Problems
... 1.50 m/s. The pulling force is 100 N parallel to the incline, which makes an angle of 20.0° with the horizontal. The coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.400, and the crate is pulled 5.00 m. (a) How much work is done by the gravitational force on the crate? (b) Determine the increase in internal energ ...
... 1.50 m/s. The pulling force is 100 N parallel to the incline, which makes an angle of 20.0° with the horizontal. The coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.400, and the crate is pulled 5.00 m. (a) How much work is done by the gravitational force on the crate? (b) Determine the increase in internal energ ...
CEENbot Pull - Mechatronics
... INSTRUCTING Concepts (Pulling with a CEENBoT!) Friction Putting “Friction” in Recognizable terms: Friction is a force between two objects that tends to “damp out” or oppose motion. It always acts in complete opposition to another force applied to an object. There are two main types of friction. Sta ...
... INSTRUCTING Concepts (Pulling with a CEENBoT!) Friction Putting “Friction” in Recognizable terms: Friction is a force between two objects that tends to “damp out” or oppose motion. It always acts in complete opposition to another force applied to an object. There are two main types of friction. Sta ...
Normal Force Example: Incline
... Problem: Pushing a crate at an angle A crate of mass 100 kg is being pushed across a horizontal surface. The coefficient of friction between the crate and the surface is μ = 0.2. The force is being applied downward on the crate at a 30º angle with respect to the vertical axis. What is the minimum f ...
... Problem: Pushing a crate at an angle A crate of mass 100 kg is being pushed across a horizontal surface. The coefficient of friction between the crate and the surface is μ = 0.2. The force is being applied downward on the crate at a 30º angle with respect to the vertical axis. What is the minimum f ...
Notes in pdf format
... The police car immediately gives chase, accelerating uniformly to reach a speed of 90 km/h in 10 s and continues at this speed until he overtakes the other car. Find: (a) the time taken by the police to catch up with the car, (b) the distance travelled by the police car when this happens. 2.) Draw f ...
... The police car immediately gives chase, accelerating uniformly to reach a speed of 90 km/h in 10 s and continues at this speed until he overtakes the other car. Find: (a) the time taken by the police to catch up with the car, (b) the distance travelled by the police car when this happens. 2.) Draw f ...
17.4 Inertia and Newton`s 1st law of motion
... road will slow down if we stop pedalling. This happens because the force of friction, including water resistance and air resistance, slows them down (see Module 10.3 about friction). The more we reduce friction, the better we maintain speed. The ice skater on the left is moving fast and there is ver ...
... road will slow down if we stop pedalling. This happens because the force of friction, including water resistance and air resistance, slows them down (see Module 10.3 about friction). The more we reduce friction, the better we maintain speed. The ice skater on the left is moving fast and there is ver ...
Physical Science Final Study Guide I KEY Name __ ___
... b. What is its acceleration? 0 14. An object is in projectile motion when GRAVITY is the only force acting on it. 15. What is an object orbiting Earth really doing? FALLING AROUND EARTH 16. Newton’s 3rd Law says that for every action FORCE THERE IS AN EQUAL AND OPPOSITE REACTION ...
... b. What is its acceleration? 0 14. An object is in projectile motion when GRAVITY is the only force acting on it. 15. What is an object orbiting Earth really doing? FALLING AROUND EARTH 16. Newton’s 3rd Law says that for every action FORCE THERE IS AN EQUAL AND OPPOSITE REACTION ...
Astronomy
... Physics Current Events Assignment 4.1. Development of Force Concept Understand the definition of force. Newton’s Dark Secrets (Nova DVD) 4.2. Newton’s First Law of Motion: Inertia Define mass and inertia. Understand Newton's first law of motion. 4.3. Newton’s Second Law of Motion: Concept of a ...
... Physics Current Events Assignment 4.1. Development of Force Concept Understand the definition of force. Newton’s Dark Secrets (Nova DVD) 4.2. Newton’s First Law of Motion: Inertia Define mass and inertia. Understand Newton's first law of motion. 4.3. Newton’s Second Law of Motion: Concept of a ...
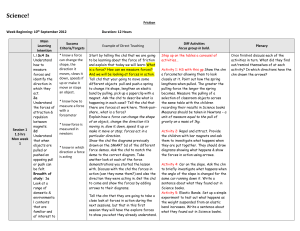
Science! - WhiteHouseCurriculum
... and explain that today we will learn-What is a force? How can we measure forces? And we will be looking at forces in action. Tell chd that your going to move some different objects pull and push a spring to change its shape, lengthen an elastic band by pulling, pick up a paperclip with a magnet. Ask ...
... and explain that today we will learn-What is a force? How can we measure forces? And we will be looking at forces in action. Tell chd that your going to move some different objects pull and push a spring to change its shape, lengthen an elastic band by pulling, pick up a paperclip with a magnet. Ask ...
newtons laws_ppt
... when a round object such as a train rolling on a track or a ball rolling on a surface. ...
... when a round object such as a train rolling on a track or a ball rolling on a surface. ...
Sample problems
... 12. An automobile of mass 2 000 kg moving at 20 m/s is braked suddenly with a constant braking force of 5 000 N. How far does the car travel before stopping? a. 2.5 m b. 66 m c. 80 m d. 20 m e. 102 m 13. A 5-kg object is moving at 7 m/s. A 2-N force is applied in the opposite direction of motion an ...
... 12. An automobile of mass 2 000 kg moving at 20 m/s is braked suddenly with a constant braking force of 5 000 N. How far does the car travel before stopping? a. 2.5 m b. 66 m c. 80 m d. 20 m e. 102 m 13. A 5-kg object is moving at 7 m/s. A 2-N force is applied in the opposite direction of motion an ...
Newton`s Laws of Motion
... moving in the same direction. A force was applied to the car to stop it but no force was applied to the quarters. Another example is how you move forward when you are riding in a car and it stops suddenly or the book sitting on the car seat goes forward when slam on the brakes. ...
... moving in the same direction. A force was applied to the car to stop it but no force was applied to the quarters. Another example is how you move forward when you are riding in a car and it stops suddenly or the book sitting on the car seat goes forward when slam on the brakes. ...
1. Why must an object at rest have either no force or at least two
... 1. Why must an object at rest have either no force or at least two forces acting on it? 2. A 50 kg wood block is being dragged at an angle of 20o above horizontal across a wood floor, where the coefficient of friction is 0.5. The dragging force is 750N. Find the acceleration of the block. 3. A 20 kg ...
... 1. Why must an object at rest have either no force or at least two forces acting on it? 2. A 50 kg wood block is being dragged at an angle of 20o above horizontal across a wood floor, where the coefficient of friction is 0.5. The dragging force is 750N. Find the acceleration of the block. 3. A 20 kg ...
Dynamics Review Sheet Solutions
... 11. A child is riding on a merry-go-round. As the speed of the merry-go-round is doubled, the magnitude of the centripetal force acting on the child A. remains the same C. is halved B. is doubled D. is quadrupled 12. A 1,200-kilogram car traveling at 10 meters per second hits a tree that is brought ...
... 11. A child is riding on a merry-go-round. As the speed of the merry-go-round is doubled, the magnitude of the centripetal force acting on the child A. remains the same C. is halved B. is doubled D. is quadrupled 12. A 1,200-kilogram car traveling at 10 meters per second hits a tree that is brought ...
Force and Newton` s Laws Study Guide
... direction, why is an unbalanced force involved? If an unbalanced force was not involved then there would be no change in the object’s motion. 16.Draw the equation triangle for force, mass, and ...
... direction, why is an unbalanced force involved? If an unbalanced force was not involved then there would be no change in the object’s motion. 16.Draw the equation triangle for force, mass, and ...