* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download worksheet 3 with scaffolding
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Center of mass wikipedia , lookup
Modified Newtonian dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Centrifugal force wikipedia , lookup
Equations of motion wikipedia , lookup
Classical central-force problem wikipedia , lookup
Centripetal force wikipedia , lookup
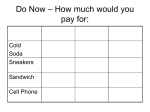
Name: _________________ Date:__________ Block:______ Constant Force Unit: Worksheet 3 1. A 10,000 kg rocket is acted upon by an upward thrust of 118,000N. How fast will the rocket be moving after 20 seconds? How far will it have moved in this time? Draw a diagram Consider the forces (if applicable): Fearthobject (determine from the mass if necessary) Fsurfaceobject (friction) Applied force or thrust Fstringobject (tension) Fgroundobject (normal) Determine the net force (Fnet or F) (this will be along the direction of motion) List the mass of the object with units (or determine from weight if necessary) m=____________ Use Newton’s Second Law to find acceleration Write equation Substitute values with units Calculate values with units Use Kinematics to find “how far” or “how fast” or both Write equation(s) Substitute values with units Calculate values with units 2. A 500kg crate is pushed with a 2000N Force. The force of sliding friction acting on the crate is 1900N. How fast will the crate be moving after 10 seconds? How far will it have moved in this time? Draw a diagram Consider the forces (if applicable): Fearthobject (determine from the mass if necessary) Fsurfaceobject (friction) Applied force or thrust Fstringobject (tension) Fgroundobject (normal) Determine the net force (Fnet or F) (this will be along the direction of motion) List the mass of the object with units (or determine from weight if necessary) m=____________ Use Newton’s Second Law to find acceleration Write equation Substitute values with units Calculate values with units Use Kinematics to find “how far” or “how fast” or both Write equation(s) Substitute values with units Calculate values with units 3. An elevator is lifted with a tension (Fcableelevator) of 50,000 N. The weight of the elevator is 49,000N. How fast will the elevator be moving after 5 seconds if it starts from rest? Draw a diagram Consider the forces (if applicable): Fearthobject (determine from the mass if necessary) Fsurfaceobject (friction) Applied force or thrust Fstringobject (tension) Fgroundobject (normal) Determine the net force (Fnet or F) (this will be along the direction of motion) List the mass of the object with units (or determine from weight if necessary) m=____________ Use Newton’s Second Law to find acceleration Write equation Substitute values with units Calculate values with units Use Kinematics to find “how far” or “how fast” or both Write equation(s) Substitute values with units Calculate values with units 4. A car with a mass of 1500 kg has an engine which can produce 4000N of thrust. Assume that the air resistance on the car is a constant 500N. If the car starts from rest, how fast will it be moving after 10 seconds? How far will it have moved in this time? Draw a diagram Consider the forces (if applicable): Fearthobject (determine from the mass if necessary) Fsurfaceobject (friction) Applied force or thrust Fstringobject (tension) Fgroundobject (normal) Determine the net force (Fnet or F) (this will be along the direction of motion) List the mass of the object with units (or determine from weight if necessary) m=____________ Use Newton’s Second Law to find acceleration Write equation Substitute values with units Calculate values with units Use Kinematics to find “how far” or “how fast” or both Write equation(s) Substitute values with units Calculate values with units 5. A 225 kg crate is pushed horizontally with a force of 710 N. If the coefficient of friction (mu, or ) is 0.20, calculate how far it will have travelled and how fast it will be going after 15 seconds. Draw a diagram Consider the forces (if applicable): Fearthobject (determine from the mass if necessary) Fsurfaceobject (friction) Applied force or thrust Fstringobject (tension) Fgroundobject (normal) Determine the net force (Fnet or F) (this will be along the direction of motion) List the mass of the object with units (or determine from weight if necessary) m=____________ Use Newton’s Second Law to find acceleration Write equation Substitute values with units Calculate values with units Use Kinematics to find “how far” or “how fast” or both Write equation(s) Substitute values with units Calculate values with units 6. A 50 kg sled is pulled along a snow-covered ground. If the coefficient of friction between the sled and the ground (mu, or ) is 0.10, what force must be applied in order to move the sled from rest to a speed of 6.0m/s in 2.0seconds? Draw a diagram Consider the forces (if applicable): Fearthobject (determine from the mass if necessary) Fsurfaceobject (friction) Applied force or thrust Fstringobject (tension) Fgroundobject (normal) Determine the net force (Fnet or F) (this will be along the direction of motion) List the mass of the object with units (or determine from weight if necessary) m=____________ Use Newton’s Second Law to find acceleration Write equation Substitute values with units Calculate values with units Use Kinematics to find “how far” or “how fast” or both Write equation(s) Substitute values with units Calculate values with units