File
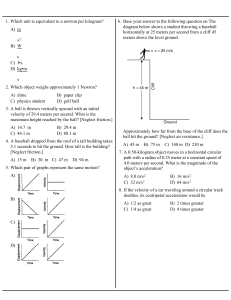
... 1. ___ Inertia a. rate of change of the velocity of an object 2. ___ Force b. the total distance an object travels divided by the total time of travel 3. ___ Net force c. physical movement or a change in position relative to a starting point st 4. ___ Newton’s 1 Law d. the measure of how far an obje ...
... 1. ___ Inertia a. rate of change of the velocity of an object 2. ___ Force b. the total distance an object travels divided by the total time of travel 3. ___ Net force c. physical movement or a change in position relative to a starting point st 4. ___ Newton’s 1 Law d. the measure of how far an obje ...
19. H Forces at Angles Questions
... of the horizontal then, calculate or find: a) Total horizontal force exerted on the ship. b) Initial acceleration of the ship. c) The total force of friction acting on the ship if it then moves with a constant velocity. (M+D’s !!!!) ...
... of the horizontal then, calculate or find: a) Total horizontal force exerted on the ship. b) Initial acceleration of the ship. c) The total force of friction acting on the ship if it then moves with a constant velocity. (M+D’s !!!!) ...
You Can Not FORCE Me to Do It!
... • Gravity is the force that pulls all objects in the universe towards each other’s center. • Earth’s gravity constantly pulls all things on earth towards earth’s center. – This is why when you drop something, it always falls down and does not float up. ...
... • Gravity is the force that pulls all objects in the universe towards each other’s center. • Earth’s gravity constantly pulls all things on earth towards earth’s center. – This is why when you drop something, it always falls down and does not float up. ...
Newton`s Laws of Motion
... Once airborne, unless acted on by an unbalanced force (gravity and air – fluid friction), it would never stop! ...
... Once airborne, unless acted on by an unbalanced force (gravity and air – fluid friction), it would never stop! ...
Newton`s First Law
... • Each object experiences the same amount of air resistance, yet the elephant experiences the greatest force of gravity. • Each object experiences the same amount of air resistance, yet the feather experiences the greatest force of gravity. • The feather weighs more than the elephant, and therefore ...
... • Each object experiences the same amount of air resistance, yet the elephant experiences the greatest force of gravity. • Each object experiences the same amount of air resistance, yet the feather experiences the greatest force of gravity. • The feather weighs more than the elephant, and therefore ...
Force - FHS gators love Science
... If the Earth causes the moon to stay in a circular orbit, what force does the moon apply on the earth? Gravitational pull from moon causes two bulges in earth’s ...
... If the Earth causes the moon to stay in a circular orbit, what force does the moon apply on the earth? Gravitational pull from moon causes two bulges in earth’s ...
Chapter 4 Forces and Newton’s Laws of Motion continued
... Warning: Newton’s 1st law can appear to be violated if you don’t recognize the existence of contact forces. Newton’s 1st law: for an object to remain at rest, or move with constant speed & direction, the Net Force acting on it must be ZERO. ...
... Warning: Newton’s 1st law can appear to be violated if you don’t recognize the existence of contact forces. Newton’s 1st law: for an object to remain at rest, or move with constant speed & direction, the Net Force acting on it must be ZERO. ...
Lecture 11
... Need to know all of chapter 3 and up to and including sect 4.5 (Newton’s 3rd law): average velocity, average acceleration, displacement, the four equations of kinematics, relative motion, Newton’s laws of motion. ...
... Need to know all of chapter 3 and up to and including sect 4.5 (Newton’s 3rd law): average velocity, average acceleration, displacement, the four equations of kinematics, relative motion, Newton’s laws of motion. ...
Circular Motion and the Law of Gravity
... Rotational motion – the motion of an object that is spinning 1. The object spins about an axis. 2. The axis of rotation is the line about which the rotation occurs. 3. Circular motion is defined as a point on an object that moves (rotates) around an axis. Since the direction of the motion is constan ...
... Rotational motion – the motion of an object that is spinning 1. The object spins about an axis. 2. The axis of rotation is the line about which the rotation occurs. 3. Circular motion is defined as a point on an object that moves (rotates) around an axis. Since the direction of the motion is constan ...