Document
... 14. From A to B, friction acts down the incline. Work done by friction = Fs = 2.6 x AB cos 180o = -2.6 x 10/sin 30o = - 52 J From B to C, friction acts up the incline . Work done by friction = 2.6 x BC cos 180o = -2.6 x 10 / sin 30o = - 52 J Total work done by friction = -52 + -52 = -104 J For gravi ...
... 14. From A to B, friction acts down the incline. Work done by friction = Fs = 2.6 x AB cos 180o = -2.6 x 10/sin 30o = - 52 J From B to C, friction acts up the incline . Work done by friction = 2.6 x BC cos 180o = -2.6 x 10 / sin 30o = - 52 J Total work done by friction = -52 + -52 = -104 J For gravi ...
Newton`s First Law of Motion
... Weight–a measure of the gravitational force acting on an object – Weight depends on an object’s location – The weight of an object would be very different on the earth and on the moon, and still different in outer space – On the moon, the object would have only one-sixth the weight it has on the ear ...
... Weight–a measure of the gravitational force acting on an object – Weight depends on an object’s location – The weight of an object would be very different on the earth and on the moon, and still different in outer space – On the moon, the object would have only one-sixth the weight it has on the ear ...
Document
... The normal force and friction: Rest your hand on a table; the atoms that form the molecules that make up the table and your hand are in contact with each other. If you press harder, the atoms are also pressed closer together. The electrons in the atoms begin to repel each other and your hand is pus ...
... The normal force and friction: Rest your hand on a table; the atoms that form the molecules that make up the table and your hand are in contact with each other. If you press harder, the atoms are also pressed closer together. The electrons in the atoms begin to repel each other and your hand is pus ...
Friction Force - NeuLog Sensors
... Friction force is created when two surfaces move or try to move against each other. The direction of the friction force is always opposite to the direction of motion (or motion attempt) and parallel to the surface, therefore it resists the relative motion of the surfaces. Friction force depends on t ...
... Friction force is created when two surfaces move or try to move against each other. The direction of the friction force is always opposite to the direction of motion (or motion attempt) and parallel to the surface, therefore it resists the relative motion of the surfaces. Friction force depends on t ...
Forces
... • If gravity is exerting a force of 98 Newtons on an object in air, and the acceleration due to gravity is 9.8 m/s2, what is the object’s mass? ...
... • If gravity is exerting a force of 98 Newtons on an object in air, and the acceleration due to gravity is 9.8 m/s2, what is the object’s mass? ...
Factors That Affect Motion
... • Simply put, momentum is mass that is in motion. Any object in motion has momentum. Increasing the mass or speed will increase the momentum. Conversely, decreasing the mass or speed will decrease the momentum. • Example, throwing a heavy bowling ball with a high acceleration will have more momentu ...
... • Simply put, momentum is mass that is in motion. Any object in motion has momentum. Increasing the mass or speed will increase the momentum. Conversely, decreasing the mass or speed will decrease the momentum. • Example, throwing a heavy bowling ball with a high acceleration will have more momentu ...
Forces and Motion
... • With what force will a car hit a tree if the car has a mass of 3000kg and it is accelerating at a rate of 2m/s2? ...
... • With what force will a car hit a tree if the car has a mass of 3000kg and it is accelerating at a rate of 2m/s2? ...
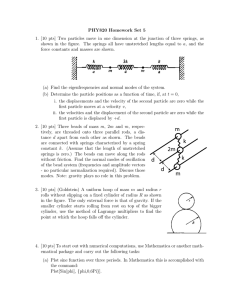
PHY820 Homework Set 5
... 2. [10 pts] Three beads of mass m, 2m and m, respectively, are threaded onto three parallel rods, a distance d apart from each other as shown. The beads are connected with springs characterized by a spring constant k. (Assume that the length of unstretched springs is zero.) The beads can move along ...
... 2. [10 pts] Three beads of mass m, 2m and m, respectively, are threaded onto three parallel rods, a distance d apart from each other as shown. The beads are connected with springs characterized by a spring constant k. (Assume that the length of unstretched springs is zero.) The beads can move along ...
Frictional Force
... Let's say you had a crate and you wanted to move it somewhere. First, you have to overcome the static friction between the floor and the crate to get it moving. Once you have it moving, you have to keep it moving by overcoming the kinetic (moving) friction - which is always much easier! ...
... Let's say you had a crate and you wanted to move it somewhere. First, you have to overcome the static friction between the floor and the crate to get it moving. Once you have it moving, you have to keep it moving by overcoming the kinetic (moving) friction - which is always much easier! ...
333 UNIT 2 - mrdsample
... What happens to speed of skydiver after parachute has been open for awhile? Forces on skydiver? ...
... What happens to speed of skydiver after parachute has been open for awhile? Forces on skydiver? ...
Physical Science Chapter 3
... force applied to the ball and to show how the ball moves after it is kicked. ...
... force applied to the ball and to show how the ball moves after it is kicked. ...
Forces in 1
... 6. THE BIG CONNECTION: Using your observations and data from questions 1-4, a. determine a mathematical relationship between Force, Mass and Acceleration. Show all your work! Be sure to analyze your solution and explain why it makes sense! ...
... 6. THE BIG CONNECTION: Using your observations and data from questions 1-4, a. determine a mathematical relationship between Force, Mass and Acceleration. Show all your work! Be sure to analyze your solution and explain why it makes sense! ...
Forces and Friction Worksheet
... Key Concept: In free fall, the force of gravity is an unbalanced force that causes an object to accelerate. • Gravity is the force that pulls objects toward Earth. • If gravity is the only force pulling on a falling object, the object is in free fall. • Most objects move through air. Friction cause ...
... Key Concept: In free fall, the force of gravity is an unbalanced force that causes an object to accelerate. • Gravity is the force that pulls objects toward Earth. • If gravity is the only force pulling on a falling object, the object is in free fall. • Most objects move through air. Friction cause ...
2.3 FRICTION The property by virtue of which a resisting force is
... The opposing force is the force of friction. The frictional force always acts opposite to the direction of motion or the direction of the applied force. Properties of frictional forces: 1. Frictional force always acts parallel to two planes in contact with each other and in a direction opposite to t ...
... The opposing force is the force of friction. The frictional force always acts opposite to the direction of motion or the direction of the applied force. Properties of frictional forces: 1. Frictional force always acts parallel to two planes in contact with each other and in a direction opposite to t ...
Forces Chapter 10 - Powers Physical Science
... The law of universal gravitation states that any two objects in the universe, without exception ...
... The law of universal gravitation states that any two objects in the universe, without exception ...