File
... in the wall will move towards the balloon Some negative charges in the wall will move towards the balloon Some positive charges in the wall will go onto the balloon Some negative charges on the balloon will go to the wall ...
... in the wall will move towards the balloon Some negative charges in the wall will move towards the balloon Some positive charges in the wall will go onto the balloon Some negative charges on the balloon will go to the wall ...
Electric Fields and Potentials
... g F / m (Newton/kg) Note that the units of the gravitational force field are Newtons per unit mass, which are also the units for acceleration. Gravitational fields surrounds all objects with mass but can only be detected by placing another object with mass at some distance away and measuring the g ...
... g F / m (Newton/kg) Note that the units of the gravitational force field are Newtons per unit mass, which are also the units for acceleration. Gravitational fields surrounds all objects with mass but can only be detected by placing another object with mass at some distance away and measuring the g ...
On the Classical Coupling between Gravity and Electromagnetism
... Coupling between gravity and electromagnetism through the deflection of light around a massive object is a well-known effect. It was made popular by Einstein, who correctly predicted the angle of deflection of starlight around the Sun during a solar eclipse, verifying his general theory of relativit ...
... Coupling between gravity and electromagnetism through the deflection of light around a massive object is a well-known effect. It was made popular by Einstein, who correctly predicted the angle of deflection of starlight around the Sun during a solar eclipse, verifying his general theory of relativit ...
On the electromagnetic force on a polarizable body
... is somewhat more subtle. The point is that we have only considered the electric part of the stress tensor in the medium whereas the total force must clearly be related to the surface integral of the total stress tensor Tijtotal . But in equilibrium we must have ∂j Tijtotal = 0 (otherwise there would ...
... is somewhat more subtle. The point is that we have only considered the electric part of the stress tensor in the medium whereas the total force must clearly be related to the surface integral of the total stress tensor Tijtotal . But in equilibrium we must have ∂j Tijtotal = 0 (otherwise there would ...
On the Possibility of Nuclear Synthesis During Orthopositronium
... The latest work of the Michigan group has created a new situation for the hypothesis adduced herein. It is necessary to emphasize that the result of the last set of Michigan measurements, after introduction of a dc electric field up to ∼7 kV/cm in a measuring cell [16], we treat as the first observa ...
... The latest work of the Michigan group has created a new situation for the hypothesis adduced herein. It is necessary to emphasize that the result of the last set of Michigan measurements, after introduction of a dc electric field up to ∼7 kV/cm in a measuring cell [16], we treat as the first observa ...
Introduction to Energy Concepts
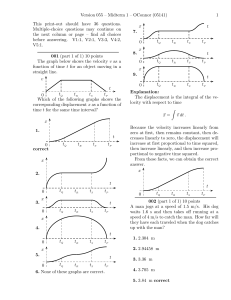
... conditions. The charge on each is +q, the distance between them is R, and the electric force acting between them is F. If the distance between the objects were halved, the force between them would ...
... conditions. The charge on each is +q, the distance between them is R, and the electric force acting between them is F. If the distance between the objects were halved, the force between them would ...
f - Edublogs
... something MUST be pushing on it. Things don’t move all by themselves! Aristotle ...
... something MUST be pushing on it. Things don’t move all by themselves! Aristotle ...
Force Summation
... skill and sport. Some skills, such as punches in boxing, require tremendous forces applied over a very short time frame. Other skills like throwing a javelin require forces applied over a longer timeframe. An expert javelin thrower accelerates the javelin by pulling it from way behind his body and r ...
... skill and sport. Some skills, such as punches in boxing, require tremendous forces applied over a very short time frame. Other skills like throwing a javelin require forces applied over a longer timeframe. An expert javelin thrower accelerates the javelin by pulling it from way behind his body and r ...
Review questions
... 8) A child's toy is suspended from the ceiling by means of a string. The Earth pulls downward on the toy with its weight force of 8 N. If this is the "action force;' what is the "reaction force"? A) the string pulling downward on the ceiling with an 8-N force B) the ceiling pulling upward on the str ...
... 8) A child's toy is suspended from the ceiling by means of a string. The Earth pulls downward on the toy with its weight force of 8 N. If this is the "action force;' what is the "reaction force"? A) the string pulling downward on the ceiling with an 8-N force B) the ceiling pulling upward on the str ...