No Slide Title
... – When you strike a wall, does it hurt your hand? You might say the wall struck you. Newton would say the force you applied to the wall was the same as that which the wall applied to you. The wall is bigger and more massive, therefore has more inertia and was not harmed as much as you. ...
... – When you strike a wall, does it hurt your hand? You might say the wall struck you. Newton would say the force you applied to the wall was the same as that which the wall applied to you. The wall is bigger and more massive, therefore has more inertia and was not harmed as much as you. ...
THIS IS A PRACTICE ASSESSMENT
... 2. Why is the field view preferable to the action-at-a-distance view of forces? ____________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________ ...
... 2. Why is the field view preferable to the action-at-a-distance view of forces? ____________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________ ...
Forces and Newtons laws
... If you let go of the ball, it always rolls up the opposite side until it reaches its original height (this actually comes from the conservation of energy). ...
... If you let go of the ball, it always rolls up the opposite side until it reaches its original height (this actually comes from the conservation of energy). ...
Force 1
... a known magnitude F1, while the second force has an unknown magnitude, and the angle is unknown. Knowing that the acceleration of the block has a magnitude a, and is directed at a known angle as shown in the figure, derive an algebraic expression for the magnitude F2 of the second force, and for ...
... a known magnitude F1, while the second force has an unknown magnitude, and the angle is unknown. Knowing that the acceleration of the block has a magnitude a, and is directed at a known angle as shown in the figure, derive an algebraic expression for the magnitude F2 of the second force, and for ...
Energy, Work and Simple Machines
... A massive, fast-moving vehicle can do damage to the objects around it. A baseball hit at a high speed can rise high into the air. What property of an object can produce a change in the object itself or the world around it? Answer: Energy. Both the vehicle and the baseball possess energy that is asso ...
... A massive, fast-moving vehicle can do damage to the objects around it. A baseball hit at a high speed can rise high into the air. What property of an object can produce a change in the object itself or the world around it? Answer: Energy. Both the vehicle and the baseball possess energy that is asso ...
Force = Mass x Acceleration - GZ @ Science Class Online
... Objects create a gravitational field around them >the bigger the object; the stronger the field >the further away from the object, the less gravitational pull Any other object within the field is pulled to the center of the mass: ...
... Objects create a gravitational field around them >the bigger the object; the stronger the field >the further away from the object, the less gravitational pull Any other object within the field is pulled to the center of the mass: ...
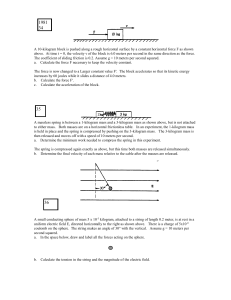
A 10 kilogram block Is pushed along a rough horizontal surface by a
... The coefficient of sliding friction is 0.2. Assume g = 10 meters per second squared. a. Calculate the force F necessary to keep the velocity constant. The force is now changed to a Larger constant value F'. The block accelerates so that its kinetic energy increases by 60 joules while it slides a dis ...
... The coefficient of sliding friction is 0.2. Assume g = 10 meters per second squared. a. Calculate the force F necessary to keep the velocity constant. The force is now changed to a Larger constant value F'. The block accelerates so that its kinetic energy increases by 60 joules while it slides a dis ...
Newtons Law Review - McKinney ISD Staff Sites
... b. will continue moving at the same velocity unless acted on by an outside force c. will continue moving in a straight line unless acted on by an outside force d. that is not moving will never move unless a force acts on it e. all of the above 2. The law of inertia applies to _____. a. moving object ...
... b. will continue moving at the same velocity unless acted on by an outside force c. will continue moving in a straight line unless acted on by an outside force d. that is not moving will never move unless a force acts on it e. all of the above 2. The law of inertia applies to _____. a. moving object ...
Do now
... have with the net force for a given mass. Explain this relationship by writing the formula and then explaining if there is a direct or inverse relationship between the force and the acceleration (1 pt), what happens to the acceleration if the mass changes (1 pt), and then explain what conditions mus ...
... have with the net force for a given mass. Explain this relationship by writing the formula and then explaining if there is a direct or inverse relationship between the force and the acceleration (1 pt), what happens to the acceleration if the mass changes (1 pt), and then explain what conditions mus ...
Motion & Force
... Distance Proportional to Time of Fall Squared Demonstration - 'Whys Guy' Video Clip (3:30 mins) Falling distance proportional to the time of fall squared. (2nd of 2 clips some microphone problems) Lunar Lander - PhET - Can you avoid the boulder field and land safely, just before your fuel runs out, ...
... Distance Proportional to Time of Fall Squared Demonstration - 'Whys Guy' Video Clip (3:30 mins) Falling distance proportional to the time of fall squared. (2nd of 2 clips some microphone problems) Lunar Lander - PhET - Can you avoid the boulder field and land safely, just before your fuel runs out, ...
IV. Force & Acceleration
... Mass and Acceleration • If you throw a softball and a baseball as hard as you can, why don’t they have the same speed? • The difference is due to their masses. • If it takes the same amount of time to throw both balls, the softball would have less. • Force, mass, acceleration and acceleration are r ...
... Mass and Acceleration • If you throw a softball and a baseball as hard as you can, why don’t they have the same speed? • The difference is due to their masses. • If it takes the same amount of time to throw both balls, the softball would have less. • Force, mass, acceleration and acceleration are r ...