Newtons 2nd Law - VCC Library
... Gravity. Gravity acts on all objects near the Earth’s surface. (If the problem doesn’t explicitly say we’re in space, there’s gravity!) The force of gravity is equal to the object’s weight: W or Fg = mg, where g = 9.81 m⁄s² is the acceleration due to gravity. You might be told to round to 10 m⁄s². G ...
... Gravity. Gravity acts on all objects near the Earth’s surface. (If the problem doesn’t explicitly say we’re in space, there’s gravity!) The force of gravity is equal to the object’s weight: W or Fg = mg, where g = 9.81 m⁄s² is the acceleration due to gravity. You might be told to round to 10 m⁄s². G ...
COEFFICIENT OF FRICTION
... series of different masses. When pulling horizontally on a level surface, the normal force is the total weight (mg) of the block plus any added mass. To measure the force of friction Fk , use the force sensor. a) Draw below a free body diagram for the block while is pulled by the sensor: ...
... series of different masses. When pulling horizontally on a level surface, the normal force is the total weight (mg) of the block plus any added mass. To measure the force of friction Fk , use the force sensor. a) Draw below a free body diagram for the block while is pulled by the sensor: ...
force
... 2. Friction between two surfaces that are not moving past each other is called static friction 3. Sliding friction – force that opposes motion of two surfaces sliding past each other 4. Friction between a rolling object and the surface it rolls on is called rolling friction ...
... 2. Friction between two surfaces that are not moving past each other is called static friction 3. Sliding friction – force that opposes motion of two surfaces sliding past each other 4. Friction between a rolling object and the surface it rolls on is called rolling friction ...
exam2_T131_solution
... to the right by a distance x = 0.20 m from equilibrium and released from rest as shown in Figures 6(a) and 6(b). What is the coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the horizontal surface if the block passes through the equilibrium position with a speed of 1.8 m/s? A) B) C) D) E) ...
... to the right by a distance x = 0.20 m from equilibrium and released from rest as shown in Figures 6(a) and 6(b). What is the coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the horizontal surface if the block passes through the equilibrium position with a speed of 1.8 m/s? A) B) C) D) E) ...
04_Force and Motion
... increases; then the kinetic frictional force takes over as the object begins to move. ...
... increases; then the kinetic frictional force takes over as the object begins to move. ...
Practice Problems
... a) Stone one strikes the ground first. b) Stone two strikes the ground first. c) The stones strike the ground at the same time. d) Stone one lands with a higher speed than stone two. e) Stone two lands with a higher speed than stone one. f) The stones land with the same speed. ...
... a) Stone one strikes the ground first. b) Stone two strikes the ground first. c) The stones strike the ground at the same time. d) Stone one lands with a higher speed than stone two. e) Stone two lands with a higher speed than stone one. f) The stones land with the same speed. ...
Static Friction - Blue Valley Schools
... object. The normal force is defined as the perpendicular component of the force exerted by the surface. In this case, the normal force is equal to the weight of the object. Once the box starts to slide, you must continue to exert a force to keep the object moving, or friction will slow it to a stop. ...
... object. The normal force is defined as the perpendicular component of the force exerted by the surface. In this case, the normal force is equal to the weight of the object. Once the box starts to slide, you must continue to exert a force to keep the object moving, or friction will slow it to a stop. ...
Chapters One and Two - elementaryscienceteachers
... Because the moon has one sixth the gravity of Earth, you would weigh six times less than what you weigh on Earth. This is why the astronauts were able to move easily in their heavy space suits. In the photo to the right, John Young, commander of the Apollo 16 lunar landing mission, jumps up from the ...
... Because the moon has one sixth the gravity of Earth, you would weigh six times less than what you weigh on Earth. This is why the astronauts were able to move easily in their heavy space suits. In the photo to the right, John Young, commander of the Apollo 16 lunar landing mission, jumps up from the ...
Exam 1A
... More than 300 years ago, Isaac Newton claimed that the moon is accelerating toward the planet Earth. Explain how we know that the moon is accelerating toward the earth and why it hasn’t hit the earth over the past 300 years. ...
... More than 300 years ago, Isaac Newton claimed that the moon is accelerating toward the planet Earth. Explain how we know that the moon is accelerating toward the earth and why it hasn’t hit the earth over the past 300 years. ...
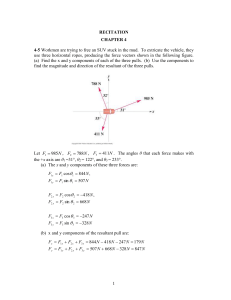
Recitation Ch 4-1
... The stopping distance is proportional to the square of the initial speed. 4-34 A factory worker pushes horizontally on a 250 N crate with a force of 75 N on a horizontal rough floor. A 135 N crate rests on top of the one being pushed and moves along with it. Make a free-body diagram of each crate if ...
... The stopping distance is proportional to the square of the initial speed. 4-34 A factory worker pushes horizontally on a 250 N crate with a force of 75 N on a horizontal rough floor. A 135 N crate rests on top of the one being pushed and moves along with it. Make a free-body diagram of each crate if ...
Newton`s Laws of Motion - McMaster Physics and Astronomy
... Examples : A heavy block on a table • The table must push up on the block to prevent it from falling ...
... Examples : A heavy block on a table • The table must push up on the block to prevent it from falling ...
UNIT 2
... Which of the following statements is correct? a. The acceleration of block X to the right is less than the acceleration of block Y downward because of the friction on block X. b. The acceleration of block X to the right has the same magnitude as the acceleration of block Y downward and is slightly l ...
... Which of the following statements is correct? a. The acceleration of block X to the right is less than the acceleration of block Y downward because of the friction on block X. b. The acceleration of block X to the right has the same magnitude as the acceleration of block Y downward and is slightly l ...
Formula: F coefficent of friction*m*g
... MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Solve the problem. (Use g = 9.8 m/s2 .) 1) A 21 kg box must be slid across the floor. If the coefficient of static friction between the box and floor is 0.37, what is the minimum force needed to st ...
... MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Solve the problem. (Use g = 9.8 m/s2 .) 1) A 21 kg box must be slid across the floor. If the coefficient of static friction between the box and floor is 0.37, what is the minimum force needed to st ...
ME 101: Engineering Mechanics
... Single threaded screw of the vise has a mean diameter of 25 mm and a lead of 5 mm. A 300 N pull applied normal to the handle at A produces a clamping force of 5 kN between the jaws of the vise. Determine: (a) Frictional moment MB developed at B due to thrust of the screw against body of the jaw (b) ...
... Single threaded screw of the vise has a mean diameter of 25 mm and a lead of 5 mm. A 300 N pull applied normal to the handle at A produces a clamping force of 5 kN between the jaws of the vise. Determine: (a) Frictional moment MB developed at B due to thrust of the screw against body of the jaw (b) ...
Chapter 3 Dynamics: Motion and Force 3.1 Homework # 19
... 04. A 103.0-kg swat team member descends a 27.5-m cable attached to a helicopter. If he wishes to reach the bottom in 3.50 s, what average force should he apply to the cable? 05. What minimum force is needed to lift a 3.72-kg object off the floor up onto the table 82.5 cm above? 06. A 640-kg elevato ...
... 04. A 103.0-kg swat team member descends a 27.5-m cable attached to a helicopter. If he wishes to reach the bottom in 3.50 s, what average force should he apply to the cable? 05. What minimum force is needed to lift a 3.72-kg object off the floor up onto the table 82.5 cm above? 06. A 640-kg elevato ...