Friction and Gravity - elementaryscienceteachers
... • Identify separately the two or more forces that are acting on a single static object, including gravity, elastic forces due to tension or compression in matter, and friction. ...
... • Identify separately the two or more forces that are acting on a single static object, including gravity, elastic forces due to tension or compression in matter, and friction. ...
Problem Solving Tip Sheet
... 1) Does the problem state definitively if the surface of the object is moving in relation to the other surface? If it is moving in relation to the other surface, then use kinetic friction (3). If it is not necessarily moving, then use static friction (2). Note that the surface of an object that is r ...
... 1) Does the problem state definitively if the surface of the object is moving in relation to the other surface? If it is moving in relation to the other surface, then use kinetic friction (3). If it is not necessarily moving, then use static friction (2). Note that the surface of an object that is r ...
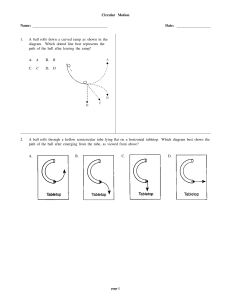
Gravity and Motion
... object, there must be an unbalanced force working on any object in a circular motion. • The unbalanced force that causes objects to move in a circular path is called centripetal force. ...
... object, there must be an unbalanced force working on any object in a circular motion. • The unbalanced force that causes objects to move in a circular path is called centripetal force. ...
Work - HRSBSTAFF Home Page
... 1. What is the impulse given to a golf ball of mass 45.9g if it starts at rest and attains a final velocity of 35m/s? 2. If the golf ball in problem 1 was in contact with the golf club for 0.027s, what force acted on the golf ball? 3. If there is no acceleration is there momentum? Is there impulse? ...
... 1. What is the impulse given to a golf ball of mass 45.9g if it starts at rest and attains a final velocity of 35m/s? 2. If the golf ball in problem 1 was in contact with the golf club for 0.027s, what force acted on the golf ball? 3. If there is no acceleration is there momentum? Is there impulse? ...
4. acceleration and terminal velocity
... Forces and acceleration calculations • You should know the equation that shows the relationship between resultant force, mass and acceleration, and be able to use it. The equation Resultant force (newton, N) = mass (kg) × acceleration (m/s2). • You can see from this equation that 1 N is the force ...
... Forces and acceleration calculations • You should know the equation that shows the relationship between resultant force, mass and acceleration, and be able to use it. The equation Resultant force (newton, N) = mass (kg) × acceleration (m/s2). • You can see from this equation that 1 N is the force ...
Slide 1
... • Gravity causes objects to accelerate downward, whereas air resistance acts in the direction opposite to the motion and reduces acceleration. ...
... • Gravity causes objects to accelerate downward, whereas air resistance acts in the direction opposite to the motion and reduces acceleration. ...
Forces and Motion - Catawba County Schools
... object moving at a constant speed. * Galileo – concluded that moving objects not subjected to friction or any other force would continue to move indefinitely. * Newton – Defined mass and force and laid out his laws of motion. Newton’s First Law of Motion The state of motion of an object does not cha ...
... object moving at a constant speed. * Galileo – concluded that moving objects not subjected to friction or any other force would continue to move indefinitely. * Newton – Defined mass and force and laid out his laws of motion. Newton’s First Law of Motion The state of motion of an object does not cha ...
Basic Physics Semester 1 Final Review Thing Name: Basic Physics
... 1. The momentum of an object is defined as A) the object’s mass times it acceleration B) the object’s mass times its velocity C) the object’s force times its acceleration D) the object’s force times the time interval 2. Which has more momentum, Billy Bob in a large truck moving at 30 miles per hour ...
... 1. The momentum of an object is defined as A) the object’s mass times it acceleration B) the object’s mass times its velocity C) the object’s force times its acceleration D) the object’s force times the time interval 2. Which has more momentum, Billy Bob in a large truck moving at 30 miles per hour ...
An intro to forces
... the mass, the more gravitational force is present. LAW OF UNIVERSAL GRAVITATION: Every object in the universe attracts every other object in the universe with a force that is directly related to the product of their mass and opposite to the square of the distance between them. An object’s mass stays ...
... the mass, the more gravitational force is present. LAW OF UNIVERSAL GRAVITATION: Every object in the universe attracts every other object in the universe with a force that is directly related to the product of their mass and opposite to the square of the distance between them. An object’s mass stays ...
Forces and Newton`s Laws of Motion
... than is necessary for students to know on the proficiency test, but is not as detailed as what would be discussed in a physics class. I made no effort to make this super-fancy because I just don’t know how. Sorry!! There are links to the RPDP site at the end of this presentation. There are also a fe ...
... than is necessary for students to know on the proficiency test, but is not as detailed as what would be discussed in a physics class. I made no effort to make this super-fancy because I just don’t know how. Sorry!! There are links to the RPDP site at the end of this presentation. There are also a fe ...