1 - HCC Learning Web
... block between A and B is 1.6 N and points A and B are 0.5 m apart. If the kinetic energies of the block at A and B are 4.0 J and 5.6 J, respectively, how much work is done on the block by the force P between A and B? ...
... block between A and B is 1.6 N and points A and B are 0.5 m apart. If the kinetic energies of the block at A and B are 4.0 J and 5.6 J, respectively, how much work is done on the block by the force P between A and B? ...
PH1H_PNT_IsaacNewtonMe_V01x
... To insure safety have students sit on the skateboards or scooter cars or if they are using roller skates or blades have another student jog along beside them as a catcher to reduce the possibility of falls. If you do not have large spring scales you may use a parallel combination of smaller scales o ...
... To insure safety have students sit on the skateboards or scooter cars or if they are using roller skates or blades have another student jog along beside them as a catcher to reduce the possibility of falls. If you do not have large spring scales you may use a parallel combination of smaller scales o ...
Net Force Problems
... • The forces exerted by two objects on each other are often called and action-reaction force pair. • Either force can be considered the action force or the reaction force. • Action and reaction force pairs don’t cancel because they act on different objects. ...
... • The forces exerted by two objects on each other are often called and action-reaction force pair. • Either force can be considered the action force or the reaction force. • Action and reaction force pairs don’t cancel because they act on different objects. ...
Force I PPT
... 8. A force is applied to the right to drag a sled across loosely packed snow with a rightward acceleration. Neglect air resistance. Diagram the forces acting upon the sled ...
... 8. A force is applied to the right to drag a sled across loosely packed snow with a rightward acceleration. Neglect air resistance. Diagram the forces acting upon the sled ...
TT work and machines notes with answers 12
... example: raising a flag on a flagpole, weight machine, sailboat ...
... example: raising a flag on a flagpole, weight machine, sailboat ...
N - Youngstown State University
... The SI unit of force is the Newton (N). 1N = 1 kg-m/s2. In the US, force is measured in pounds. 1.00 lb = 4.448 N and 1.00 N = 0.2248 lb. Robert Hooke (1635 – 1703) found that when a spring is pulled by a force F, it extends proportionally by an amount x. • Hooke’s law: F = -kx • k = spring constant ...
... The SI unit of force is the Newton (N). 1N = 1 kg-m/s2. In the US, force is measured in pounds. 1.00 lb = 4.448 N and 1.00 N = 0.2248 lb. Robert Hooke (1635 – 1703) found that when a spring is pulled by a force F, it extends proportionally by an amount x. • Hooke’s law: F = -kx • k = spring constant ...
Measuring Motion
... that causes a resting object to move, or it can accelerate a moving object by changing its speed or direction. O Unit = Newton (N) O 1 kg m/s2 O Combination of all forces acting on an object is called the net force. ...
... that causes a resting object to move, or it can accelerate a moving object by changing its speed or direction. O Unit = Newton (N) O 1 kg m/s2 O Combination of all forces acting on an object is called the net force. ...
Circular Motion and Gravity
... and tangential acceleration, consider a car traveling in a circular track. – Because the car is moving in a circle, the car has a centripetal component of acceleration. – If the car’s speed changes, the car also has a tangential component of acceleration. ...
... and tangential acceleration, consider a car traveling in a circular track. – Because the car is moving in a circle, the car has a centripetal component of acceleration. – If the car’s speed changes, the car also has a tangential component of acceleration. ...
August 29, 2007
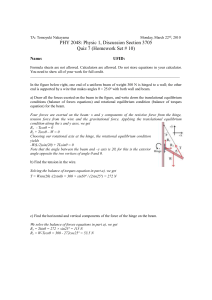
... You need to show all of your work for full credit. ________________________________________________________________________________ In the figure below right, one end of a uniform beam of weight 300 N is hinged to a wall; the other end is supported by a wire that makes angles θ = 25.0º with both wal ...
... You need to show all of your work for full credit. ________________________________________________________________________________ In the figure below right, one end of a uniform beam of weight 300 N is hinged to a wall; the other end is supported by a wire that makes angles θ = 25.0º with both wal ...
Centripetal Force Lab
... 1. Measure the mass of a couple of washers on a balance. Record the WEIGHT in the data table...THIS IS YOUR CENTRIPETAL FORCE. ALSO measure the stopper's mass and record. MASS OF STOPPER_______________ 2. Practice swinging the stopper around so that the clip is directly under the tube without touchi ...
... 1. Measure the mass of a couple of washers on a balance. Record the WEIGHT in the data table...THIS IS YOUR CENTRIPETAL FORCE. ALSO measure the stopper's mass and record. MASS OF STOPPER_______________ 2. Practice swinging the stopper around so that the clip is directly under the tube without touchi ...
Part 2
... Suppose that you glue a pea to the edge of the record and spin the record at this frequency. Find the pea’s (a) angular speed , (b) tangential speed, and (c) centripetal acceleration . Now suppose that you glue another pea closer to the center of the record and spin the record. (a) Is the angular sp ...
... Suppose that you glue a pea to the edge of the record and spin the record at this frequency. Find the pea’s (a) angular speed , (b) tangential speed, and (c) centripetal acceleration . Now suppose that you glue another pea closer to the center of the record and spin the record. (a) Is the angular sp ...
Student Word - Nuffield Foundation
... her suitcase in her hand. The mass of the hotel guest is 70 kg and the mass of the suitcase is 20 kg. The lift accelerates at 0.5 m s–2 as it sets off from the ground floor, and decelerates at 0.4 m s–2 as it nears the 4th floor. a Draw force diagrams showing the forces acting on: i the suitcase ii ...
... her suitcase in her hand. The mass of the hotel guest is 70 kg and the mass of the suitcase is 20 kg. The lift accelerates at 0.5 m s–2 as it sets off from the ground floor, and decelerates at 0.4 m s–2 as it nears the 4th floor. a Draw force diagrams showing the forces acting on: i the suitcase ii ...
NewtonS-LawS
... • According to the first law, can an object begins to move all by itself? • No! A force is needed to start it moving. • If an object is moving in a straight line, will it continue to move in a straight line at a constant velocity? • Yes! Unless a force acts to slow it down, speed it up, or changes i ...
... • According to the first law, can an object begins to move all by itself? • No! A force is needed to start it moving. • If an object is moving in a straight line, will it continue to move in a straight line at a constant velocity? • Yes! Unless a force acts to slow it down, speed it up, or changes i ...
Review - prettygoodphysics
... An object acted on by three forces moves with constant velocity. One force acting on the object is in the positive x direction and has a magnitude of 6.5 N; a second force has a magnitude of 4.4 N and points in the negative y direction. Find the direction and magnitude of the third force acting on t ...
... An object acted on by three forces moves with constant velocity. One force acting on the object is in the positive x direction and has a magnitude of 6.5 N; a second force has a magnitude of 4.4 N and points in the negative y direction. Find the direction and magnitude of the third force acting on t ...
Concepts and Skills
... Newton's Second Law is often described by the equation F = m a. His second law says that “when an unbalanced force acts on an object, the object will experience acceleration proportional to the size of the unbalanced force”. The direction of the acceleration will be the same as the direction of the ...
... Newton's Second Law is often described by the equation F = m a. His second law says that “when an unbalanced force acts on an object, the object will experience acceleration proportional to the size of the unbalanced force”. The direction of the acceleration will be the same as the direction of the ...
6. falling objects
... big enough to _______ the skydiver’s weight. At this point the forces are balanced so his speed becomes ________ - this is called TERMINAL VELOCITY ...
... big enough to _______ the skydiver’s weight. At this point the forces are balanced so his speed becomes ________ - this is called TERMINAL VELOCITY ...