force - Cloudfront.net
... water, etc.) the fluid exerts a __________on the moving object in the direction _______ to its motion. The drag force is dependent on the ______ of the object, the ________ of the object, and the _______ of the fluid that the object is moving ...
... water, etc.) the fluid exerts a __________on the moving object in the direction _______ to its motion. The drag force is dependent on the ______ of the object, the ________ of the object, and the _______ of the fluid that the object is moving ...
Newton`s Law of Motion
... • Newton’s third law of motion states that when one object exerts a force on a second object, the second one exerts a force on the first that is equal in strength and opposite in direction. • These forces are sometimes called the action and ...
... • Newton’s third law of motion states that when one object exerts a force on a second object, the second one exerts a force on the first that is equal in strength and opposite in direction. • These forces are sometimes called the action and ...
Physics 7B - AB Lecture 3 April 24 Vectors
... Models in 7B are based on Galilean SpaceTime model. Good news is, The predictions of special relativity agree well with Galilean SpaceTime model in their common realm of applicability, specifically in experiments in which all velocities are small compared to the speed of light. z ...
... Models in 7B are based on Galilean SpaceTime model. Good news is, The predictions of special relativity agree well with Galilean SpaceTime model in their common realm of applicability, specifically in experiments in which all velocities are small compared to the speed of light. z ...
Force - Edublogs
... something MUST be pushing on it. Things don’t move all by themselves! Aristotle ...
... something MUST be pushing on it. Things don’t move all by themselves! Aristotle ...
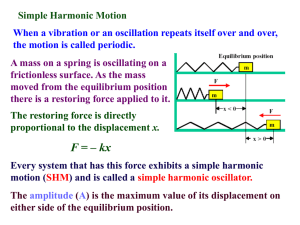
12.1 Forces
... The path of a projectile is always a curve Air resistance and gravity are the only forces acting on a projectile The combination of an initial forward velocity and the downward force of gravity causes the ball to follow a curved path ...
... The path of a projectile is always a curve Air resistance and gravity are the only forces acting on a projectile The combination of an initial forward velocity and the downward force of gravity causes the ball to follow a curved path ...
Forces 12.1 Pg 356-362 - Physical Science 2014-2015
... The path of a projectile is always a curve Air resistance and gravity are the only forces acting on a projectile The combination of an initial forward velocity and the downward force of gravity causes the ball to follow a curved path ...
... The path of a projectile is always a curve Air resistance and gravity are the only forces acting on a projectile The combination of an initial forward velocity and the downward force of gravity causes the ball to follow a curved path ...
6-2 Circular Motion
... every banked curve, there is one speed where the entire centripetal force is supplied by the horizontal component of the normal force, and no friction is required. This occurs when: ...
... every banked curve, there is one speed where the entire centripetal force is supplied by the horizontal component of the normal force, and no friction is required. This occurs when: ...
Chapter 4 Forces and Newton’s Laws of Motion Conclusion
... • A mass accelerated to a non-zero speed carries energy (mechanical) • A mass raised up carries energy (gravitational) • The atom in a molecule carries energy (chemical) • The molecule in a hot gas carries energy (thermal) • The nucleus of an atom carries energy (nuclear) (The energy carried by radi ...
... • A mass accelerated to a non-zero speed carries energy (mechanical) • A mass raised up carries energy (gravitational) • The atom in a molecule carries energy (chemical) • The molecule in a hot gas carries energy (thermal) • The nucleus of an atom carries energy (nuclear) (The energy carried by radi ...
Mechanics II - Thierry Karsenti
... quantities to describe rotational motion are introduced and used. It will be show that the equations of motion that describe linear motion possess a rotational counterpart . The third activity is on Gravitation Up to now we have described various forces from an entirely empirical point of view. To g ...
... quantities to describe rotational motion are introduced and used. It will be show that the equations of motion that describe linear motion possess a rotational counterpart . The third activity is on Gravitation Up to now we have described various forces from an entirely empirical point of view. To g ...
Momentum - Red Hook Central Schools
... wall with a velocity of 15 m/s. If it rebounds with a velocity of 12 m/s: a) what was its Dv? b) What was its Dp? ...
... wall with a velocity of 15 m/s. If it rebounds with a velocity of 12 m/s: a) what was its Dv? b) What was its Dp? ...