Soda Can and Atmospheric Pressure
... bottom of the can, just like pressure is highest at the bottom of the atmosphere at the ground. Water is a fluid just like air. We can visualize this effect with water since the cumulative weight of the water (or air) is greatest at the bottom of the can, where the pressure is highest, so the water ...
... bottom of the can, just like pressure is highest at the bottom of the atmosphere at the ground. Water is a fluid just like air. We can visualize this effect with water since the cumulative weight of the water (or air) is greatest at the bottom of the can, where the pressure is highest, so the water ...
Chapter 9
... DATA: specific gravity of lead = 11.3 specific gravity of gold = 19.3 specific gravity of mercury = 13.6 Which statement is true? a) #1 and #2 have the same buoyant force b) #1 and #2 register the same weights on the scales c) #1 and #3 have the same buoyant force d) #1 and #3 register the same weig ...
... DATA: specific gravity of lead = 11.3 specific gravity of gold = 19.3 specific gravity of mercury = 13.6 Which statement is true? a) #1 and #2 have the same buoyant force b) #1 and #2 register the same weights on the scales c) #1 and #3 have the same buoyant force d) #1 and #3 register the same weig ...
Chapter 9 Solids and Fluids (c)
... DATA: specific gravity of lead = 11.3 specific gravity of gold = 19.3 specific gravity of mercury = 13.6 Which statement is true? a) #1 and #2 have the same buoyant force b) #1 and #2 register the same weights on the scales c) #1 and #3 have the same buoyant force d) #1 and #3 register the same weig ...
... DATA: specific gravity of lead = 11.3 specific gravity of gold = 19.3 specific gravity of mercury = 13.6 Which statement is true? a) #1 and #2 have the same buoyant force b) #1 and #2 register the same weights on the scales c) #1 and #3 have the same buoyant force d) #1 and #3 register the same weig ...
Cohesion
... Water Molecule H2O is the chemical formula, this means that each molecule is made up of 2 Hydrogen atoms and 1 oxygen atom ...
... Water Molecule H2O is the chemical formula, this means that each molecule is made up of 2 Hydrogen atoms and 1 oxygen atom ...
First_Semester_Year_28_29
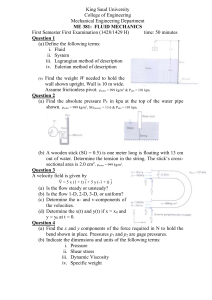
... First Semester First Examination (1428/1429 H) time: 50 minutes Question 1 (a) Define the following terms: i. Fluid ii. System iii. Lagrangian method of description iv. Eulerian method of description Find the weight W needed to hold the wall shown upright. Wall is 10 m wide. Assume frictionless pivo ...
... First Semester First Examination (1428/1429 H) time: 50 minutes Question 1 (a) Define the following terms: i. Fluid ii. System iii. Lagrangian method of description iv. Eulerian method of description Find the weight W needed to hold the wall shown upright. Wall is 10 m wide. Assume frictionless pivo ...
Fluids Glossary
... Chlorine – chemical used to disinfect water (i.e., kill organisms) Desalination – process of removing salt from water Flow rate – measure of the speed at which a fluid flows from one point to another; determined by measuring the amount of fluid that flows past a given point in a given time Fluid – a ...
... Chlorine – chemical used to disinfect water (i.e., kill organisms) Desalination – process of removing salt from water Flow rate – measure of the speed at which a fluid flows from one point to another; determined by measuring the amount of fluid that flows past a given point in a given time Fluid – a ...
What do we want to understand?
... – Is the wedge mantle “wet” throughout, or is it “wet” only in limited regions? (Comparison to the continental tectosphere.) ...
... – Is the wedge mantle “wet” throughout, or is it “wet” only in limited regions? (Comparison to the continental tectosphere.) ...
Jeopardy - Fairmont State College
... What is a large body of ice moving slowly down a slope or valley or spreading outward on a land surface? ...
... What is a large body of ice moving slowly down a slope or valley or spreading outward on a land surface? ...
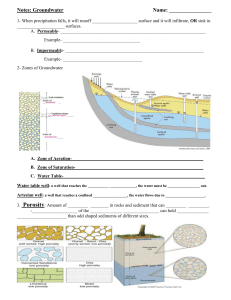
Notes: Groundwater
... 2. During a drought what will happen to the water table? ___________________________________ 3. What type of weathering causes the limestone to break down? (chemical or mechanical)_ 4. Water is a renewable resource (true or false) 5. What are stalactites and stalagmites made from? __________________ ...
... 2. During a drought what will happen to the water table? ___________________________________ 3. What type of weathering causes the limestone to break down? (chemical or mechanical)_ 4. Water is a renewable resource (true or false) 5. What are stalactites and stalagmites made from? __________________ ...