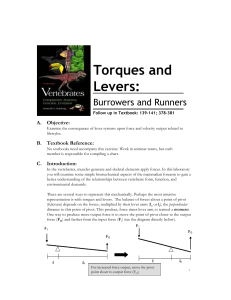
Further Forces
... What do you observe? What does this tell you about the pressure in fluids? The water is forced out a greater distance as you move down the tin can. This is because the pressure is greatest at the bottom - pressure in ...
... What do you observe? What does this tell you about the pressure in fluids? The water is forced out a greater distance as you move down the tin can. This is because the pressure is greatest at the bottom - pressure in ...
μ = μ =
... motorcyclist emerge from the sandy stretch without having to start the engine if the sand lasts for 15 m? If so, what will be the speed upon emerging? Since we do not know if the motorcyclist makes it or not, we will assume that he does not make it and find out how far he travels before stopping. If ...
... motorcyclist emerge from the sandy stretch without having to start the engine if the sand lasts for 15 m? If so, what will be the speed upon emerging? Since we do not know if the motorcyclist makes it or not, we will assume that he does not make it and find out how far he travels before stopping. If ...
Chapter 4 Kinetics of a particle
... Therefore, any path Fc dr is a function of initial and end points only, It is defined as the change of potential energy, P.E. P.E. between two points is equal to the work done by an external force against the field of a conservative force for bringing the particle from the starting point ...
... Therefore, any path Fc dr is a function of initial and end points only, It is defined as the change of potential energy, P.E. P.E. between two points is equal to the work done by an external force against the field of a conservative force for bringing the particle from the starting point ...
Offline HW 3 solutions
... In the initial state, ball 1 is rolling towards the magnet with some initial x-velocity v1i,x just before the collision. We took the final state to be the time of the first video frame after the collision (not the time of the collision itself). In the final state, the recoiling 1-M-2 system has a (n ...
... In the initial state, ball 1 is rolling towards the magnet with some initial x-velocity v1i,x just before the collision. We took the final state to be the time of the first video frame after the collision (not the time of the collision itself). In the final state, the recoiling 1-M-2 system has a (n ...
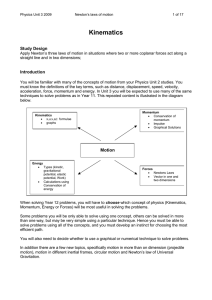
Kinematics - Vicphysics
... an object causes the object to accelerate (change its velocity). The amount of acceleration that occurs depends on the size of the force and the mass of the object. Large forces cause large accelerations. Objects with large mass accelerate less when they experience the same force as a small mass. Th ...
... an object causes the object to accelerate (change its velocity). The amount of acceleration that occurs depends on the size of the force and the mass of the object. Large forces cause large accelerations. Objects with large mass accelerate less when they experience the same force as a small mass. Th ...
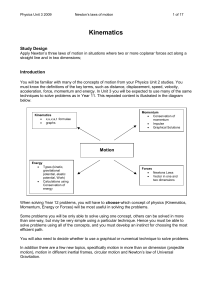
Kinematics - Vicphysics
... an object causes the object to accelerate (change its velocity). The amount of acceleration that occurs depends on the size of the force and the mass of the object. Large forces cause large accelerations. Objects with large mass accelerate less when they experience the same force as a small mass. Th ...
... an object causes the object to accelerate (change its velocity). The amount of acceleration that occurs depends on the size of the force and the mass of the object. Large forces cause large accelerations. Objects with large mass accelerate less when they experience the same force as a small mass. Th ...
ch.14 student notes
... In each example, the object has one position at which the net force on it is zero. At that position, the object is in equilibrium. Whenever the object is pulled away from its equilibrium position, the net force on the system becomes nonzero and pulls the object back toward equilibrium. If the force ...
... In each example, the object has one position at which the net force on it is zero. At that position, the object is in equilibrium. Whenever the object is pulled away from its equilibrium position, the net force on the system becomes nonzero and pulls the object back toward equilibrium. If the force ...
C4_SecondLaw
... Mass & Weight Mass: Quantity of matter in an object Weight: Force of gravity on an object Weight ...
... Mass & Weight Mass: Quantity of matter in an object Weight: Force of gravity on an object Weight ...
Monday, April 6, 2009
... The principle of energy conservation can be used to solve problems that are harder to solve just using Newton’s laws. It is used to describe motion of an object or a system of objects. A new concept of linear momentum can also be used to solve physical problems, especially the problems involving col ...
... The principle of energy conservation can be used to solve problems that are harder to solve just using Newton’s laws. It is used to describe motion of an object or a system of objects. A new concept of linear momentum can also be used to solve physical problems, especially the problems involving col ...
Period 3 Activity Sheet: Motion and Forces
... How does force acting on an object change its velocity? 1) Stack three wooden blocks under one end of a board to form a ramp. Roll a metal cart down the ramp and note the cart’s velocity after it leaves the ramp. 2) Remove one of the blocks supporting the ramp. Roll the cart down this ramp. Is the v ...
... How does force acting on an object change its velocity? 1) Stack three wooden blocks under one end of a board to form a ramp. Roll a metal cart down the ramp and note the cart’s velocity after it leaves the ramp. 2) Remove one of the blocks supporting the ramp. Roll the cart down this ramp. Is the v ...