Answer
... calculations. Note: a ½ mark will be deducted for any final answer with the incorrect number of significant figures. You are provided with a Periodic Table and data sheet on the last page of the examination. You may detach this sheet. HAND IN THIS PAPER IN ITS ENTIRITY AT THE END OF THE EXAMINATION. ...
... calculations. Note: a ½ mark will be deducted for any final answer with the incorrect number of significant figures. You are provided with a Periodic Table and data sheet on the last page of the examination. You may detach this sheet. HAND IN THIS PAPER IN ITS ENTIRITY AT THE END OF THE EXAMINATION. ...
work is done - Portal UniMAP
... • It is impossible to completely isolate a reaction from its surroundings, but it is possible to measure the change in the internal energy of the system, ΔU, as energy flows into the system from the surroundings or flows from the system into the surroundings. ...
... • It is impossible to completely isolate a reaction from its surroundings, but it is possible to measure the change in the internal energy of the system, ΔU, as energy flows into the system from the surroundings or flows from the system into the surroundings. ...
Topic 1: Quantitative chemistry
... Alternatively this means that there are 3 times as much particles of CO as Fe2 O3 particles; for the reaction to go to completion (=both reactants are completely used up) 3 times as much CO is needed as Fe2 O3. By multiplying each number of particles by 6.02 x 1023, the above balanced equation state ...
... Alternatively this means that there are 3 times as much particles of CO as Fe2 O3 particles; for the reaction to go to completion (=both reactants are completely used up) 3 times as much CO is needed as Fe2 O3. By multiplying each number of particles by 6.02 x 1023, the above balanced equation state ...
application of hydroxyapatite in protein purification
... formation CO32- by the reaction of adsorbed CO2. The incorporation of CO2 into CaHAp exist only as CO32[3]. The bands around 1515 cm-1 can be assigned to varios C-O stretching vibration modes of CO32- ions, substituted at phosphate site (type A) because the formation CO32- by the reaction of adsorbe ...
... formation CO32- by the reaction of adsorbed CO2. The incorporation of CO2 into CaHAp exist only as CO32[3]. The bands around 1515 cm-1 can be assigned to varios C-O stretching vibration modes of CO32- ions, substituted at phosphate site (type A) because the formation CO32- by the reaction of adsorbe ...
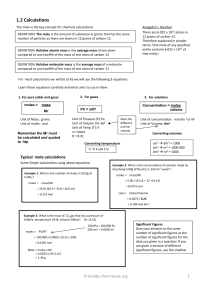
1.2 Calculations
... water so the beaker and its contents could be heated gently until all the solid had dissolved. Pour solution into a 250cm3 graduated flask via a funnel. Rinse beaker and funnel and add washings from the beaker and glass rod to the volumetric flask. • make up to the mark with distilled water using a ...
... water so the beaker and its contents could be heated gently until all the solid had dissolved. Pour solution into a 250cm3 graduated flask via a funnel. Rinse beaker and funnel and add washings from the beaker and glass rod to the volumetric flask. • make up to the mark with distilled water using a ...
2015_Final Exam Study Guide
... separate the solute particles from each other. separate the solvent molecules from each other. warm the solvent and solute. Answers a and b are both correct. The energy involved in the formation of a solution will be a. given off if it is a water solution. b. absorbed if the solution is solid. c. ex ...
... separate the solute particles from each other. separate the solvent molecules from each other. warm the solvent and solute. Answers a and b are both correct. The energy involved in the formation of a solution will be a. given off if it is a water solution. b. absorbed if the solution is solid. c. ex ...
The Generation of VOCs from Stationary Gas Turbines and the Impact on Oxydation Catalyst Performance
... The volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions from natural gas fired gas turbines as used for combined cycle power plants are examined with regard to the split between saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbons. How the saturated to unsaturated hydrocarbon ratio in the emissions influences the perfo ...
... The volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions from natural gas fired gas turbines as used for combined cycle power plants are examined with regard to the split between saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbons. How the saturated to unsaturated hydrocarbon ratio in the emissions influences the perfo ...
to view or the PHOTOSYNTHESIS Presentation
... Procedure Mark how far up the paper the alcohol traveled with a pencil Determine how many bands of pigment you have, what color they are, and measure how far each band traveled from the origin line ...
... Procedure Mark how far up the paper the alcohol traveled with a pencil Determine how many bands of pigment you have, what color they are, and measure how far each band traveled from the origin line ...
Unit 1 Atoms, Molecules and Stoichiometry
... The molar mass The molar mass ( M ) of a substance is the mass per mole of that substance. Molar mass has the unit : g mol-1. It follows from the definition of the mole that the molar mass of carbon-12 is exactly 12 g mol-1. The term molar mass applies not only to elements in the atomic state but al ...
... The molar mass The molar mass ( M ) of a substance is the mass per mole of that substance. Molar mass has the unit : g mol-1. It follows from the definition of the mole that the molar mass of carbon-12 is exactly 12 g mol-1. The term molar mass applies not only to elements in the atomic state but al ...
Document
... curve. This is a graph of the change in temperature of a substance as energy is added in the form of heat. The pressure of the system is assumed to be held constant, at normal pressure (1 atm). As you can see from the graph below, at normal pressure water freezes at 0ºC and boils at 100ºC. The plate ...
... curve. This is a graph of the change in temperature of a substance as energy is added in the form of heat. The pressure of the system is assumed to be held constant, at normal pressure (1 atm). As you can see from the graph below, at normal pressure water freezes at 0ºC and boils at 100ºC. The plate ...
הקימנידומרתב ןושארה קוחה
... 10. Two liters of N2 at 0 °C and 5 atm pressure are expanded isothermally against a constant pressure of 1 atm until the pressure of the gas is also 1 atm. Assuming the gas to be ideal, what are the values of w, ∆U, ∆H, and q for the process? Calculate the efficiency of this process. 11. Calculate t ...
... 10. Two liters of N2 at 0 °C and 5 atm pressure are expanded isothermally against a constant pressure of 1 atm until the pressure of the gas is also 1 atm. Assuming the gas to be ideal, what are the values of w, ∆U, ∆H, and q for the process? Calculate the efficiency of this process. 11. Calculate t ...
Chemistry
... Use the Kinetic Molecular theory to answer questions 12-14. All answers must include explanations. 12. If the number of moles of gas in a flask is doubled, what happens to the pressure inside the flask? 13. What happens to an aerosol can (which contains compressed gas) when you throw it into a fire? ...
... Use the Kinetic Molecular theory to answer questions 12-14. All answers must include explanations. 12. If the number of moles of gas in a flask is doubled, what happens to the pressure inside the flask? 13. What happens to an aerosol can (which contains compressed gas) when you throw it into a fire? ...
C - Thierry Karsenti
... Solutions are important in that many chemical reactions occur in solutions. In order for a chemical reaction to occur, molecules must come into contact. Solutions allow intimate contact of molecules of different types thereby facilitating chemical reactions. The study of solutions is important as mo ...
... Solutions are important in that many chemical reactions occur in solutions. In order for a chemical reaction to occur, molecules must come into contact. Solutions allow intimate contact of molecules of different types thereby facilitating chemical reactions. The study of solutions is important as mo ...
Physical Chemistry II
... physical equilibrium among the phases of one or more pure substances under different conditions of temperature and pressure. In electrochemistry, we focus on chemical systems that involve the transfer of electrons or charged species i.e. oxidation – reduction reaction s.. Nuclear chemistry looks at ...
... physical equilibrium among the phases of one or more pure substances under different conditions of temperature and pressure. In electrochemistry, we focus on chemical systems that involve the transfer of electrons or charged species i.e. oxidation – reduction reaction s.. Nuclear chemistry looks at ...
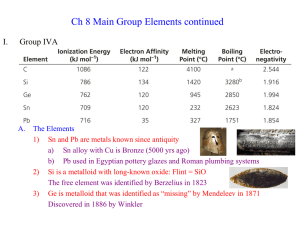
InorgCh8.2
... Nitrogen is a nonmetal diatomic gas making up 78.1% of Earths’ atmosphere a) Isolated from air in 1772 by Rutherford, Cavendish, and Scheele b) Colorless, odorless, nonreactive gas i. :N≡N: structure has strong stable triple bond ii. Used as inert atmosphere for performing chemical reactions iii. N ...
... Nitrogen is a nonmetal diatomic gas making up 78.1% of Earths’ atmosphere a) Isolated from air in 1772 by Rutherford, Cavendish, and Scheele b) Colorless, odorless, nonreactive gas i. :N≡N: structure has strong stable triple bond ii. Used as inert atmosphere for performing chemical reactions iii. N ...
Heat transfer mechanisms of laminar flames of hydrogen+ oxygen
... to an initially relatively cold plate is studied analytically and numerically. For the case of very small distances to the solid surface, the situation can be regarded effectively as one-dimensional. Fig. 1 presents the one-dimensional (1D) computational setup. By fixing the gas composition, tempera ...
... to an initially relatively cold plate is studied analytically and numerically. For the case of very small distances to the solid surface, the situation can be regarded effectively as one-dimensional. Fig. 1 presents the one-dimensional (1D) computational setup. By fixing the gas composition, tempera ...
Grade 11 review answers
... 37) Nitrogen tri-iodide will explode at the slightest contact to produce Nitrogen gas and Iodine gas in the following reaction: 2NI3(s) —> N2(g) + 3I2(g) If 15.5 g of NI3 explodes at a temperature of 25.5 oC and a pressure of 100.3 kPa. a) What volume of gas will be produced? We will ignore part b f ...
... 37) Nitrogen tri-iodide will explode at the slightest contact to produce Nitrogen gas and Iodine gas in the following reaction: 2NI3(s) —> N2(g) + 3I2(g) If 15.5 g of NI3 explodes at a temperature of 25.5 oC and a pressure of 100.3 kPa. a) What volume of gas will be produced? We will ignore part b f ...
Spontaniety Worked Examples
... Plan We expect ΔS to be positive if there is an increase in temperature, increase in volume, or increase in number of gas particles. The question states that the temperature is constant, and so we need to concern ourselves only with volume and number of particles. Solve (a) Evaporation involves a la ...
... Plan We expect ΔS to be positive if there is an increase in temperature, increase in volume, or increase in number of gas particles. The question states that the temperature is constant, and so we need to concern ourselves only with volume and number of particles. Solve (a) Evaporation involves a la ...
Equilib - C.R.C.T.
... between H2O(g) [ideal gas phase] and H2O(L1) [i.e., the ideal boiling point] Equilib 9.2 ...
... between H2O(g) [ideal gas phase] and H2O(L1) [i.e., the ideal boiling point] Equilib 9.2 ...
Physical Chemistry 2.pdf
... The module, Physical Chemistry 2, focuses on five (5) areas of physical chemistry important to many aspects of our lives: solutions, colloids, phase equilibrium, electrochemistry and nuclear chemistry. Solutions are often necessary to facilitate many chemical reactions in life processes or industry ...
... The module, Physical Chemistry 2, focuses on five (5) areas of physical chemistry important to many aspects of our lives: solutions, colloids, phase equilibrium, electrochemistry and nuclear chemistry. Solutions are often necessary to facilitate many chemical reactions in life processes or industry ...
5. Formulae, equations and amounts of substance
... Working out average titre results Only make an average of the concordant titre results lf 2 or 3 values are within 0.10cm3 and therefore concordant or close then we can say results are accurate and reproducible and the titration technique is good/ consistent ...
... Working out average titre results Only make an average of the concordant titre results lf 2 or 3 values are within 0.10cm3 and therefore concordant or close then we can say results are accurate and reproducible and the titration technique is good/ consistent ...
EquiSage
... between H2O(g) [ideal gas phase] and H2O(L1) [i.e., the ideal boiling point] Equilib 9.2 ...
... between H2O(g) [ideal gas phase] and H2O(L1) [i.e., the ideal boiling point] Equilib 9.2 ...
1. Introduction
... The synthesis and deposition of the sensing layer is obviously the most crucial part in the preparation of gas sensors. Three main groups can be distinguished: powder/slurry deposition, chemical vapour deposition (CVD) and physical vapour deposition (PVD) [8,14] (Table 2). The main difference betwee ...
... The synthesis and deposition of the sensing layer is obviously the most crucial part in the preparation of gas sensors. Three main groups can be distinguished: powder/slurry deposition, chemical vapour deposition (CVD) and physical vapour deposition (PVD) [8,14] (Table 2). The main difference betwee ...
CHAPTER 1
... any substance that has a definite composition. For example, consider the material called sucrose, or cane sugar. It has a definite composition in terms of the atoms that compose it. It is produced by certain plants in the chemical process of photosynthesis. Sucrose is a chemical. Carbon dioxide, wat ...
... any substance that has a definite composition. For example, consider the material called sucrose, or cane sugar. It has a definite composition in terms of the atoms that compose it. It is produced by certain plants in the chemical process of photosynthesis. Sucrose is a chemical. Carbon dioxide, wat ...
Gas chromatography

Gas chromatography (GC) is a common type of chromatography used in analytical chemistry for separating and analyzing compounds that can be vaporized without decomposition. Typical uses of GC include testing the purity of a particular substance, or separating the different components of a mixture (the relative amounts of such components can also be determined). In some situations, GC may help in identifying a compound. In preparative chromatography, GC can be used to prepare pure compounds from a mixture.In gas chromatography, the mobile phase (or ""moving phase"") is a carrier gas, usually an inert gas such as helium or an unreactive gas such as nitrogen. The stationary phase is a microscopic layer of liquid or polymer on an inert solid support, inside a piece of glass or metal tubing called a column (a homage to the fractionating column used in distillation). The instrument used to perform gas chromatography is called a gas chromatograph (or ""aerograph"", ""gas separator"").The gaseous compounds being analyzed interact with the walls of the column, which is coated with a stationary phase. This causes each compound to elute at a different time, known as the retention time of the compound. The comparison of retention times is what gives GC its analytical usefulness.Gas chromatography is in principle similar to column chromatography (as well as other forms of chromatography, such as HPLC, TLC), but has several notable differences. First, the process of separating the compounds in a mixture is carried out between a liquid stationary phase and a gas mobile phase, whereas in column chromatography the stationary phase is a solid and the mobile phase is a liquid. (Hence the full name of the procedure is ""Gas–liquid chromatography"", referring to the mobile and stationary phases, respectively.) Second, the column through which the gas phase passes is located in an oven where the temperature of the gas can be controlled, whereas column chromatography (typically) has no such temperature control. Finally, the concentration of a compound in the gas phase is solely a function of the vapor pressure of the gas.Gas chromatography is also similar to fractional distillation, since both processes separate the components of a mixture primarily based on boiling point (or vapor pressure) differences. However, fractional distillation is typically used to separate components of a mixture on a large scale, whereas GC can be used on a much smaller scale (i.e. microscale).Gas chromatography is also sometimes known as vapor-phase chromatography (VPC), or gas–liquid partition chromatography (GLPC). These alternative names, as well as their respective abbreviations, are frequently used in scientific literature. Strictly speaking, GLPC is the most correct terminology, and is thus preferred by many authors.