1 PHYSICS 231 Lecture 7: Newton`s Laws
... Two Forces that luckily act upon us nearly all the time. Normal Force: elastic force acting perpendicular to the surface the object is resting on. Name: n 1. No net force: remains at rest. 2. Fg=mg=n 3. Fmass-ground=-Fground-mass ...
... Two Forces that luckily act upon us nearly all the time. Normal Force: elastic force acting perpendicular to the surface the object is resting on. Name: n 1. No net force: remains at rest. 2. Fg=mg=n 3. Fmass-ground=-Fground-mass ...
Force and Motion
... Shove a book across the table Some are obvious (car hits tree), others are not (floor pushing on feet). ...
... Shove a book across the table Some are obvious (car hits tree), others are not (floor pushing on feet). ...
Dynamics Worksheet Feb. 21, 2008
... 1) A rocket moves through empty space in a straight line with constant speed. It is far from the gravitational effect of any star or planet. Under these conditions, the force that must be applied to the rocket in order to sustain its motion is 1) _______ A) equal to its mass. B) equal to its weight. ...
... 1) A rocket moves through empty space in a straight line with constant speed. It is far from the gravitational effect of any star or planet. Under these conditions, the force that must be applied to the rocket in order to sustain its motion is 1) _______ A) equal to its mass. B) equal to its weight. ...
Forces and Motion Notes
... Force – a push or pull on an object 3 Types of Forces: 1. Contact Force – when one object pushes or pulls another object by touching it 2. Gravity – the force of attraction between two objects 3. Friction – a force that resists motion between two surfaces that are pressed together Net Force – the ov ...
... Force – a push or pull on an object 3 Types of Forces: 1. Contact Force – when one object pushes or pulls another object by touching it 2. Gravity – the force of attraction between two objects 3. Friction – a force that resists motion between two surfaces that are pressed together Net Force – the ov ...
AP Sample Questions
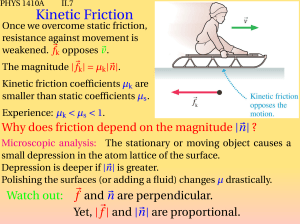
... Is mass the same quantity as weight? What is g? What is μ? On a flat surface, what is equal to the Fn ? ...
... Is mass the same quantity as weight? What is g? What is μ? On a flat surface, what is equal to the Fn ? ...
Force and Newton`s Laws
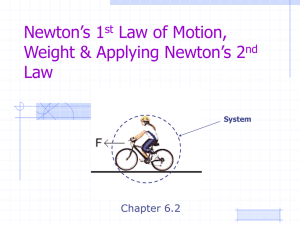
... Balanced forces: no change in motion Unbalanced forces: acceleration occurs Newton’s First law of motion: (Law of Inertia) An object in motion tends to stay in motion; an object at rest tends to stay at rest, unless acted on by an outside force. “An object will remain at rest or move with ...
... Balanced forces: no change in motion Unbalanced forces: acceleration occurs Newton’s First law of motion: (Law of Inertia) An object in motion tends to stay in motion; an object at rest tends to stay at rest, unless acted on by an outside force. “An object will remain at rest or move with ...
Sects. 4.1 through 4.4
... A ball is held in a person’s hand. a) Identify all the external forces acting on the ball and the reaction to each. b) If the ball is dropped, what force is exerted on it while it is falling? Identify the reaction force in this case. ...
... A ball is held in a person’s hand. a) Identify all the external forces acting on the ball and the reaction to each. b) If the ball is dropped, what force is exerted on it while it is falling? Identify the reaction force in this case. ...
Weightlessness

Weightlessness, or an absence of 'weight', is an absence of stress and strain resulting from externally applied mechanical contact-forces, typically normal forces from floors, seats, beds, scales, and the like. Counterintuitively, a uniform gravitational field does not by itself cause stress or strain, and a body in free fall in such an environment experiences no g-force acceleration and feels weightless. This is also termed ""zero-g"" where the term is more correctly understood as meaning ""zero g-force.""When bodies are acted upon by non-gravitational forces, as in a centrifuge, a rotating space station, or within a space ship with rockets firing, a sensation of weight is produced, as the contact forces from the moving structure act to overcome the body's inertia. In such cases, a sensation of weight, in the sense of a state of stress can occur, even if the gravitational field was zero. In such cases, g-forces are felt, and bodies are not weightless.When the gravitational field is non-uniform, a body in free fall suffers tidal effects and is not stress-free. Near a black hole, such tidal effects can be very strong. In the case of the Earth, the effects are minor, especially on objects of relatively small dimension (such as the human body or a spacecraft) and the overall sensation of weightlessness in these cases is preserved. This condition is known as microgravity and it prevails in orbiting spacecraft.