Chapter 6: Forces
... The acceleration of an object as produced by a net force is directly proportional to the magnitude of the net force, in the same direction as the net force, and inversely proportional to the mass of the object. ...
... The acceleration of an object as produced by a net force is directly proportional to the magnitude of the net force, in the same direction as the net force, and inversely proportional to the mass of the object. ...
Exam 2
... down the rope faster and faster, she becomes frightened and grabs harder on the rope, increasing the tension in the rope. As soon as the upward tension in the rope becomes equal to Sue’s weight, (a) (b) (c) (d) ...
... down the rope faster and faster, she becomes frightened and grabs harder on the rope, increasing the tension in the rope. As soon as the upward tension in the rope becomes equal to Sue’s weight, (a) (b) (c) (d) ...
Energy is the ability to do work
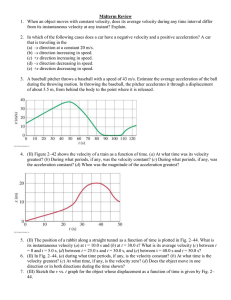
... (a) How fast must a 3000-kg elephant move to have the same kinetic energy as a 65.0-kg sprinter running at 10.0 m/s? (b) Discuss how the larger energies needed for the movement of larger animals would relate to metabolic rates. ...
... (a) How fast must a 3000-kg elephant move to have the same kinetic energy as a 65.0-kg sprinter running at 10.0 m/s? (b) Discuss how the larger energies needed for the movement of larger animals would relate to metabolic rates. ...
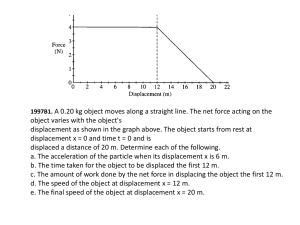
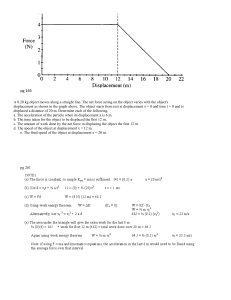
1997B1. A 0.20 kg object moves along a straight line.
... 1975B7. A pendulum consists of a small object of mass m fastened to the end of an inextensible cord of length L. Initially, the pendulum is drawn aside through an angle of 60° with the vertical and held by a horizontal string as shown in the diagram above. This string is burned so that the pendulu ...
... 1975B7. A pendulum consists of a small object of mass m fastened to the end of an inextensible cord of length L. Initially, the pendulum is drawn aside through an angle of 60° with the vertical and held by a horizontal string as shown in the diagram above. This string is burned so that the pendulu ...
Forces
... When an object moves through any fluid, such as air or water, the fluid exerts a drag force on the moving object in the direction opposite to its motion. As the speed of the object increases, so does the magnitude of the drag force. The size and shape of the object also affects the drag force, ...
... When an object moves through any fluid, such as air or water, the fluid exerts a drag force on the moving object in the direction opposite to its motion. As the speed of the object increases, so does the magnitude of the drag force. The size and shape of the object also affects the drag force, ...
17 Energy in SHM - Blue Valley Schools
... 1. Mount the 200-g mass and spring as shown in Figure 1. Connect the Motion Detector to DIG/SONIC 2 of the LabQuest Mini. Position the Motion Detector directly below the hanging mass, taking care that no extraneous objects could send echoes back to the detector. Protect the Motion Detector by placin ...
... 1. Mount the 200-g mass and spring as shown in Figure 1. Connect the Motion Detector to DIG/SONIC 2 of the LabQuest Mini. Position the Motion Detector directly below the hanging mass, taking care that no extraneous objects could send echoes back to the detector. Protect the Motion Detector by placin ...
Chapter 12 Forces and Motion
... Velocity is speed with direction. 6. How is acceleration related to velocity? Acceleration is change in velocity, that is, any change in speed, direction, or both. 7. A backpack falls out of an open window. The backpack starts from rest and hits the ground 1.0 second later with a velocity of 9.8 m/s ...
... Velocity is speed with direction. 6. How is acceleration related to velocity? Acceleration is change in velocity, that is, any change in speed, direction, or both. 7. A backpack falls out of an open window. The backpack starts from rest and hits the ground 1.0 second later with a velocity of 9.8 m/s ...
act04
... the string, and friction of the cart on the track. Check to see if any of these forces are related by Newton’s Third Law (Third Law pairs). Newton’s Third Law pairs are forces between the same two objects, but which object is exerting the force and which is being acted on are exchanged. (For the pur ...
... the string, and friction of the cart on the track. Check to see if any of these forces are related by Newton’s Third Law (Third Law pairs). Newton’s Third Law pairs are forces between the same two objects, but which object is exerting the force and which is being acted on are exchanged. (For the pur ...
Document
... Isaac Newton, an Englishman who lived later in the 17th century, began his theories of motion by looking at a concept that he called “Inertia”. It can be thought of as ‘object laziness’. Objects tend to keep doing what they are doing. It takes force to make an object start moving or change direction ...
... Isaac Newton, an Englishman who lived later in the 17th century, began his theories of motion by looking at a concept that he called “Inertia”. It can be thought of as ‘object laziness’. Objects tend to keep doing what they are doing. It takes force to make an object start moving or change direction ...