File
... If there is no net force acting on an object, the object will remain at rest or will keep moving at the same constant velocity. (Conversely, if an object is at rest or is moving at constant velocity, there is no net force acting upon it.) ...
... If there is no net force acting on an object, the object will remain at rest or will keep moving at the same constant velocity. (Conversely, if an object is at rest or is moving at constant velocity, there is no net force acting upon it.) ...
Mechanical Equilibrium Questions/Answers PPT
... Net force is the combination (sum) of all acting forces. ...
... Net force is the combination (sum) of all acting forces. ...
Lecture2_Freefall
... comes to a stop, and so its velocity is zero. However, since the ball is in free fall, its acceleration is g = 9.8 m/s2 (at every moment). ...
... comes to a stop, and so its velocity is zero. However, since the ball is in free fall, its acceleration is g = 9.8 m/s2 (at every moment). ...
Physics 123/5 - UConn Physics
... 4.5 cm in a tree. Subsequent measurements showed that the tree would exert a stopping force of 70N on the straw. What was the straw’s speed when it hit the tree? Since the stopping force (70 N) is so much larger than the weight of the straw (0.0049 N), we may assume that the net work done is essenti ...
... 4.5 cm in a tree. Subsequent measurements showed that the tree would exert a stopping force of 70N on the straw. What was the straw’s speed when it hit the tree? Since the stopping force (70 N) is so much larger than the weight of the straw (0.0049 N), we may assume that the net work done is essenti ...
Force - springsphysics
... You only feel the forces exerted on you. The forces must be equal, however the ...
... You only feel the forces exerted on you. The forces must be equal, however the ...
Chapter 18: Fields and Forces
... Propose a general explanation for how forces act over a distance. ...
... Propose a general explanation for how forces act over a distance. ...
L-6 – Newton`s Second Law Force is a vector quantity The NET
... account both how strong the forces are and in what direction they act • The Net Force determines the acceleration of the object ...
... account both how strong the forces are and in what direction they act • The Net Force determines the acceleration of the object ...
Motion
... Newton's third law. The skaters' forces on each other are equal in magnitude, and in opposite directions ...
... Newton's third law. The skaters' forces on each other are equal in magnitude, and in opposite directions ...
Work and Kinetic Energy - University of Utah Physics
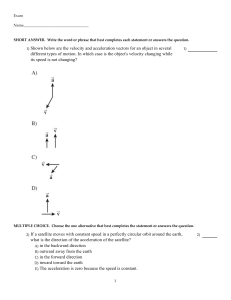
... Kinematics may be described in different coordinate systems. These systems may be in relative motion. Circular motion at constant linear speed is accelerated motion. Acceleration is towards center of circle. ...
... Kinematics may be described in different coordinate systems. These systems may be in relative motion. Circular motion at constant linear speed is accelerated motion. Acceleration is towards center of circle. ...
Objective: Conservation of Energy I
... On the downward parts of the trip, the gravitational force does positive work, increasing the car’s kinetic energy and ultimately increasing its “speed”. Conversely, on the upward parts of the motion, the gravitational force does negative work, decreasing the car’s kinetic energy as well as decreas ...
... On the downward parts of the trip, the gravitational force does positive work, increasing the car’s kinetic energy and ultimately increasing its “speed”. Conversely, on the upward parts of the motion, the gravitational force does negative work, decreasing the car’s kinetic energy as well as decreas ...
Newton to Einstein Exercise 2 – Kinetics
... Check: (a) 0.8 nm is an atomic-scale separation, so we should not be surprised that some velocity has been lost – i.e. our answer is in the right ballpark, 0 < v < initial velocity. (b) 2.8 10–10m is 0.28 nm which is >0 and < the distance of part (a), so again in the right ballpark. (c) This is a ...
... Check: (a) 0.8 nm is an atomic-scale separation, so we should not be surprised that some velocity has been lost – i.e. our answer is in the right ballpark, 0 < v < initial velocity. (b) 2.8 10–10m is 0.28 nm which is >0 and < the distance of part (a), so again in the right ballpark. (c) This is a ...