGC 7469 is pro ...
... and also from inner spiral arms. These extend up to about 15’’ from the nucleus, and fainter arms can be observed further out at about 30’’. We also see (top left) UV emission from the non-interacting companion galaxy IC 5283 (z=0.016024), 1.3’ away. Some of the non-AGN emission from NGC 7469 is pro ...
Section 4 Galaxies and the Universe
... 2. Spiral galaxies—spiral arms wind out from inner section; some have barred spirals with stars and gas in a central bar 3. Elliptical galaxies—large, three-dimensional ellipses; most common shape 4. Irregular galaxies—smaller, less common galaxies with various different shapes B. The Milky Way Gala ...
... 2. Spiral galaxies—spiral arms wind out from inner section; some have barred spirals with stars and gas in a central bar 3. Elliptical galaxies—large, three-dimensional ellipses; most common shape 4. Irregular galaxies—smaller, less common galaxies with various different shapes B. The Milky Way Gala ...
Hubble`s Classification of Galaxies (PDF version)
... they can appear perfectly round or somewhat elongated, with very smooth brightness (no spiral arms or structure) ...
... they can appear perfectly round or somewhat elongated, with very smooth brightness (no spiral arms or structure) ...
galaxies
... How are the lives of galaxies connected with the history of the universe? What are the three major types of galaxies? How are galaxies grouped together? How do we measure the distances to galaxies? How did Hubble prove that galaxies lie far beyond the Milky way? What is Hubble’s Law? How do distance ...
... How are the lives of galaxies connected with the history of the universe? What are the three major types of galaxies? How are galaxies grouped together? How do we measure the distances to galaxies? How did Hubble prove that galaxies lie far beyond the Milky way? What is Hubble’s Law? How do distance ...
Lecture notes 19: Active Galaxies
... processes with line widths indicating velocities of up to 10 000 km/s. Radio quiet quasars (QSO’s) are observed to associated with spiral galaxies while the radio loud quasars are found in elliptical galaxies. A large percentage of quasars have close lying neighbors, seem perturbed in some way, or s ...
... processes with line widths indicating velocities of up to 10 000 km/s. Radio quiet quasars (QSO’s) are observed to associated with spiral galaxies while the radio loud quasars are found in elliptical galaxies. A large percentage of quasars have close lying neighbors, seem perturbed in some way, or s ...
Stellar Evolution
... Hubble’s system only based on appearance Now we know there are other differences Elliptical Galaxies: mostly old stars, very little gas and dust Spiral Galaxies: mixture of young and old stars, lots of gas & dust so new stars ...
... Hubble’s system only based on appearance Now we know there are other differences Elliptical Galaxies: mostly old stars, very little gas and dust Spiral Galaxies: mixture of young and old stars, lots of gas & dust so new stars ...
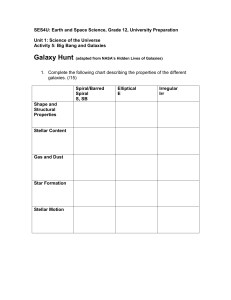
Galaxy Hunt Assignment.
... 2. The galaxy we live in is called the Milky Way. Using the Internet or other resources, research answers to the following questions. ...
... 2. The galaxy we live in is called the Milky Way. Using the Internet or other resources, research answers to the following questions. ...
633 infrared, ultraviolet, x-ray, and gamma
... Scientists currently recognize many phenomena associated with active galaxies, including quasars and blazars. Quasars are extremely distant objects, some as far away as 12 billion light-years. A quasar is also extremely luminous, perhaps a hundred or even a thousand times brighter than a normal gala ...
... Scientists currently recognize many phenomena associated with active galaxies, including quasars and blazars. Quasars are extremely distant objects, some as far away as 12 billion light-years. A quasar is also extremely luminous, perhaps a hundred or even a thousand times brighter than a normal gala ...
Black Holes - World of Teaching
... Black Holes The intense gravitational field left when a giant star collapses ...
... Black Holes The intense gravitational field left when a giant star collapses ...
Seyfert galaxy

Seyfert galaxies are one of the two largest groups of active galaxies, along with quasars. They have quasar-like nuclei (very luminous, distant and bright sources of electromagnetic radiation) with very high surface brightnesses whose spectra reveal strong, high-ionisation emission lines, but unlike quasars, their host galaxies are clearly detectable.Seyfert galaxies account for about 10% of all galaxies and are some of the most intensely studied objects in astronomy, as they are thought to be powered by the same phenomena that occur in quasars, although they are closer and less luminous than quasars. These galaxies have supermassive black holes at their centers which are surrounded by accretion discs of in-falling material. The accretion discs are believed to be the source of the observed ultraviolet radiation. Ultraviolet emission and absorption lines provide the best diagnostics for the composition of the surrounding material.Seen in visible light, most Seyfert galaxies look like normal spiral galaxies, but when studied under other wavelengths, it becomes clear that the luminosity of their cores is of comparable intensity to the luminosity of whole galaxies the size of the Milky Way.Seyfert galaxies are named after Carl Seyfert, who first described this class in 1943.