6-04a,04b -Momentum and Impulse Wkst-Key
... Use the impulse-momentum equation to answer questions 6-9: 6. Why is it important to “ follow through”when trying to hit a home run? Following through maximizes the length of time the bat is in contact with the ball. This maximizes the impulse, allowing the greatest change in momentum and the greate ...
... Use the impulse-momentum equation to answer questions 6-9: 6. Why is it important to “ follow through”when trying to hit a home run? Following through maximizes the length of time the bat is in contact with the ball. This maximizes the impulse, allowing the greatest change in momentum and the greate ...
Centripetal Force Lab
... 1. Get the Centripetal Force Apparatus from your teacher. 2. Ensure that there is a piece of tape in the shape of a flag on the string below the glass tube. 3. Pull the rubber stopper until the tape flag hits the glass tube, but does not get stuck inside. 4. Measure the length of the string from the ...
... 1. Get the Centripetal Force Apparatus from your teacher. 2. Ensure that there is a piece of tape in the shape of a flag on the string below the glass tube. 3. Pull the rubber stopper until the tape flag hits the glass tube, but does not get stuck inside. 4. Measure the length of the string from the ...
Lect-10
... associated with the centripetal acceleration The force is also directed toward the center of the circle Applying Newton’s Second Law along the radial direction gives v2 F mac m r ...
... associated with the centripetal acceleration The force is also directed toward the center of the circle Applying Newton’s Second Law along the radial direction gives v2 F mac m r ...
Newton`s Second Law of Motion
... Two forces act on a book resting on a table: its weight and the support force from the table. Does a force of friction act as well? No, not unless the book tends to slide. Friction only acts when there is motion ...
... Two forces act on a book resting on a table: its weight and the support force from the table. Does a force of friction act as well? No, not unless the book tends to slide. Friction only acts when there is motion ...
Slide 1
... A Review of Forces What is a force? What are the 2 categories of forces? What are 7 kinds of forces we have learned so far? ...
... A Review of Forces What is a force? What are the 2 categories of forces? What are 7 kinds of forces we have learned so far? ...
Chapter 4 forces - student practice notes
... What are Newton’s 2nd and 3rd Laws of Motion? How are mass and acceleration related in the formula F = ma? How do the 2nd and 3rd laws relate to each other to explain the motion of shooting a three point basket? ...
... What are Newton’s 2nd and 3rd Laws of Motion? How are mass and acceleration related in the formula F = ma? How do the 2nd and 3rd laws relate to each other to explain the motion of shooting a three point basket? ...
Chapter 10 Simple Harmonic Motion and Elasticity continued
... A 0.20-kg ball is attached to a vertical spring. The spring constant is 28 N/m. When released from rest, how far does the ball fall before being brought to a momentary stop by the spring? ...
... A 0.20-kg ball is attached to a vertical spring. The spring constant is 28 N/m. When released from rest, how far does the ball fall before being brought to a momentary stop by the spring? ...
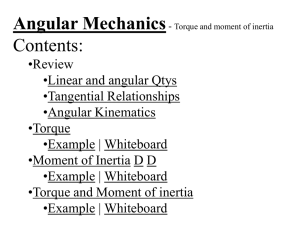
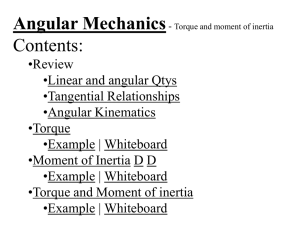
2AngDyn - TuHS Physics
... Angular Mechanics - Angular Quantities Linear: Angular: (m) s - Angle (Radians) (m/s) u o - Initial angular velocity (Rad/s) (m/s) v - Final angular velocity (Rad/s) (m/s/s) a - Angular acceleration (Rad/s/s) (s) t t ...
... Angular Mechanics - Angular Quantities Linear: Angular: (m) s - Angle (Radians) (m/s) u o - Initial angular velocity (Rad/s) (m/s) v - Final angular velocity (Rad/s) (m/s/s) a - Angular acceleration (Rad/s/s) (s) t t ...
Secondary Robot
... Motion states that the acceleration of an object is produced by a net force in the same direction as the acceleration, is directly proportional to the magnitude of the net force, and inversely proportional to the mass of the object. This means that the acceleration (a) of an object is dependant on a ...
... Motion states that the acceleration of an object is produced by a net force in the same direction as the acceleration, is directly proportional to the magnitude of the net force, and inversely proportional to the mass of the object. This means that the acceleration (a) of an object is dependant on a ...