Unit 8 Momentum 6 lessons - science-b
... The 1st car has a mass of 1875 Kg and an initial velocity of 23.00 m/s @ 0.00º The 2nd car has a mass of 1025 Kg and an initial velocity of 17.00 m/s @ 0.00º After the collision: What is the velocity of the two cars if they both move off @ 0.00º ? #2 Two cars collide…and they stick together. The 1st ...
... The 1st car has a mass of 1875 Kg and an initial velocity of 23.00 m/s @ 0.00º The 2nd car has a mass of 1025 Kg and an initial velocity of 17.00 m/s @ 0.00º After the collision: What is the velocity of the two cars if they both move off @ 0.00º ? #2 Two cars collide…and they stick together. The 1st ...
Physics 207: Lecture 2 Notes
... Example: Rotating Rod A uniform rod of length L=0.5 m and mass m=1 kg is free to rotate ...
... Example: Rotating Rod A uniform rod of length L=0.5 m and mass m=1 kg is free to rotate ...
Spring Forces and Simple Harmonic Motion
... If the only force doing work on an object is the spring force (conservative), its mechanical energy is conserved. If frictional forces also do work, the object’s mechanical energy decreases, and the SHM is called damped. If the frictional force is just large enough to prevent oscillation as the obje ...
... If the only force doing work on an object is the spring force (conservative), its mechanical energy is conserved. If frictional forces also do work, the object’s mechanical energy decreases, and the SHM is called damped. If the frictional force is just large enough to prevent oscillation as the obje ...
Physics 50 Sample Midterm Exam #1
... the magnitude of the velocity of the projectile at time t = 15.0 s (in mid-flight). Remember that for projectile motion, the x and y motions are independent, with y acceleration given by gravity and x acceleration zero. First let's figure out the vertical velocity of the projectile at t = 15.0 s. Fi ...
... the magnitude of the velocity of the projectile at time t = 15.0 s (in mid-flight). Remember that for projectile motion, the x and y motions are independent, with y acceleration given by gravity and x acceleration zero. First let's figure out the vertical velocity of the projectile at t = 15.0 s. Fi ...
212 Lecture 12
... Springs often provide a linear force (-k x) towards its equilibrium position (Chapter 10) Collisions often involve a varying force F(t): 0 maximum 0 We can plot force vs time for a typical collision. The impulse, Δρ, of the force is a vector defined as the integral of the force during the ti ...
... Springs often provide a linear force (-k x) towards its equilibrium position (Chapter 10) Collisions often involve a varying force F(t): 0 maximum 0 We can plot force vs time for a typical collision. The impulse, Δρ, of the force is a vector defined as the integral of the force during the ti ...
Dynamics of Uniform Circular Motion
... In this case, the centripetal force is not merely the tension force in the string. Since centripetal force is always the net force acting on an object following a circular path, the centripetal force in this case is a combination of the tension force in the string and the weight of the ball. Notice ...
... In this case, the centripetal force is not merely the tension force in the string. Since centripetal force is always the net force acting on an object following a circular path, the centripetal force in this case is a combination of the tension force in the string and the weight of the ball. Notice ...
Energy - Spring
... of the spring measured from the equilibrium position. The mass and spring system also has gravitational potential energy (PEgravitational = mgy), but we do not have to include the gravitational potential energy term if we measure the spring length from the hanging equilibrium position. We can then c ...
... of the spring measured from the equilibrium position. The mass and spring system also has gravitational potential energy (PEgravitational = mgy), but we do not have to include the gravitational potential energy term if we measure the spring length from the hanging equilibrium position. We can then c ...
Multiple-Choice Questions
... ___ 17. The scientist who hypothesized that the acceleration produced by gravity is the same for all objects is a. Galileo b. Newton c. Copernicus d. Archimedes ___ 18. In a "coin and feather" jar, the feather falls at a slower rate than the coin because of a. inertia b. buoyant force c. momentum d. ...
... ___ 17. The scientist who hypothesized that the acceleration produced by gravity is the same for all objects is a. Galileo b. Newton c. Copernicus d. Archimedes ___ 18. In a "coin and feather" jar, the feather falls at a slower rate than the coin because of a. inertia b. buoyant force c. momentum d. ...
Jeopardy
... What is the net force on a 10 kg box if it is being dragged to the left with a force of 30 N and there is a 12 N frictional force? ...
... What is the net force on a 10 kg box if it is being dragged to the left with a force of 30 N and there is a 12 N frictional force? ...
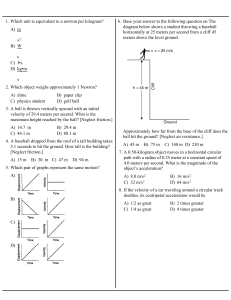
2009 Final Exam
... An aircraft can fly at 355 km/h with respect to the air. The wind is blowing towards the west at 95.0 km/h with respect to the ground. The pilot wants to land at an airport that is directly north of his present location. Calculate the direction in which the plane should head and its speed with respe ...
... An aircraft can fly at 355 km/h with respect to the air. The wind is blowing towards the west at 95.0 km/h with respect to the ground. The pilot wants to land at an airport that is directly north of his present location. Calculate the direction in which the plane should head and its speed with respe ...
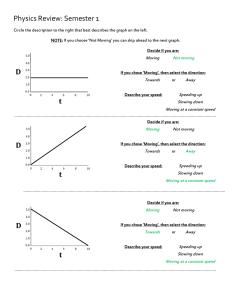
Acceleration
... 4.Marisa’s car accelerates at an average rate of 2.6 m/s2. Calculate how long it takes her car to accelerate from 24.6 m/s to 26.8 m/s. Use this formula: time = (final v – initial v)/ acceleration. ...
... 4.Marisa’s car accelerates at an average rate of 2.6 m/s2. Calculate how long it takes her car to accelerate from 24.6 m/s to 26.8 m/s. Use this formula: time = (final v – initial v)/ acceleration. ...