Lesson 20 questions – moments and torque - science
... The tabletop has a mass of 5.0 kg and its centre of gravity is 0.40m from the axis of the hinge at A. The computer has a weight of 200N acting through a point 0.25 m from the hinge at A. The tabletop is supported to maintain it in a horizontal position by a force F acting vertically at B. The distan ...
... The tabletop has a mass of 5.0 kg and its centre of gravity is 0.40m from the axis of the hinge at A. The computer has a weight of 200N acting through a point 0.25 m from the hinge at A. The tabletop is supported to maintain it in a horizontal position by a force F acting vertically at B. The distan ...
Exam II Difficult Problems
... • A rock is dropped from a high tower and falls freely under the influence of gravity. Which one of the following statements concerning the rock as it falls is true? Neglect the effects of air resistance. Momentum changed by Impulse ...
... • A rock is dropped from a high tower and falls freely under the influence of gravity. Which one of the following statements concerning the rock as it falls is true? Neglect the effects of air resistance. Momentum changed by Impulse ...
Ph211_CH5_worksheet-f06
... Since the masses are attached their accelerations are equal: a1y = a2x = asystem Solving for asystem: m2gsin – m1asystem - m1g = m2asystem asystem = (m2gsin – m1g)/(m1 + m2) = -1.03 m/s2 (i.e. up the incline!) e. What are the tension forces acting on each mass? Express the tension vectors in compo ...
... Since the masses are attached their accelerations are equal: a1y = a2x = asystem Solving for asystem: m2gsin – m1asystem - m1g = m2asystem asystem = (m2gsin – m1g)/(m1 + m2) = -1.03 m/s2 (i.e. up the incline!) e. What are the tension forces acting on each mass? Express the tension vectors in compo ...
Friction
... Does the textbook model work in real life? Your task is to design and carry out experiments to test the four predictions of the model. Experimental Suggestions You may measure the frictional force with either a spring scale or the force probe. Be sure the surface of the track is clean. Finger prints ...
... Does the textbook model work in real life? Your task is to design and carry out experiments to test the four predictions of the model. Experimental Suggestions You may measure the frictional force with either a spring scale or the force probe. Be sure the surface of the track is clean. Finger prints ...
Notes Format - AVC Distance Education
... This is called kinetic friction. The kinetic friction force is directed tangent to the surface, and opposite to the velocity of the object relative to the surface. Kinetic friction tends to slow down the sliding motion of an object in contact with a surface. ...
... This is called kinetic friction. The kinetic friction force is directed tangent to the surface, and opposite to the velocity of the object relative to the surface. Kinetic friction tends to slow down the sliding motion of an object in contact with a surface. ...
Stacey Carpenter
... 2. You can also graph total mass vs. acceleration. You'll get a hyperbola because they are inversely related. That's a good lesson. If mass is the independent variable, 1/acceleration is the dependent variable, and force is a control, you'll get a straight line through the origin. (Don't worry about ...
... 2. You can also graph total mass vs. acceleration. You'll get a hyperbola because they are inversely related. That's a good lesson. If mass is the independent variable, 1/acceleration is the dependent variable, and force is a control, you'll get a straight line through the origin. (Don't worry about ...
biomechanics2008
... Force = mass X acceleration F = ma How could you apply Newton’s 2nd Law to sporting situations? The harder you hit the ball, the faster and possibly further it will travel. For example, swinging a golf club slowly with force gives the golf ball less force hence acceleration than if you swung the gol ...
... Force = mass X acceleration F = ma How could you apply Newton’s 2nd Law to sporting situations? The harder you hit the ball, the faster and possibly further it will travel. For example, swinging a golf club slowly with force gives the golf ball less force hence acceleration than if you swung the gol ...
Answers
... Remember ACCELERATION? The change in velocity over time? FORCES cause objects to speed up (+ acceleration), slow down (- acceleration), or to change direction. If that direction is rotational, it is called centripetal acceleration, as you know. Once a force is applied to anything to make it accelera ...
... Remember ACCELERATION? The change in velocity over time? FORCES cause objects to speed up (+ acceleration), slow down (- acceleration), or to change direction. If that direction is rotational, it is called centripetal acceleration, as you know. Once a force is applied to anything to make it accelera ...
2.1 Work in Mechanical Systems
... 9. A man who weighs 180 pounds is lifted 200 feet by an elevator. How much work does the elevator do on the man? How much work does the gravitational force do on the man? 10. An automotive technician applies a torque of 120 lb • ft to tighten a cylinder head bolt. The bolt turns 1/8 of a revolution. ...
... 9. A man who weighs 180 pounds is lifted 200 feet by an elevator. How much work does the elevator do on the man? How much work does the gravitational force do on the man? 10. An automotive technician applies a torque of 120 lb • ft to tighten a cylinder head bolt. The bolt turns 1/8 of a revolution. ...
A1 Physics Unit 5: Newton`s Laws Conceptual Physics Newton`s
... c. is the force to overcome when an object is moving at a constant velocity. d. all of the above 19. According to Newton’s ____ Law, an object with no net force acting on it can move with a constant velocity. 20. Newton’s _____ law states that the larger the force the larger the acceleration and the ...
... c. is the force to overcome when an object is moving at a constant velocity. d. all of the above 19. According to Newton’s ____ Law, an object with no net force acting on it can move with a constant velocity. 20. Newton’s _____ law states that the larger the force the larger the acceleration and the ...
RP 1P1 Force and Motion - NC Science Wiki
... Motion is as much a part of the physical world as matter and energy are. Everything moves—atoms and molecules; the stars, planets, and moons; the earth and its surface and everything on its surface; all living things, and every part of living things. Nothing in the universe is at rest. Since everyth ...
... Motion is as much a part of the physical world as matter and energy are. Everything moves—atoms and molecules; the stars, planets, and moons; the earth and its surface and everything on its surface; all living things, and every part of living things. Nothing in the universe is at rest. Since everyth ...
PS 5.7 - S2TEM Centers SC
... If a net force (braking force) is exerted on the car in a direction opposite to the motion, the car will slow down or stop. If the people in the car are not wearing their set belts, because of their inertia, they keep going forward until something exerts an opposite force on them. The people will co ...
... If a net force (braking force) is exerted on the car in a direction opposite to the motion, the car will slow down or stop. If the people in the car are not wearing their set belts, because of their inertia, they keep going forward until something exerts an opposite force on them. The people will co ...
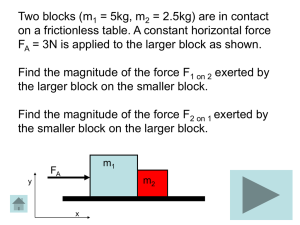
Tutorial_blocks
... “If body A exerts a force on body B (action), then body B exerts a force on body A (reaction) that is equal in magnitude and opposite in direction.” ...
... “If body A exerts a force on body B (action), then body B exerts a force on body A (reaction) that is equal in magnitude and opposite in direction.” ...
How Do Objects Move?
... Moon is in constant, or steady, motion as it revolves around Earth. As you walk through your day, you have variable motion. You speed up, slow down, and change direction. When you are on a swing you have periodic motion, because you go back and forth at a steady rate. The strings on a guitar move wi ...
... Moon is in constant, or steady, motion as it revolves around Earth. As you walk through your day, you have variable motion. You speed up, slow down, and change direction. When you are on a swing you have periodic motion, because you go back and forth at a steady rate. The strings on a guitar move wi ...
Newton`s Laws
... 2. The amount of inertia possessed by an object is dependent solely upon its __________. 3. Two bricks are resting on edge of the lab table. Shirley Sheshort stands on her toes and spots the two bricks. She acquires an intense desire to know which of the two bricks are most massive. Since Shirley is ...
... 2. The amount of inertia possessed by an object is dependent solely upon its __________. 3. Two bricks are resting on edge of the lab table. Shirley Sheshort stands on her toes and spots the two bricks. She acquires an intense desire to know which of the two bricks are most massive. Since Shirley is ...
Newton`s Second Law
... 2. The acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net force acting on it and is inversely proportional to its mass. The direction of the acceleration is in the direction of the applied net force. 3. When one object exerts a force on a second object, the second object exerts an equal a ...
... 2. The acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net force acting on it and is inversely proportional to its mass. The direction of the acceleration is in the direction of the applied net force. 3. When one object exerts a force on a second object, the second object exerts an equal a ...