ch 4 Giancoli
... An object sliding down an incline has three forces acting on it: the normal force, gravity, and the frictional force. • The normal force is always perpendicular to the surface. • The friction force is parallel to it. • The gravitational force points down. If the object is at rest, the forces are the ...
... An object sliding down an incline has three forces acting on it: the normal force, gravity, and the frictional force. • The normal force is always perpendicular to the surface. • The friction force is parallel to it. • The gravitational force points down. If the object is at rest, the forces are the ...
dynamics
... Newton’s second law answers the question of what happens to an object that has a nonzero resultant force acting on it. Newton’s second law states that; if a net force acts on a body, the body will accelerate. The acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the resultant force acting on it ...
... Newton’s second law answers the question of what happens to an object that has a nonzero resultant force acting on it. Newton’s second law states that; if a net force acts on a body, the body will accelerate. The acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the resultant force acting on it ...
Rotational and Translational Motion
... Answer 3. Energy is not conserved because there are energy losses due to kinetic friction. Angular momentum about the center of mass is not constant because the friction exerts a torque about the center of mass. Angular momentum about a fixed point on the ground is constant because the sum of the to ...
... Answer 3. Energy is not conserved because there are energy losses due to kinetic friction. Angular momentum about the center of mass is not constant because the friction exerts a torque about the center of mass. Angular momentum about a fixed point on the ground is constant because the sum of the to ...
UNIT 2 REVIEW SHEET Answers sp 10
... acceleration due to gravity is 25 m/s2, that same object would weigh what on Earth and on Jupiter? On Jupiter it would have a mass of ? Weight on Earth Fw = mg 120(10) = Weight on Jupiter Fw = mg 120 (25)= The object would have the same mass on Jupiter as it does on Earth. Mass doesn’t change. 2. Wh ...
... acceleration due to gravity is 25 m/s2, that same object would weigh what on Earth and on Jupiter? On Jupiter it would have a mass of ? Weight on Earth Fw = mg 120(10) = Weight on Jupiter Fw = mg 120 (25)= The object would have the same mass on Jupiter as it does on Earth. Mass doesn’t change. 2. Wh ...
Activity Document
... In this activity, you will be reviewing most of what you have learned in Physics I up to this point. This will give you a chance to see how well you have learned the material and what areas you need to study. Consider a 500 g cart rolling down an inclined track. The length of the track is 1.000 m an ...
... In this activity, you will be reviewing most of what you have learned in Physics I up to this point. This will give you a chance to see how well you have learned the material and what areas you need to study. Consider a 500 g cart rolling down an inclined track. The length of the track is 1.000 m an ...
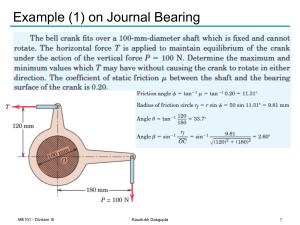
Example (1) on Journal Bearing
... Low Rolling Resistance between rubber tyre and tar road due to wet field ...
... Low Rolling Resistance between rubber tyre and tar road due to wet field ...
Newton`s Laws MC test
... 12) When a 45-kg person steps on a scale in an elevator, the scale reads a steady 480 N. Which of the following statements must be true? (There could be more than one correct choice.) A) The elevator is accelerating upward at a constant rate. B) The elevator is accelerating downward at a constant ra ...
... 12) When a 45-kg person steps on a scale in an elevator, the scale reads a steady 480 N. Which of the following statements must be true? (There could be more than one correct choice.) A) The elevator is accelerating upward at a constant rate. B) The elevator is accelerating downward at a constant ra ...
Ch 11 Rolling, Torque and Angular Momentum
... Forces of rolling If a wheel rolls smoothly, there is no sliding at the contact point so there is no friction. However, if there is an external force that produces an acceleration, there will be an angular acceleration, . The acceleration will make the wheel want to slide at the contact point. Then ...
... Forces of rolling If a wheel rolls smoothly, there is no sliding at the contact point so there is no friction. However, if there is an external force that produces an acceleration, there will be an angular acceleration, . The acceleration will make the wheel want to slide at the contact point. Then ...
PHYSICS 111 HOMEWORK SOLUTION #5 March 3, 2013
... string is pushing the object rather than pulling it. ...
... string is pushing the object rather than pulling it. ...
PCM_Ideas4
... Measure reaction forces to evaluate leg trajectories and foot compliance, How much does leg squeezing reduce reaction forces? Is 2.5kg excessive? How much do we gain/pay for changing mass? What leg trajectories minimize adhesion forces? How much adhesion will feet need to provide? And for how long? ...
... Measure reaction forces to evaluate leg trajectories and foot compliance, How much does leg squeezing reduce reaction forces? Is 2.5kg excessive? How much do we gain/pay for changing mass? What leg trajectories minimize adhesion forces? How much adhesion will feet need to provide? And for how long? ...
J S U N I L T U... Force Created by Jsunil Tutorial Panjabi colony Gali no. 01
... : An agent that change or try to change the state of an object is called force . A force may be i. Push ii. Pull iii. Gravitational force iv . Frictional force The force applied on a body can bring about the following changes: ☼ It can change the state of rest of a body or change its position ☼ It c ...
... : An agent that change or try to change the state of an object is called force . A force may be i. Push ii. Pull iii. Gravitational force iv . Frictional force The force applied on a body can bring about the following changes: ☼ It can change the state of rest of a body or change its position ☼ It c ...