Name Date ______ Block ___ Physics Mid
... 8. What is the total displacement experienced by an object thrown straight up into the air and caught at the original release point? 9. Consider a tennis ball thrown straight up. Does it take more time for the ball to travel upward or downward? 10. Once an object is launched, what is the only force ...
... 8. What is the total displacement experienced by an object thrown straight up into the air and caught at the original release point? 9. Consider a tennis ball thrown straight up. Does it take more time for the ball to travel upward or downward? 10. Once an object is launched, what is the only force ...
Chapter 1 - asmasaid
... You stand on a scale that rests on the floor of an elevator that is accelerating upward. What is the relationship between the force due to gravity and the normal force exerted by the scale? A. N > mg B. N = mg C. N
... You stand on a scale that rests on the floor of an elevator that is accelerating upward. What is the relationship between the force due to gravity and the normal force exerted by the scale? A. N > mg B. N = mg C. N
Static Equilibrium (print version)
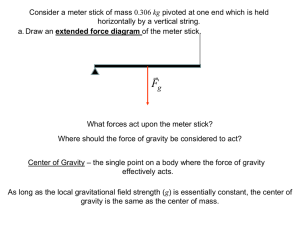
... Fg Since the angular velocity of the meter stick doesn’t change, the torques must be balanced! ...
... Fg Since the angular velocity of the meter stick doesn’t change, the torques must be balanced! ...
AP Practice Test Circular motion and gravitation MPC
... C) Neither car will slide. D) It depends on if the pavement is wet or dry. Answer: C 7) Two small balls, A and B, attract each other gravitationally with a force of magnitude F. If we now double both masses and the separation of the balls, what will now be the magnitude of the attractive force on ea ...
... C) Neither car will slide. D) It depends on if the pavement is wet or dry. Answer: C 7) Two small balls, A and B, attract each other gravitationally with a force of magnitude F. If we now double both masses and the separation of the balls, what will now be the magnitude of the attractive force on ea ...
Acceleration Due to Gravity
... century, the English scientist Isaac Newton was able to show that gravity is a universal force that extends beyond Earth. It is the force that causes the moon to orbit the Earth and the Earth to orbit the Sun. When an object is in “free fall”, the only force acting on it is the force of gravity. As ...
... century, the English scientist Isaac Newton was able to show that gravity is a universal force that extends beyond Earth. It is the force that causes the moon to orbit the Earth and the Earth to orbit the Sun. When an object is in “free fall”, the only force acting on it is the force of gravity. As ...
Chapter 03
... • Law of Universal Gravitation – Every particle in the universe attracts every other particle with a force that is directly proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them ...
... • Law of Universal Gravitation – Every particle in the universe attracts every other particle with a force that is directly proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them ...
Physics Lab Exam - La Salle University
... height 88 cm. One end of a string is attached to the block and the other end to hanger. A range of masses can be placed on the hanger without setting the system into motion. Draw all the forces acting on the block in each scenario. Draw the forces acting on the hanger. Fil in the table below. Normal ...
... height 88 cm. One end of a string is attached to the block and the other end to hanger. A range of masses can be placed on the hanger without setting the system into motion. Draw all the forces acting on the block in each scenario. Draw the forces acting on the hanger. Fil in the table below. Normal ...