Gravity and SHM Review Questions
... done by the field depends on the mass of the object and (A) the positions of A and B only (B) the path taken between A and B only (C) both the positions of A and B and the path taken between them (D) the velocity of the object as it moves between A and B (E) the nature of the external force moving t ...
... done by the field depends on the mass of the object and (A) the positions of A and B only (B) the path taken between A and B only (C) both the positions of A and B and the path taken between them (D) the velocity of the object as it moves between A and B (E) the nature of the external force moving t ...
Chapter 3 - Mrs. Wiedeman
... How would you throw a long pass with a football? Anything that has mass is attracted by gravity Gravity: attractive force between two objects that depends on masses and distance Stronger force? More mass/closer together ...
... How would you throw a long pass with a football? Anything that has mass is attracted by gravity Gravity: attractive force between two objects that depends on masses and distance Stronger force? More mass/closer together ...
Important situations in circular motion
... ball on it with and without a wall As the cart turns, what happens to the ball? A force toward the center is necessary to cause turning. ...
... ball on it with and without a wall As the cart turns, what happens to the ball? A force toward the center is necessary to cause turning. ...
HW#6: Fallin` Up
... Date___________________ Block__________________ HW#6 Reading: Gravity and Motion ...
... Date___________________ Block__________________ HW#6 Reading: Gravity and Motion ...
Mass and weight
... The weight of an object is a force and is so is measured in Newtons, while the mass of an object is measured in kilograms. To find the weight of an object you simply multiply its mass (in kilograms) by the force of the Earth’s gravity on 1 kg (10N). Weight (W, Newtons) = Mass (m, kg) x Gravitational ...
... The weight of an object is a force and is so is measured in Newtons, while the mass of an object is measured in kilograms. To find the weight of an object you simply multiply its mass (in kilograms) by the force of the Earth’s gravity on 1 kg (10N). Weight (W, Newtons) = Mass (m, kg) x Gravitational ...
Jeopardy - QuestGarden.com
... equal pull, the reason the Earth goes around the Sun and not the other way round is due to the Sun’s _____ ______ ...
... equal pull, the reason the Earth goes around the Sun and not the other way round is due to the Sun’s _____ ______ ...
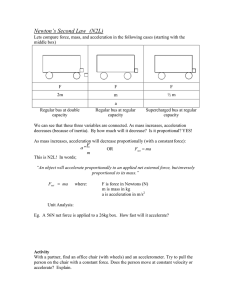
F=m*a Worksheet
... The following problems are practice problems for Newton’s second law of gravity. The two equations you will use are F=m*a (Force=mass times acceleration) and W=m*g (Weight=mass times the acceleration due to gravity. In each of these problems you will need to list your variables, label your numbers w ...
... The following problems are practice problems for Newton’s second law of gravity. The two equations you will use are F=m*a (Force=mass times acceleration) and W=m*g (Weight=mass times the acceleration due to gravity. In each of these problems you will need to list your variables, label your numbers w ...
Motion, Energy, and Gravity
... proportional to the force and inversely proportional to the mass of the object (a = F/m) • 3rd Law - For any force, there is an equal and opposite reaction force • These laws govern the motion of all objects in the Universe, except the very fast (relativity) and the very small (QM) ...
... proportional to the force and inversely proportional to the mass of the object (a = F/m) • 3rd Law - For any force, there is an equal and opposite reaction force • These laws govern the motion of all objects in the Universe, except the very fast (relativity) and the very small (QM) ...
Ch. 2
... Newton’s Third Law if one object exerts a force on another object, then the second object will exert a force of equal strength in the opposite direction back on the first object. ...
... Newton’s Third Law if one object exerts a force on another object, then the second object will exert a force of equal strength in the opposite direction back on the first object. ...
Day 1 Notes: Dealing with projectiles in two dimensions. There are
... lines x and y axis. Then, the original horizontal and vertical line will become diagonal line. From then, everything is the same as the mothod introduced in D. ...
... lines x and y axis. Then, the original horizontal and vertical line will become diagonal line. From then, everything is the same as the mothod introduced in D. ...